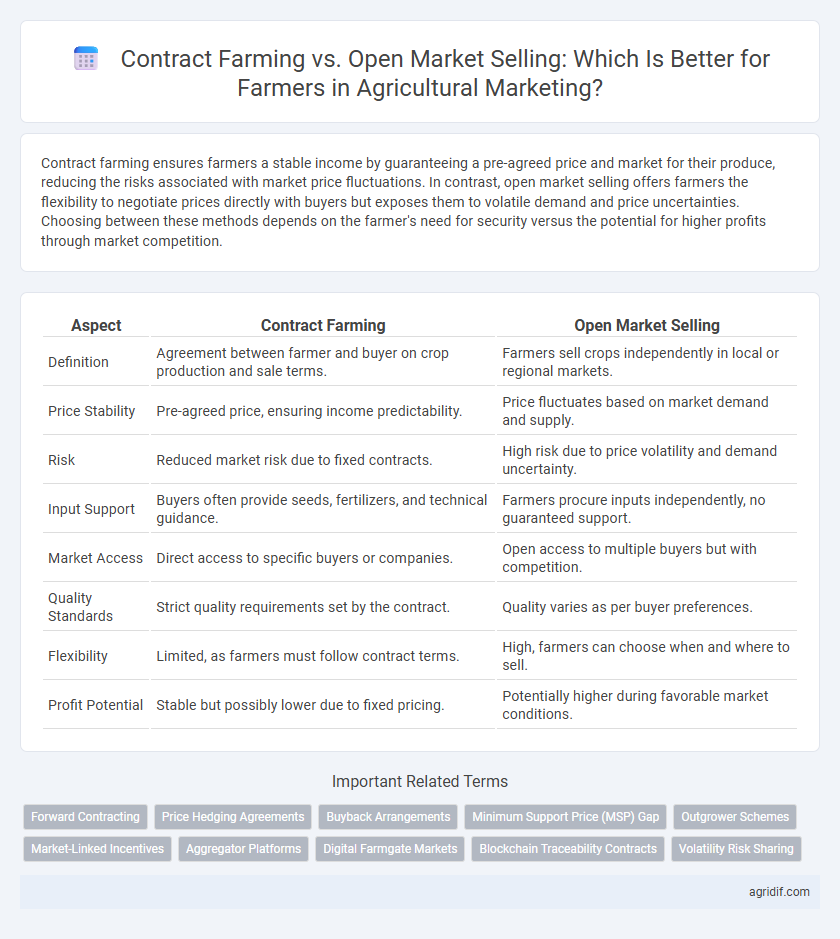
Contract farming ensures farmers a stable income by guaranteeing a pre-agreed price and market for their produce, reducing the risks associated with market price fluctuations. In contrast, open market selling offers farmers the flexibility to negotiate prices directly with buyers but exposes them to volatile demand and price uncertainties. Choosing between these methods depends on the farmer's need for security versus the potential for higher profits through market competition.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Contract Farming | Open Market Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement between farmer and buyer on crop production and sale terms. | Farmers sell crops independently in local or regional markets. |
| Price Stability | Pre-agreed price, ensuring income predictability. | Price fluctuates based on market demand and supply. |
| Risk | Reduced market risk due to fixed contracts. | High risk due to price volatility and demand uncertainty. |
| Input Support | Buyers often provide seeds, fertilizers, and technical guidance. | Farmers procure inputs independently, no guaranteed support. |
| Market Access | Direct access to specific buyers or companies. | Open access to multiple buyers but with competition. |
| Quality Standards | Strict quality requirements set by the contract. | Quality varies as per buyer preferences. |
| Flexibility | Limited, as farmers must follow contract terms. | High, farmers can choose when and where to sell. |
| Profit Potential | Stable but possibly lower due to fixed pricing. | Potentially higher during favorable market conditions. |
Introduction to Contract Farming and Open Market Selling
Contract farming establishes a formal agreement between farmers and buyers, ensuring fixed prices and guaranteed markets, which reduces farmers' risks and improves income stability. Open market selling allows farmers to sell produce freely to any buyer, promoting competitive pricing but exposing them to market price volatility and uncertainty. Both methods significantly impact farmers' revenue models, supply chain dynamics, and market access strategies in agricultural marketing.
Key Features of Contract Farming
Contract farming ensures predetermined crop prices, reducing market uncertainty and financial risks for farmers through binding agreements with buyers. It provides access to quality inputs, technical support, and advanced farming practices, enhancing productivity and crop quality. Unlike open market selling, contract farming guarantees a secure market outlet, thereby stabilizing income and fostering long-term buyer-supplier relationships.
Advantages of Contract Farming for Farmers
Contract farming offers farmers guaranteed market access and stable prices, reducing income uncertainty and financial risk. It provides technical support and access to quality inputs, enhancing crop yields and product quality. Farmers benefit from timely payments and reduced marketing costs compared to open market selling.
Challenges and Risks in Contract Farming
Contract farming presents risks such as price fixation leading to limited bargaining power for farmers, potential breach of contract by buyers, and dependency on a single purchaser, increasing vulnerability to market fluctuations. Challenges include stringent quality standards imposed by companies, difficulties in contract enforcement due to weak legal frameworks, and delayed payments affecting farmers' cash flow. Unlike open market selling, contract farming can restrict farmers' flexibility to respond to market signals and diversify buyers, thereby elevating economic risks.
Open Market Selling: An Overview
Open market selling offers farmers immediate access to diverse buyers, enhancing price competition and potential profits. This method empowers farmers with direct negotiation, increasing transparency and reducing dependency on intermediaries. Despite market price volatility, open market selling provides flexibility and the opportunity to respond swiftly to demand changes.
Benefits of Open Market Selling for Farmers
Open market selling empowers farmers with price discovery and the ability to negotiate directly with multiple buyers, ensuring competitive rates that can enhance their income. This approach provides farmers with greater flexibility in choosing buyers and selling volumes based on real-time market demand, reducing dependency on intermediaries. Access to diverse markets through open selling can also encourage innovation in crop selection and improve responsiveness to consumer trends.
Drawbacks and Uncertainties in Open Market Selling
Open market selling exposes farmers to price volatility and unpredictable demand, leading to uncertain income and potential losses. Lack of guaranteed buyers increases risks of unsold produce and wasted resources. Farmers face challenges in negotiating fair prices due to limited market information and buyer power imbalance.
Income Stability: Contract vs Open Market
Contract farming provides farmers with income stability through pre-agreed pricing and guaranteed purchase contracts, reducing exposure to market price fluctuations. In contrast, open market selling subjects farmers to volatile prices influenced by supply-demand dynamics, weather conditions, and market trends, often resulting in unpredictable earnings. The structured income from contract farming supports financial planning and investment, whereas open market sales risk income variability despite the potential for higher prices during peak demand.
Market Access and Bargaining Power Comparison
Contract farming offers farmers improved market access by securing pre-agreed sales channels and prices, reducing uncertainty and ensuring steady income. In contrast, open market selling exposes farmers to price volatility and limited bargaining power, as buyers often dominate negotiations. Enhanced bargaining power through contract farming enables better resource allocation and risk management for smallholder farmers.
Choosing the Best Marketing Strategy for Farmers
Contract farming guarantees farmers a fixed price and assured market access, reducing price volatility and demand uncertainties. Open market selling offers flexibility and potential for higher profits but exposes farmers to price fluctuations and market risks. Farmers should evaluate crop type, market stability, and access to resources to select the most beneficial strategy for maximizing income and minimizing risks.
Related Important Terms
Forward Contracting
Forward contracting in contract farming guarantees farmers a predetermined price and assured market access, reducing price volatility and production risks compared to open market selling. This approach enhances income stability and facilitates access to quality inputs and technical support, improving overall farm productivity and profitability.
Price Hedging Agreements
Contract farming provides farmers with price hedging agreements that lock in prices before harvest, reducing market price volatility risks and ensuring stable income. In contrast, open market selling exposes farmers to fluctuating prices, offering potential for higher profits but increasing income uncertainty.
Buyback Arrangements
Contract farming with buyback arrangements guarantees farmers a predetermined price and assured market, reducing post-harvest losses and price uncertainty. In contrast, open market selling exposes farmers to volatile prices and demand fluctuations, often resulting in lower bargaining power and increased financial risk.
Minimum Support Price (MSP) Gap
Contract farming ensures farmers a predetermined price, reducing the risk of price volatility often seen in open market selling where Minimum Support Price (MSP) gaps leave farmers vulnerable to fluctuating market rates. The MSP gap in open markets causes income uncertainty, whereas contract farming stabilizes revenue by aligning agreed prices closer to or above MSP, offering better financial security for farmers.
Outgrower Schemes
Outgrower schemes under contract farming provide farmers with guaranteed markets and stable prices by linking them directly to agribusiness firms, enhancing income security compared to the price volatility and competitive pressures faced in open market selling. This structured approach often includes input supply, technical support, and access to credit, which collectively improve crop quality and yield, thereby strengthening rural livelihoods and fostering sustainable agricultural development.
Market-Linked Incentives
Contract farming offers farmers guaranteed prices and access to inputs, reducing market uncertainties and enabling better financial planning, while open market selling exposes farmers to price volatility but allows for potential higher earnings. Market-linked incentives in contract farming include quality premiums and timely payments, which directly motivate farmers to improve production standards and align supply with demand trends.
Aggregator Platforms
Aggregator platforms enhance farmer sales by facilitating contract farming agreements that guarantee fixed prices and reduce market risks, promoting stable income streams. These platforms also enable direct access to open markets, increasing competitive pricing opportunities while minimizing intermediaries and transaction costs.
Digital Farmgate Markets
Contract farming ensures farmers guaranteed prices and access to inputs, reducing market uncertainties, while open market selling offers price flexibility but exposes farmers to volatile demand and lower bargaining power. Digital Farmgate Markets enhance transparency and direct access to buyers, bridging gaps between contract farming and open market models by enabling secure, real-time transactions and price discovery.
Blockchain Traceability Contracts
Contract farming with blockchain traceability contracts offers farmers transparent, secure agreements that ensure fair pricing, reduce risk, and enhance trust through immutable digital records. Open market selling lacks this traceability, exposing farmers to price volatility and potential exploitation without verifiable transaction histories or quality assurances.
Volatility Risk Sharing
Contract farming significantly reduces volatility risk for farmers by securing predetermined prices and guaranteed buyers, enhancing income stability compared to open market selling. Open market selling exposes farmers to price fluctuations and demand uncertainties, increasing their financial risks and income variability.
Contract farming vs Open market selling for farmer sales Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com