Manual feeding in poultry farming offers precise control over the diet and portion sizes, catering to specific nutritional needs of each bird. Automated feeding systems enhance efficiency by delivering consistent feed amounts, reducing labor costs, and minimizing feed wastage. Choosing between manual and automated feeding depends on farm scale, budget, and desired management control.
Table of Comparison
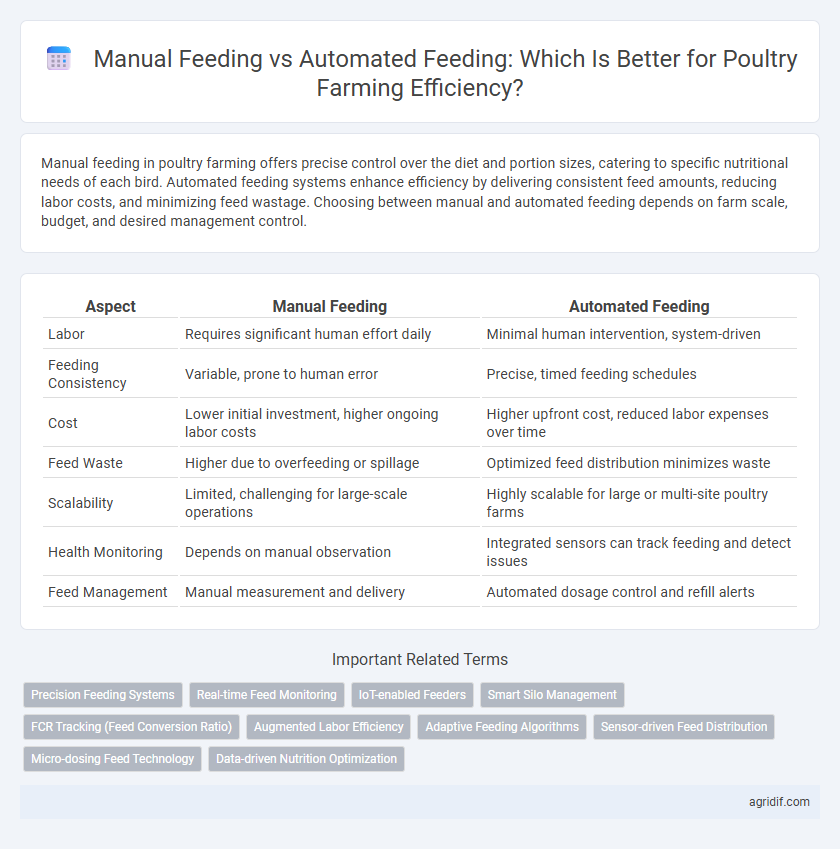
| Aspect | Manual Feeding | Automated Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| Labor | Requires significant human effort daily | Minimal human intervention, system-driven |
| Feeding Consistency | Variable, prone to human error | Precise, timed feeding schedules |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, higher ongoing labor costs | Higher upfront cost, reduced labor expenses over time |
| Feed Waste | Higher due to overfeeding or spillage | Optimized feed distribution minimizes waste |
| Scalability | Limited, challenging for large-scale operations | Highly scalable for large or multi-site poultry farms |
| Health Monitoring | Depends on manual observation | Integrated sensors can track feeding and detect issues |
| Feed Management | Manual measurement and delivery | Automated dosage control and refill alerts |
Introduction to Poultry Feeding Systems
Poultry feeding systems play a critical role in maximizing growth rates and feed efficiency in poultry farming, with manual feeding involving direct human labor to distribute feed and monitor consumption. Automated feeding systems use mechanized equipment such as feeders and conveyors to deliver precise feed amounts at scheduled intervals, optimizing feed uniformity and reducing labor costs. Understanding the differences between manual and automated feeding is essential for improving flock health, minimizing feed waste, and increasing productivity in large-scale poultry operations.
Overview of Manual Feeding in Poultry
Manual feeding in poultry farming involves hand-distributing feed to birds, allowing farmers to control portion sizes and monitor individual flock health closely. This method promotes closer observation of feed consumption patterns and behavioral changes but requires significant labor and time investment. Despite being labor-intensive, manual feeding offers flexibility in feed management ideal for small-scale or specialized poultry operations.
Understanding Automated Feeding Technologies
Automated feeding technologies in poultry farming utilize advanced systems such as conveyor belts, feed dispensers, and sensors to regulate feed distribution accurately and efficiently. These technologies improve feed conversion ratios by ensuring consistent portions and reducing waste compared to manual feeding methods. Integration of IoT devices allows real-time monitoring and remote control, enhancing productivity and animal welfare in large-scale poultry operations.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Feeding
Manual feeding in poultry farming often incurs higher labor costs due to the necessity of continuous human involvement and time, making it less cost-effective for large-scale operations. Automated feeding systems, despite an initial investment in equipment, reduce long-term expenses by minimizing labor requirements and improving feed efficiency through precise distribution. Economies of scale enhance the cost benefits of automation, leading to significant savings in feed wastage and operational overheads compared to manual methods.
Labor Requirements and Efficiency
Manual feeding in poultry farming demands significant labor, requiring workers to distribute feed consistently, which can lead to higher operational costs and variable feeding accuracy. Automated feeding systems drastically reduce labor requirements by delivering precise feed quantities at scheduled intervals, enhancing overall efficiency and promoting uniform growth among poultry. Investing in automated feeders improves productivity through time savings and optimized feed utilization, making it essential for large-scale poultry operations seeking to minimize labor intensity.
Impact on Poultry Health and Productivity
Manual feeding in poultry farming allows for close monitoring of individual bird intake and early detection of health issues but can lead to inconsistent feeding schedules and uneven nutrient distribution, impacting overall productivity. Automated feeding systems ensure precise, consistent delivery of feed, promoting uniform growth and reducing labor costs, yet lack the personalized observation that helps identify specific health problems. Optimizing feeding methods by combining automation with periodic manual checks can enhance poultry health outcomes and maximize production efficiency.
Feed Waste and Resource Optimization
Manual feeding in poultry farming often results in higher feed waste due to inconsistent portioning and spillage, which increases overall feed costs and resource inefficiency. Automated feeding systems precisely control feed distribution, minimizing wastage by delivering exact quantities tailored to the flock's needs. This optimization enhances feed conversion ratios, reduces labor expenses, and promotes sustainable resource management in poultry operations.
Scalability for Small and Large Poultry Farms
Manual feeding in poultry farming offers precise control and flexibility for small-scale farms but limits scalability due to high labor demands and time consumption. Automated feeding systems enhance efficiency and consistency, making them ideal for large-scale operations by reducing labor costs and supporting rapid farm expansion. Choosing between manual and automated feeding depends on farm size, financial resources, and growth objectives, with automation better suited for scalability in extensive poultry farming.
Maintenance and Technical Challenges
Manual feeding in poultry farming requires minimal technical expertise but demands consistent labor and time, increasing operational costs and susceptibility to human error. Automated feeding systems offer precise feed distribution and reduce labor, yet they involve complex machinery prone to technical malfunctions and require regular maintenance, such as calibration, cleaning, and mechanical inspections. Failure to address these challenges can lead to feed wastage, uneven nutrition, and compromised flock health, emphasizing the need for skilled technicians and well-planned maintenance schedules.
Choosing the Right Feeding Method for Your Farm
Selecting the appropriate feeding method for poultry farms demands evaluating factors like flock size, labor availability, and cost-effectiveness. Manual feeding allows precise control over feed quantity and quality but requires significant labor and time investment, suitable for smaller farms. Automated feeding systems enhance efficiency and consistency, reduce labor costs, and optimize feed distribution, making them ideal for large-scale operations seeking scalability and productivity.
Related Important Terms
Precision Feeding Systems
Manual feeding in poultry farming often leads to inconsistent feed distribution and increased labor costs, whereas automated precision feeding systems optimize nutrient delivery by tailoring feed amounts to individual flock needs, improving growth rates and feed efficiency. These systems utilize sensors and software analytics to monitor real-time consumption patterns, reducing waste and enhancing overall productivity in commercial poultry operations.
Real-time Feed Monitoring
Automated feeding systems enable precise real-time feed monitoring by continuously tracking feed consumption and adjusting supply to optimize poultry nutrition and growth rates. Manual feeding lacks immediate data feedback, often resulting in inconsistent feed distribution and potential nutrient imbalances that can affect flock health and productivity.
IoT-enabled Feeders
IoT-enabled feeders in poultry farming offer precise control over feed distribution, improving feed efficiency and reducing wastage compared to manual feeding methods. These automated systems collect real-time data on feeding patterns and flock behavior, enabling farmers to optimize nutrition and enhance overall flock health.
Smart Silo Management
Smart silo management enhances automated feeding by precisely monitoring feed levels, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent nutrition delivery to poultry flocks. Manual feeding lacks this efficiency, leading to potential feed shortages or overfeeding, which can impact flock health and productivity.
FCR Tracking (Feed Conversion Ratio)
Automated feeding systems enable precise control and monitoring of feed distribution, significantly improving Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) tracking by reducing feed waste and ensuring consistent nutrition intake. Manual feeding often results in variable feed quantities and timings, complicating accurate FCR measurement and potentially lowering poultry growth efficiency.
Augmented Labor Efficiency
Automated feeding systems in poultry farming significantly enhance labor efficiency by reducing manual labor time by up to 70%, allowing workers to focus on monitoring flock health and environmental conditions. These systems ensure consistent feed distribution, minimizing wastage and improving overall productivity compared to traditional manual feeding methods.
Adaptive Feeding Algorithms
Adaptive feeding algorithms in automated poultry feeding systems optimize nutrient delivery by continuously analyzing bird behavior and growth patterns, enhancing feed efficiency and reducing waste. Manual feeding lacks this precision and adaptability, often leading to inconsistent feed distribution and higher operational costs.
Sensor-driven Feed Distribution
Sensor-driven feed distribution in automated poultry feeding systems ensures precise and consistent delivery of feed based on real-time data such as flock size, activity levels, and environmental conditions, optimizing feed efficiency and reducing waste. Manual feeding lacks this precision, often leading to inconsistent feed allocation and increased labor costs, impacting overall poultry health and productivity.
Micro-dosing Feed Technology
Micro-dosing feed technology in poultry farming delivers precise nutrient quantities, improving feed efficiency and reducing waste compared to manual feeding methods. Automated feeding systems equipped with micro-dosing capabilities enable consistent nutrient supply, optimizing bird growth and health while minimizing labor costs.
Data-driven Nutrition Optimization
Automated feeding systems in poultry farming leverage data analytics to precisely deliver nutrients based on bird age, weight, and production stage, enhancing growth rates and feed conversion ratios. Manual feeding often lacks this data-driven precision, leading to inconsistent nutrient supply and suboptimal flock performance.
Manual Feeding vs Automated Feeding for Poultry Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com