Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, significantly reducing water waste and promoting efficient water use in sustainable agriculture. Flood irrigation, by contrast, often leads to substantial water loss through evaporation and runoff, making it less suitable for conserving scarce water resources. Choosing drip irrigation supports sustainable water management by minimizing consumption and enhancing crop yield with precise moisture control.
Table of Comparison
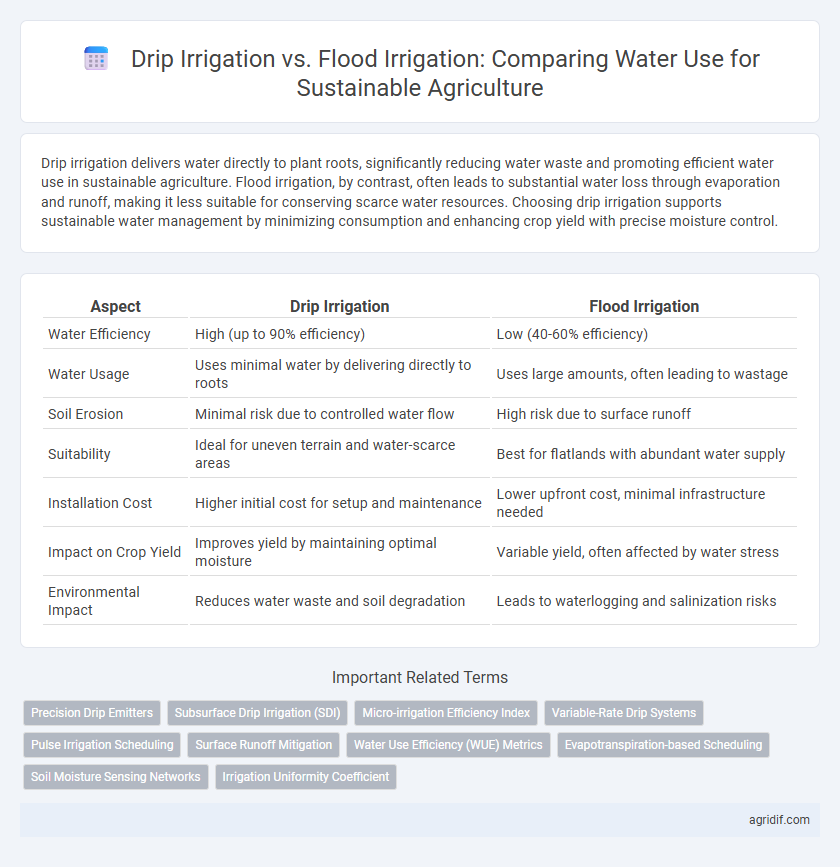
| Aspect | Drip Irrigation | Flood Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (up to 90% efficiency) | Low (40-60% efficiency) |
| Water Usage | Uses minimal water by delivering directly to roots | Uses large amounts, often leading to wastage |
| Soil Erosion | Minimal risk due to controlled water flow | High risk due to surface runoff |
| Suitability | Ideal for uneven terrain and water-scarce areas | Best for flatlands with abundant water supply |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost for setup and maintenance | Lower upfront cost, minimal infrastructure needed |
| Impact on Crop Yield | Improves yield by maintaining optimal moisture | Variable yield, often affected by water stress |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces water waste and soil degradation | Leads to waterlogging and salinization risks |
Introduction to Irrigation Methods in Sustainable Agriculture
Drip irrigation efficiently delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing water wastage by up to 50% compared to flood irrigation, which inundates entire fields and results in significant evaporation and runoff. This targeted water application supports sustainable agriculture by conserving precious water resources and enhancing crop yields through improved soil moisture control. Implementing drip irrigation aligns with sustainable farming practices, promoting resource efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Overview of Drip Irrigation Technology
Drip irrigation technology delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters, significantly reducing water waste compared to flood irrigation. This method enhances water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff, applying water precisely where plants need it. Studies show drip irrigation can save up to 50% more water than traditional flood irrigation while improving crop yield and soil health.
Understanding Flood Irrigation Practices
Flood irrigation involves inundating fields with water, which can lead to significant water loss through evaporation and runoff, making it less efficient compared to drip irrigation. This traditional method is often used in flat terrains and for crops like rice, but it requires large volumes of water and can cause soil erosion and nutrient leaching. Understanding flood irrigation practices highlights the importance of adopting more sustainable techniques like drip irrigation to optimize water use in agriculture.
Comparative Water Efficiency: Drip vs. Flood Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, achieving water use efficiency of up to 90%, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional flood irrigation, which often wastes more than 50% of applied water through percolation and surface runoff. Studies show drip systems can save up to 70% of water in crop irrigation, making them ideal for water-scarce regions aiming for sustainable agriculture. Flood irrigation's low efficiency challenges water conservation efforts, whereas drip irrigation optimizes water distribution, enhancing crop yield with minimal water input.
Impact on Crop Yields and Plant Health
Drip irrigation enhances crop yields by delivering water directly to the root zone, improving water use efficiency by up to 90% compared to flood irrigation, which often causes waterlogging and nutrient leaching. This targeted watering reduces disease incidence and promotes healthier plant growth, while flood irrigation can lead to soil erosion and uneven water distribution that stress crops. Studies report yield increases of 20-50% with drip irrigation in various crops, emphasizing its critical role in sustainable agriculture practices.
Soil Health and Fertility in Different Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation enhances soil health and fertility by delivering water directly to the root zone, reducing runoff and minimizing nutrient leaching compared to flood irrigation. Flood irrigation often leads to soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and waterlogging, which impair soil structure and microbial activity essential for fertility. Efficient water use in drip systems supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels and preserving essential nutrients.
Environmental Implications of Irrigation Choices
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water wastage compared to flood irrigation by delivering water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Flood irrigation often leads to soil erosion, waterlogging, and nutrient leaching, negatively impacting soil health and local water bodies. Choosing drip systems supports sustainable water management and reduces environmental degradation in agricultural ecosystems.
Economic Considerations: Cost and Return on Investment
Drip irrigation offers significant water savings and increased crop yields, leading to higher return on investment despite its higher initial setup costs compared to flood irrigation. Flood irrigation requires less upfront investment but results in considerable water wastage and reduced efficiency, which can lower overall economic returns over time. Investing in drip irrigation technology enhances long-term profitability by optimizing water use and improving crop productivity in sustainable agriculture.
Adoption Barriers and Challenges for Farmers
Drip irrigation offers significant water-use efficiency compared to flood irrigation by delivering precise water amounts directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. However, adoption barriers include high initial installation costs, lack of technical knowledge, and limited access to financing for smallholder farmers. Challenges also arise from the need for regular maintenance and potential clogging of drip emitters, which can deter widespread implementation despite its sustainability benefits.
Recommendations for Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water consumption by delivering moisture directly to plant roots, increasing water use efficiency by up to 90%, compared to flood irrigation's efficiency of around 40%. Experts recommend adopting drip irrigation systems to minimize water wastage, prevent soil erosion, and enhance crop yields in arid and semi-arid regions. Integrating soil moisture sensors and scheduling irrigation based on crop water requirements further optimizes water management, promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Related Important Terms
Precision Drip Emitters
Precision drip emitters in drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to plant roots, reducing water use by up to 50% compared to traditional flood irrigation methods. This targeted approach minimizes evaporation and runoff, enhancing water efficiency and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) significantly reduces water use compared to traditional flood irrigation by delivering water directly to plant roots below the soil surface, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Studies show SDI can improve irrigation efficiency to over 90%, conserving water resources in arid and semi-arid regions critical for sustainable agriculture.
Micro-irrigation Efficiency Index
Drip irrigation achieves a Micro-irrigation Efficiency Index of up to 95%, significantly outperforming flood irrigation, which typically scores below 60% due to high water runoff and evaporation losses. This substantial difference in water use efficiency makes drip irrigation a critical technology for sustainable agriculture and water conservation.
Variable-Rate Drip Systems
Variable-rate drip irrigation systems optimize water use by delivering precise amounts to specific crop zones, significantly reducing water waste compared to traditional flood irrigation, which often leads to overwatering and runoff. This technology enhances crop yield and conserves water by adapting irrigation rates based on soil moisture and plant needs, making it a superior choice for sustainable agriculture.
Pulse Irrigation Scheduling
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water usage compared to flood irrigation by delivering precise amounts of water directly to the root zone, optimizing water efficiency in pulse irrigation scheduling. This method minimizes evaporation and runoff, enhancing crop yield sustainability while conserving valuable water resources in arid and semi-arid regions.
Surface Runoff Mitigation
Drip irrigation significantly reduces surface runoff by delivering water directly to plant roots, minimizing water wastage and soil erosion compared to flood irrigation, which often leads to excessive water flow and increased runoff. Implementing drip systems enhances water use efficiency and supports sustainable agriculture by preserving soil integrity and reducing nutrient loss.
Water Use Efficiency (WUE) Metrics
Drip irrigation demonstrates significantly higher Water Use Efficiency (WUE), typically achieving 80-90% efficiency by delivering water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. In contrast, flood irrigation often results in WUE as low as 40-50%, with substantial water loss due to surface runoff and deep percolation.
Evapotranspiration-based Scheduling
Drip irrigation, utilizing evapotranspiration-based scheduling, significantly reduces water use by delivering precise moisture directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to flood irrigation. This method enhances water efficiency by aligning irrigation timing and volume with crop water demand, promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Soil Moisture Sensing Networks
Drip irrigation systems, integrated with soil moisture sensing networks, optimize water use by delivering precise amounts directly to plant roots, significantly reducing water wastage compared to flood irrigation. Flood irrigation often leads to uneven water distribution and increased evaporation, making it less efficient for sustainable water management in agriculture.
Irrigation Uniformity Coefficient
Drip irrigation achieves an Irrigation Uniformity Coefficient (IUC) often exceeding 90%, significantly enhancing water distribution efficiency compared to flood irrigation, which typically has an IUC below 70% due to uneven water spread. Higher uniformity in drip systems reduces water waste and improves crop yield consistency, positioning it as a sustainable choice for water resource management in agriculture.
Drip irrigation vs Flood irrigation for water use Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com