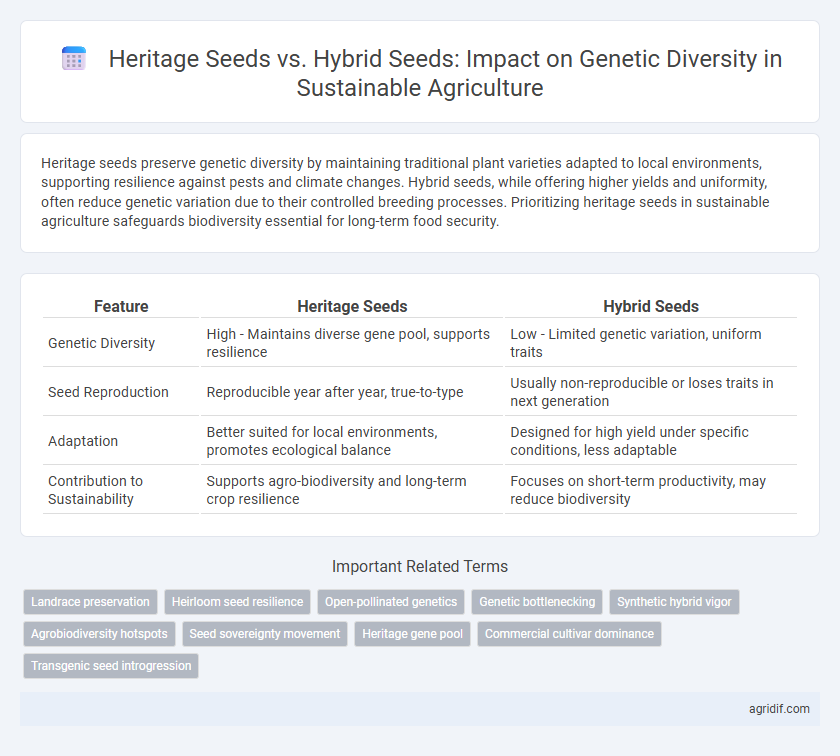
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional plant varieties adapted to local environments, supporting resilience against pests and climate changes. Hybrid seeds, while offering higher yields and uniformity, often reduce genetic variation due to their controlled breeding processes. Prioritizing heritage seeds in sustainable agriculture safeguards biodiversity essential for long-term food security.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heritage Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | High - Maintains diverse gene pool, supports resilience | Low - Limited genetic variation, uniform traits |
| Seed Reproduction | Reproducible year after year, true-to-type | Usually non-reproducible or loses traits in next generation |
| Adaptation | Better suited for local environments, promotes ecological balance | Designed for high yield under specific conditions, less adaptable |
| Contribution to Sustainability | Supports agro-biodiversity and long-term crop resilience | Focuses on short-term productivity, may reduce biodiversity |
Understanding Heritage Seeds: Preserving Genetic Legacy
Heritage seeds play a crucial role in preserving genetic diversity within sustainable agriculture by maintaining a wide range of genetic traits adapted to local environments and traditional farming practices. Unlike hybrid seeds, which are bred for uniformity and high yield but often result in genetic homogenization, heritage seeds sustain resilience against pests, diseases, and climate variations. This preservation of genetic legacy supports ecosystem health and provides a valuable resource for future breeding programs.
Hybrid Seeds: Innovation and Uniformity in Agriculture
Hybrid seeds drive agricultural innovation by combining specific parent traits to create uniform and high-yielding crops, essential for meeting global food demand. Their genetic uniformity enhances pest resistance and crop consistency, benefiting large-scale commercial farming. However, reliance on hybrids can reduce genetic diversity, necessitating balanced integration with heritage seeds to ensure long-term sustainability.
Genetic Diversity: Why It Matters in Sustainable Farming
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining unique traits adapted to local ecosystems, enhancing resilience against pests, diseases, and climate change. Hybrid seeds, while offering higher yields, often reduce genetic variability, increasing vulnerability to environmental stresses and diminishing long-term sustainability. Conserving heritage seed varieties supports sustainable agriculture by safeguarding biodiversity essential for ecosystem stability and food security.
Heritage vs Hybrid: Implications for Crop Resilience
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining a broad genetic base, which enhances crop resilience against pests, diseases, and climate variability. Hybrid seeds often show uniformity and higher short-term yields but lack the genetic variability necessary for long-term adaptability and resistance. The reliance on heritage seeds supports sustainable agriculture by promoting ecosystem stability and reducing dependency on chemical inputs.
Seed Saving Practices and Community Empowerment
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity crucial for resilient ecosystems, while hybrid seeds often reduce variability due to controlled cross-breeding. Seed saving practices enable farmers to maintain local adaptations and protect biodiversity, fostering agricultural sustainability. Community empowerment through seed exchange networks strengthens food security and nurtures cultural heritage linked to traditional crop varieties.
Biodiversity Loss: The Risks of Hybrid Seed Dominance
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity essential for resilient ecosystems, while hybrid seeds often result in uniform crops that threaten biodiversity by reducing varied plant genetics. The dominance of hybrid seeds accelerates biodiversity loss by narrowing the gene pool, making crops more vulnerable to pests, diseases, and climate change. Conserving heritage seeds supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining genetic resources crucial for adapting to environmental challenges.
Climate Adaptation: Advantages of Heritage Seed Varieties
Heritage seed varieties preserve extensive genetic diversity, enabling crops to better withstand climate stressors such as drought, heat, and pests, unlike many homogeneous hybrid seeds. Their adaptability over generations in local environments enhances resilience and supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining ecosystem balance. Utilizing heritage seeds promotes long-term food security by safeguarding genetic traits vital for breeding climate-resilient crops.
Economic Considerations: Costs and Benefits for Farmers
Heritage seeds often require lower upfront costs compared to hybrid seeds, which can be expensive due to proprietary technology and seed licensing fees. Farmers growing heritage seeds benefit from saving seeds for future planting, reducing dependency on external suppliers and enhancing long-term economic sustainability. Hybrid seeds typically offer higher yields and greater resistance to pests and diseases, translating into short-term economic gains, but their reliance on annual purchase can increase operating expenses over time.
Policy and Regulation: Supporting Genetic Diversity in Seed Systems
Policies promoting heritage seed conservation enhance genetic diversity by safeguarding traditional varieties adapted to local ecosystems, which face risks of erosion from widespread hybrid seed use. Regulatory frameworks incentivize seed banks and community seed exchanges, ensuring heritage seeds remain accessible and viable for farmers, thereby stabilizing agrobiodiversity. Hybrid seed commercialization often involves patent laws that restrict seed saving and sharing, challenging efforts to maintain genetic variability crucial for sustainable agriculture resilience.
Cultivating the Future: Integrating Heritage and Hybrid Seeds for Sustainability
Heritage seeds maintain genetic diversity through open pollination and adaptation to local environments, preserving unique traits vital for resilient crop systems. Hybrid seeds offer high yields and disease resistance, yet rely on controlled breeding, potentially narrowing genetic pools and increasing dependency on seed companies. Integrating heritage and hybrid seeds in sustainable agriculture promotes long-term ecosystem stability and food security by balancing productivity with biodiversity conservation.
Related Important Terms
Landrace preservation
Heritage seeds, often derived from traditional landraces, preserve genetic diversity essential for resilience in sustainable agriculture, whereas hybrid seeds typically offer uniformity but reduce genetic variability. Prioritizing landrace preservation supports adaptive traits in crops, ensuring ecosystem stability and food security amid changing climates.
Heirloom seed resilience
Heirloom seeds offer superior genetic diversity compared to hybrid seeds, preserving unique traits that enhance resilience against pests, diseases, and climate variability in sustainable agriculture. This genetic variability supports ecosystem stability and long-term crop adaptation, making heirloom seeds crucial for maintaining agricultural biodiversity.
Open-pollinated genetics
Heritage seeds, also known as open-pollinated seeds, maintain genetic diversity by allowing natural cross-pollination, resulting in resilient plant varieties adapted to local environments. In contrast, hybrid seeds, developed through controlled crossbreeding for uniformity and yield, often lack the genetic variability necessary for long-term ecological sustainability in agriculture.
Genetic bottlenecking
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining a wide range of alleles adapted to local environments, whereas hybrid seeds often result in genetic bottlenecking due to their limited gene pools and uniform traits. This reduction in genetic variation from hybrid seeds increases vulnerability to pests, diseases, and environmental changes, threatening long-term sustainability in agriculture.
Synthetic hybrid vigor
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional traits adapted to local environments, whereas hybrid seeds, especially synthetic hybrids, exploit hybrid vigor to enhance yield and resilience through controlled crossbreeding of distinct parent lines. Synthetic hybrid vigor boosts productivity but often reduces long-term genetic variability, making heritage seeds crucial for sustaining biodiversity in sustainable agriculture.
Agrobiodiversity hotspots
Heritage seeds, nurtured in agrobiodiversity hotspots, preserve genetic diversity essential for resilient and sustainable farming systems, unlike hybrid seeds that often reduce genetic variability through uniform traits. Preserving heritage seeds safeguards adaptive traits critical for climate resilience and local ecosystem balance, promoting sustainable agriculture in biodiversity-rich regions.
Seed sovereignty movement
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional plant varieties adapted to local environments, supporting resilient ecosystems and cultural heritage within the Seed Sovereignty movement. Hybrid seeds, though often higher yielding, reduce genetic variability and increase dependency on commercial seed companies, undermining farmers' control over their seed resources and agro-biodiversity.
Heritage gene pool
Heritage seeds preserve the rich genetic diversity of traditional crops, maintaining traits adapted to local environments and enhancing resilience against pests, diseases, and climate variation. Unlike hybrid seeds, which often focus on uniformity and short-term yields, heritage gene pools support sustainable agriculture by fostering biodiversity essential for long-term ecosystem health and food security.
Commercial cultivar dominance
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity essential for sustainable agriculture by maintaining traits adapted to local environments, while commercial hybrid seeds dominate markets due to high yield uniformity but contribute to genetic erosion. The widespread adoption of hybrid cultivars in commercial farming reduces crop genetic variation, undermining long-term resilience against pests, diseases, and climate change.
Transgenic seed introgression
Heritage seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional plant traits, whereas hybrid seeds often prioritize yield and uniformity, potentially limiting genetic variability. Transgenic seed introgression raises concerns about unintended gene flow from genetically modified crops into heritage varieties, threatening the integrity of native genetic resources in sustainable agriculture.
Heritage seeds vs Hybrid seeds for genetic diversity Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com