Demand-driven extension prioritizes the specific needs and preferences of farmers, leading to tailored services that enhance adoption rates and sustainability. Supply-driven extension often relies on pre-determined technologies and information, which may not align with local conditions or farmers' priorities, potentially reducing effectiveness. Emphasizing demand-driven approaches in agricultural extension strengthens farmer engagement, improves resource use efficiency, and fosters innovation tailored to local challenges.
Table of Comparison
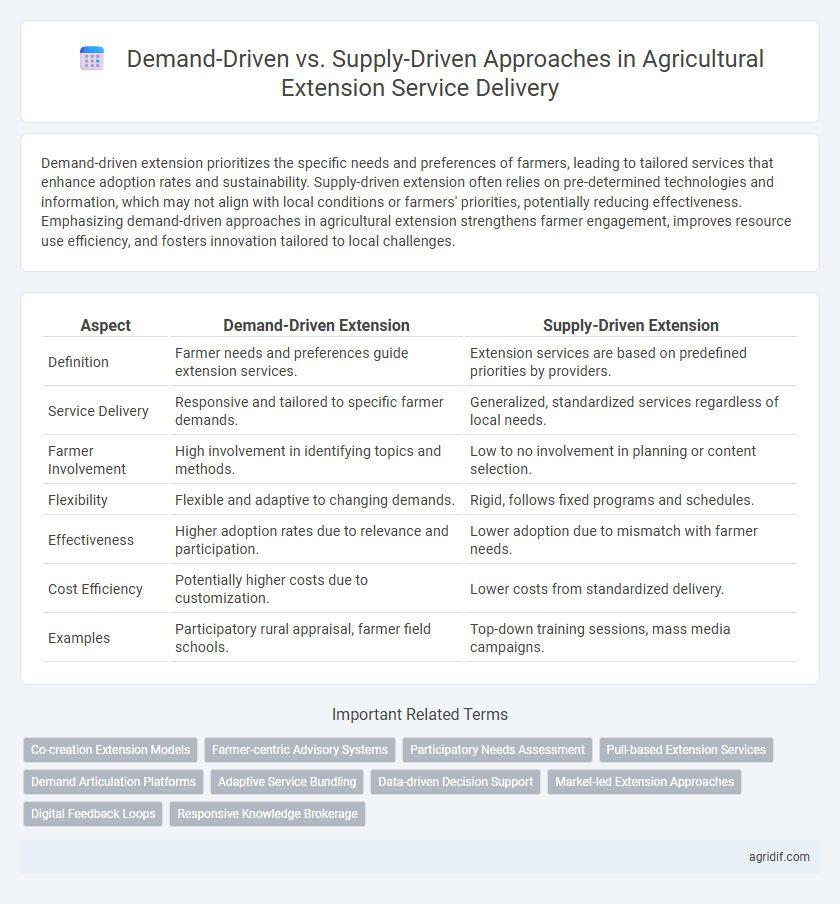
| Aspect | Demand-Driven Extension | Supply-Driven Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Farmer needs and preferences guide extension services. | Extension services are based on predefined priorities by providers. |
| Service Delivery | Responsive and tailored to specific farmer demands. | Generalized, standardized services regardless of local needs. |
| Farmer Involvement | High involvement in identifying topics and methods. | Low to no involvement in planning or content selection. |
| Flexibility | Flexible and adaptive to changing demands. | Rigid, follows fixed programs and schedules. |
| Effectiveness | Higher adoption rates due to relevance and participation. | Lower adoption due to mismatch with farmer needs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher costs due to customization. | Lower costs from standardized delivery. |
| Examples | Participatory rural appraisal, farmer field schools. | Top-down training sessions, mass media campaigns. |
Understanding Demand-Driven Extension in Agriculture
Demand-driven extension in agriculture tailors advisory services to the specific needs and priorities of farmers, enhancing relevance and adoption rates. This approach relies on farmer feedback and market signals to design interventions, ensuring efficient resource use and improved productivity. Understanding demand-driven extension enables service providers to address localized challenges and support sustainable agricultural development effectively.
Key Features of Supply-Driven Extension Approaches
Supply-driven extension approaches prioritize the dissemination of pre-determined technologies and information based on institutional capacity rather than farmer demand, often resulting in standardized solutions. Key features include a top-down communication flow, limited farmer participation in decision-making, and a focus on promoting inputs provided by research and government agencies. This model emphasizes scale and efficiency but may overlook local needs and adaptive innovation in agricultural practices.
Comparative Effectiveness: Demand-Driven vs Supply-Driven Extension
Demand-driven extension services prioritize farmer needs and local context, leading to higher adoption rates and improved agricultural productivity. Supply-driven extension often results in generalized recommendations that may not align with specific farmer challenges, reducing effectiveness and resource efficiency. Comparative studies show demand-driven models enhance farmer engagement and innovation adoption more effectively than supply-driven approaches, optimizing service delivery outcomes.
Impact on Farmer Participation and Empowerment
Demand-driven extension approaches significantly enhance farmer participation by tailoring services to the specific needs and priorities of agricultural communities, fostering greater ownership and active engagement. This method empowers farmers through knowledge-sharing and decision-making autonomy, leading to improved adoption of innovations and sustainable practices. In contrast, supply-driven extension often limits farmer involvement by imposing standardized solutions, which can reduce relevance, diminish motivation, and restrict empowerment opportunities.
Extension Service Responsiveness to Local Needs
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' specific needs, enhancing service responsiveness by adapting advice and resources to local conditions, crop preferences, and socio-economic contexts. Supply-driven extension often delivers standardized programs that may overlook unique community challenges, leading to less effective adoption and reduced impact. Tailoring extension services through participatory approaches improves relevance, farmer engagement, and sustainable agricultural outcomes.
Role of Technology in Facilitating Demand-Driven Extension
Demand-driven extension leverages digital platforms and mobile applications to connect farmers with tailored information and services based on real-time needs, enhancing precision and responsiveness in agricultural support. Technology such as GIS mapping, remote sensing, and data analytics enables extension agents to predict trends and deliver customized recommendations, increasing efficiency and farmer engagement. In contrast, supply-driven extension often relies on standardized content with limited flexibility, highlighting technology's critical role in transforming service delivery to be more adaptive and user-centric.
Challenges in Implementing Demand-Driven Extension Models
Demand-driven extension models face significant challenges including limited farmer awareness, inadequate infrastructure, and financial constraints that hinder effective service delivery. These models require robust feedback mechanisms and active farmer participation, which can be difficult to establish in regions with low literacy and poor communication networks. Additionally, scaling demand-driven approaches is often constrained by insufficient trained personnel and the need for continuous adaptive management to meet diverse farmer needs.
Policy Implications for Extension Service Reform
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' needs and local priorities, promoting participatory approaches that enhance relevance and adoption of innovations. Supply-driven extension often relies on top-down methods, focusing on delivering predetermined technologies that may not address specific community challenges. Policy reform should encourage flexible, responsive extension systems that integrate stakeholder feedback, allocate resources based on demand assessments, and foster capacity-building for adaptive service delivery.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Demand-Driven Extension
Demand-driven agricultural extension enhances farmer participation by tailoring services to specific local needs, leading to increased productivity and sustainable practices as evidenced in case studies from Kenya and India. These success stories highlight improved adoption rates of innovative technologies and better resource management compared to supply-driven models. The demand-driven approach fosters stronger farmer-extension agent partnerships, resulting in more effective knowledge transfer and heightened agricultural resilience.
Future Trends in Agricultural Extension Delivery Systems
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' specific needs and adaptive innovations, resulting in higher relevance and adoption rates of technologies. Supply-driven extension relies on predetermined agendas that often overlook localized challenges, which may limit effectiveness and farmer engagement. Future trends emphasize integrated digital platforms and participatory approaches, enabling responsive, real-time service delivery tailored to diverse agro-ecological zones.
Related Important Terms
Co-creation Extension Models
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' needs and local knowledge, enabling co-creation models that foster collaboration between extension agents and stakeholders for tailored service delivery. Supply-driven extension often relies on top-down approaches that may overlook specific community contexts, limiting the effectiveness of co-created innovations in agricultural practice.
Farmer-centric Advisory Systems
Farmer-centric Advisory Systems prioritize demand-driven extension by tailoring agricultural services to specific farmer needs, ensuring relevant and timely advice that enhances decision-making and productivity. Supply-driven extension models often deploy standardized solutions without fully addressing local contexts, leading to lower adoption rates and reduced impact on farmer livelihoods.
Participatory Needs Assessment
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' specific needs identified through participatory needs assessment, ensuring services are tailored and relevant, which enhances adoption and impact. Supply-driven extension, often relying on predetermined agendas, risks misalignment with community priorities, reducing effectiveness and farmer engagement.
Pull-based Extension Services
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmer needs by using pull-based extension services that respond directly to specific requests, enhancing relevance and adoption rates in agricultural practices. Supply-driven extension often follows a top-down approach, distributing generalized information regardless of local demand, which can limit effectiveness and engagement.
Demand Articulation Platforms
Demand-driven extension emphasizes the active involvement of farmers in identifying their specific needs through Demand Articulation Platforms, enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of service delivery. These platforms facilitate direct communication between farmers and extension providers, ensuring tailored support that contrasts with the generalized approach of supply-driven extension models.
Adaptive Service Bundling
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmers' specific needs by tailoring Adaptive Service Bundling to local contexts, enhancing relevance and adoption rates. Supply-driven extension often delivers standardized service packages that may overlook unique agricultural challenges, limiting effectiveness in diverse farming systems.
Data-driven Decision Support
Demand-driven extension tailors agricultural services based on farmers' specific needs and real-time data analysis, enhancing relevance and adoption rates; supply-driven extension relies on predefined packages with limited responsiveness to local conditions, often missing key contextual insights. Data-driven decision support systems empower demand-driven models by integrating satellite imagery, weather forecasts, and market trends to optimize recommendations and resource allocation.
Market-led Extension Approaches
Market-led extension approaches prioritize demand-driven extension by aligning agricultural services with farmers' market needs and preferences, enhancing relevance and adoption rates. Supply-driven extension often imposes generic solutions without considering local market dynamics, limiting the effectiveness of service delivery and farmer empowerment.
Digital Feedback Loops
Demand-driven extension prioritizes farmer-specific needs through real-time digital feedback loops, enabling tailored advisory services that enhance productivity and resource efficiency. Supply-driven extension relies on standardized information dissemination, often lacking adaptive mechanisms to incorporate timely farmer feedback via digital platforms, reducing responsiveness to evolving agricultural challenges.
Responsive Knowledge Brokerage
Demand-driven agricultural extension prioritizes farmer needs and local context, enhancing the relevance and effectiveness of service delivery through responsive knowledge brokerage that facilitates tailored information exchange. Supply-driven extension often relies on top-down dissemination, limiting adaptability and responsiveness, whereas demand-driven models enable dynamic interaction between researchers, extension agents, and farmers to co-create solutions aligned with real-time agricultural challenges.
Demand-driven extension vs Supply-driven extension for service delivery Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com