Face-to-face extension fosters stronger personal connections and hands-on learning experiences that enhance farmer trust and adoption of new practices. Virtual extension offers broader outreach and timely information dissemination, especially in remote areas with limited access to agricultural experts. Combining both methods maximizes outreach efficiency, ensuring diverse farmer needs are met through adaptable communication channels.
Table of Comparison
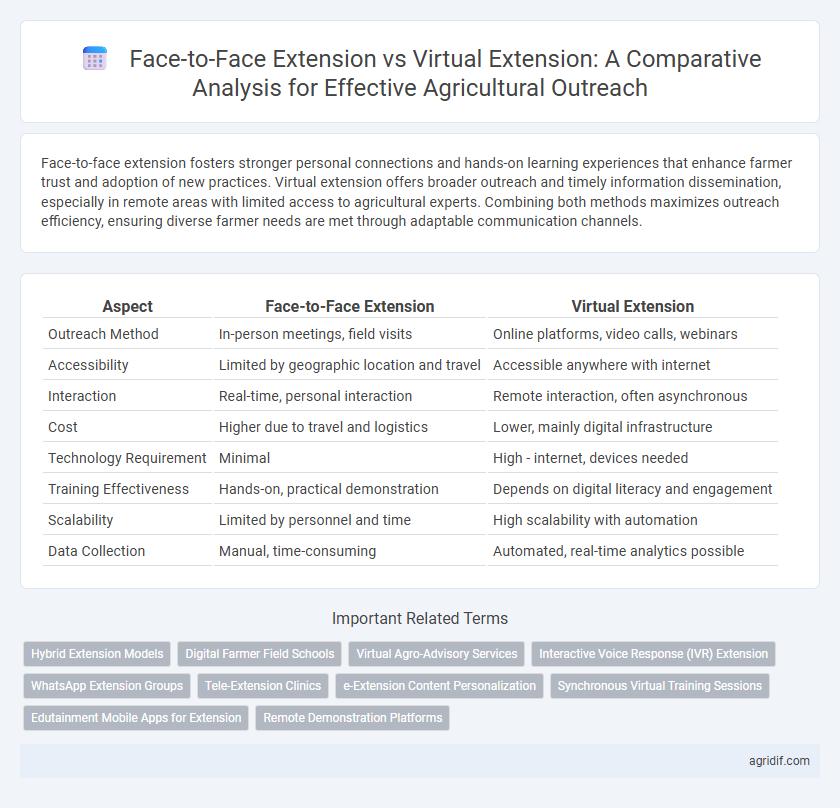
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Extension | Virtual Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Outreach Method | In-person meetings, field visits | Online platforms, video calls, webinars |
| Accessibility | Limited by geographic location and travel | Accessible anywhere with internet |
| Interaction | Real-time, personal interaction | Remote interaction, often asynchronous |
| Cost | Higher due to travel and logistics | Lower, mainly digital infrastructure |
| Technology Requirement | Minimal | High - internet, devices needed |
| Training Effectiveness | Hands-on, practical demonstration | Depends on digital literacy and engagement |
| Scalability | Limited by personnel and time | High scalability with automation |
| Data Collection | Manual, time-consuming | Automated, real-time analytics possible |
Introduction to Agricultural Extension Methods
Face-to-face extension methods enable direct, personalized interactions, facilitating immediate feedback and hands-on demonstration of agricultural practices, which improves farmer comprehension and adoption rates. Virtual extension leverages digital platforms to expand outreach, offering scalable access to training and real-time updates on innovative techniques, especially beneficial in remote or resource-limited areas. Combining both approaches harnesses the strengths of personal engagement and broad accessibility, optimizing the effectiveness of agricultural extension services.
Defining Face-to-Face Extension in Agriculture
Face-to-face extension in agriculture involves direct, in-person interactions between extension agents and farmers, enabling personalized training and immediate feedback tailored to local farming conditions. This method facilitates hands-on demonstrations of techniques, fostering trust and stronger relationships critical for effective knowledge transfer. Despite technological advancements, face-to-face extension remains essential for addressing complex agricultural issues that require nuanced communication.
Understanding Virtual Extension Approaches
Virtual extension approaches in agricultural outreach leverage digital platforms, mobile apps, and social media to provide timely, accessible information to farmers, overcoming geographical barriers inherent in face-to-face extension. These methods enable real-time interaction, personalized advisory services, and data-driven decision support, enhancing the scalability and efficiency of extension programs. Integration of virtual tools with traditional face-to-face methods maximizes outreach impact by combining technological convenience with personal engagement.
Benefits of Face-to-Face Agricultural Outreach
Face-to-face agricultural outreach fosters direct interaction, enabling personalized advice and immediate feedback that enhance farmers' understanding and adoption of new techniques. This method builds trust through personal relationships and social engagement, which are critical for influencing behavioral change in agricultural practices. Moreover, on-site visits allow extension agents to observe farm conditions firsthand, tailoring recommendations to specific environmental and resource contexts.
Advantages of Virtual Extension Services
Virtual extension services provide broader accessibility by overcoming geographical barriers, enabling farmers in remote areas to receive timely agricultural advice. They offer cost-effective and flexible learning opportunities through digital platforms, facilitating real-time interactions, webinars, and resource sharing. Enhanced data collection and personalized support are achieved through digital tools, improving the overall efficiency and impact of agricultural outreach programs.
Challenges in Traditional Extension Methods
Face-to-face agricultural extension faces challenges such as limited reach to remote farmers, high costs of repeated travel, and scheduling difficulties amidst farmers' busy seasons. Traditional methods often struggle with timely dissemination of innovations, reducing responsiveness to urgent agronomic issues. These constraints hinder scale and effectiveness compared to scalable virtual extension alternatives.
Barriers to Effective Virtual Extension Delivery
Face-to-face agricultural extension offers direct interaction and hands-on demonstration, overcoming challenges such as limited internet access and digital literacy that hinder virtual extension's effectiveness. Barriers to virtual extension include unreliable connectivity in rural areas, lack of tailored content for diverse farmer needs, and difficulties in building trust through screens. Addressing these issues requires infrastructure investment and developing user-friendly platforms to enhance virtual outreach's impact on farmer adoption rates.
Comparative Impact on Farmer Adoption Rates
Face-to-face agricultural extension methods demonstrate higher farmer adoption rates due to personalized interaction, trust-building, and hands-on demonstrations that address specific local challenges. Virtual extension platforms offer broader reach and timely information dissemination but often face limitations in user access, digital literacy, and engagement depth. Combining both approaches optimizes outreach effectiveness by balancing scalability with the tailored support necessary for sustainable adoption of farming innovations.
Technology Access and Digital Literacy in Agriculture
Face-to-face agricultural extension ensures direct interaction and hands-on demonstrations, benefiting communities with limited technology access and low digital literacy. Virtual extension offers scalable outreach and real-time updates but relies heavily on reliable internet connectivity and user familiarity with digital tools. Bridging the digital divide through technology training and infrastructure development is critical for effective adoption of virtual extension services in rural farming areas.
Future Directions: Integrating Face-to-Face and Virtual Extension
Integrating face-to-face and virtual extension methods enhances agricultural outreach by combining personalized farmer engagement with scalable digital resources. Future directions emphasize leveraging mobile applications, interactive webinars, and in-field demonstrations to optimize knowledge transfer and adoption of sustainable practices. This hybrid model supports real-time feedback, broadens access to expert advice, and fosters resilient agricultural communities.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Extension Models
Hybrid extension models combine face-to-face agricultural extension with virtual technologies, enhancing outreach by providing personalized support alongside scalable digital resources. This approach leverages direct farmer interaction for tailored advice while utilizing virtual platforms to disseminate timely information, ensuring broader access and continuous engagement.
Digital Farmer Field Schools
Face-to-face Agricultural Extension through Digital Farmer Field Schools enables hands-on learning and direct farmer engagement, fostering practical skills and immediate feedback. Virtual Extension methods expand outreach by providing flexible access to digital resources and real-time expert support, enhancing scalability and connectivity for remote farming communities.
Virtual Agro-Advisory Services
Virtual agro-advisory services leverage digital platforms to deliver timely, data-driven recommendations to farmers, enhancing reach and accessibility compared to traditional face-to-face extension methods. These services utilize mobile apps, SMS alerts, and online portals to provide crop management advice, pest and disease monitoring, and weather forecasts, optimizing agricultural productivity and resource use efficiency.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Extension
Face-to-face Agricultural Extension delivers personalized, real-time advice through direct farmer interactions, enhancing trust and immediate problem-solving. Virtual Extension via Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems offers scalable, cost-effective outreach by providing farmers with timely, automated information and feedback, especially in remote areas with limited internet connectivity.
WhatsApp Extension Groups
Face-to-face agricultural extension fosters direct engagement and personalized support, enhancing community trust and immediate problem-solving, whereas virtual extension via WhatsApp groups enables rapid information dissemination and continuous peer-to-peer learning across dispersed farmer networks. WhatsApp Extension Groups leverage multimedia messaging and real-time updates to increase outreach efficiency, facilitate expert consultations, and support collective knowledge sharing in modern agricultural practices.
Tele-Extension Clinics
Tele-Extension Clinics enhance agricultural outreach by providing timely, expert advice directly to farmers through virtual platforms, overcoming geographic barriers inherent in face-to-face extension services. These clinics leverage video consultations, real-time diagnostics, and digital data sharing to improve access, efficiency, and responsiveness in agricultural extension programs.
e-Extension Content Personalization
Face-to-face agricultural extension offers personalized, context-specific advice through direct interaction, enhancing trust and immediate feedback. Virtual extension leverages data-driven e-extension content personalization, utilizing AI and farmer profiles to tailor recommendations for scalable, accessible outreach.
Synchronous Virtual Training Sessions
Synchronous virtual training sessions in agricultural extension enhance real-time interaction and immediate feedback between experts and farmers, improving knowledge retention and practical skill application. Face-to-face extension offers hands-on experience and stronger personal relationships, but virtual sessions increase accessibility and scalability, especially for remote or resource-limited regions.
Edutainment Mobile Apps for Extension
Face-to-face extension fosters direct farmer engagement and hands-on training, enhancing trust and practical skills transfer, while virtual extension through edutainment mobile apps combines educational content with interactive entertainment to increase accessibility and user retention in rural outreach. Edutainment apps integrate multimedia tools, gamification, and real-time feedback, enabling scalable, cost-effective dissemination of agricultural innovations and best practices beyond traditional geographic limits.
Remote Demonstration Platforms
Face-to-face agricultural extension offers direct, hands-on training and real-time feedback, enhancing farmer engagement and practical learning outcomes. Virtual extension using remote demonstration platforms expands access to expert guidance across vast and remote areas, reducing travel costs while enabling interactive, timely support through digital tools.
Face-to-face Extension vs Virtual Extension for Outreach Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com