ICT extension tools enhance knowledge transfer by providing timely access to agricultural information through mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms, enabling farmers to receive expert advice regardless of location. Face-to-face extension fosters personalized interactions and trust, facilitating hands-on demonstrations and immediate feedback that can improve practical understanding. Integrating ICT with traditional extension methods optimizes farmer engagement and accelerates the adoption of innovative agricultural practices.
Table of Comparison
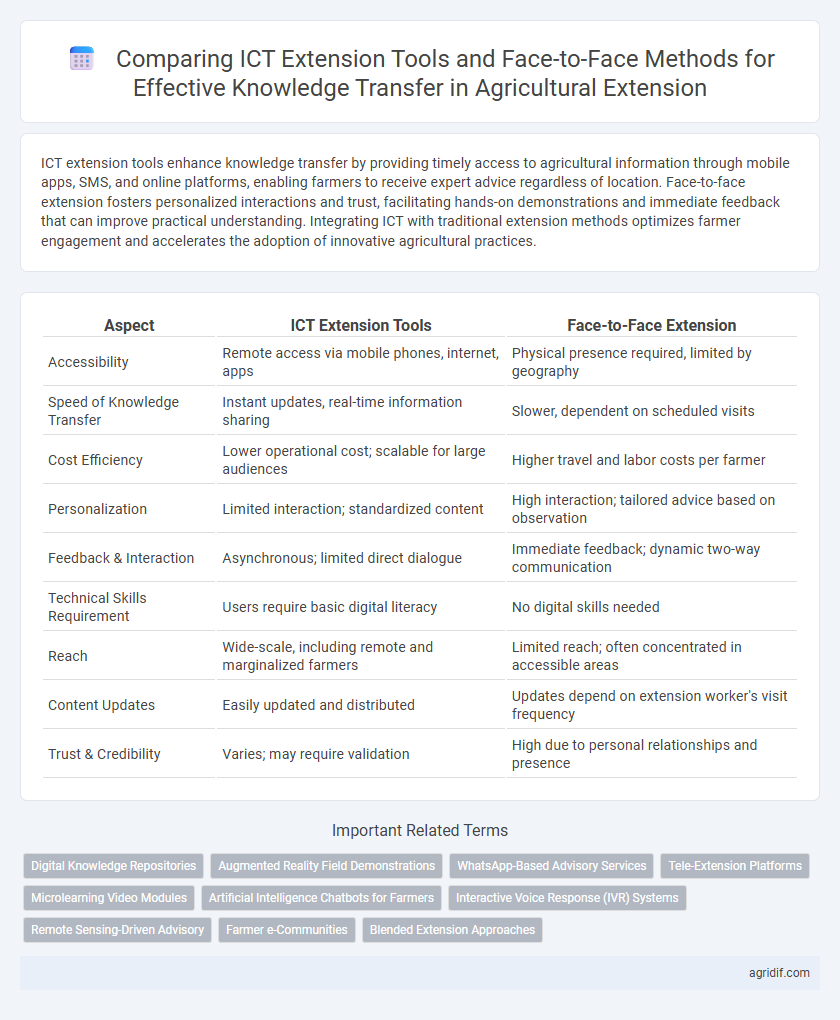
| Aspect | ICT Extension Tools | Face-to-Face Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Remote access via mobile phones, internet, apps | Physical presence required, limited by geography |
| Speed of Knowledge Transfer | Instant updates, real-time information sharing | Slower, dependent on scheduled visits |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational cost; scalable for large audiences | Higher travel and labor costs per farmer |
| Personalization | Limited interaction; standardized content | High interaction; tailored advice based on observation |
| Feedback & Interaction | Asynchronous; limited direct dialogue | Immediate feedback; dynamic two-way communication |
| Technical Skills Requirement | Users require basic digital literacy | No digital skills needed |
| Reach | Wide-scale, including remote and marginalized farmers | Limited reach; often concentrated in accessible areas |
| Content Updates | Easily updated and distributed | Updates depend on extension worker's visit frequency |
| Trust & Credibility | Varies; may require validation | High due to personal relationships and presence |
Introduction: Evolution of Knowledge Transfer in Agriculture
ICT extension tools have revolutionized knowledge transfer in agriculture by enabling real-time access to information through mobile apps, online platforms, and remote sensing technologies. These digital tools complement traditional face-to-face extension methods by providing scalable and cost-effective solutions for reaching diverse farming communities. The integration of ICT with conventional extension facilitates faster dissemination of innovations, enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
ICT Extension Tools: Definition and Key Features
ICT Extension Tools refer to digital technologies such as mobile applications, online platforms, and SMS-based services used to disseminate agricultural knowledge efficiently to farmers and stakeholders. Key features include real-time information sharing, interactive communication capabilities, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, enabling rapid updates on best practices, pest management, and weather forecasts. These tools enhance accessibility and convenience, especially in remote areas, bridging knowledge gaps that traditional face-to-face extension methods might struggle to address.
Face-to-Face Extension: Traditional Methods and Approaches
Face-to-face extension remains a cornerstone in agricultural knowledge transfer, leveraging direct interaction between extension agents and farmers to facilitate tailored advice and hands-on demonstrations. Traditional methods, such as on-field visits, farmer group meetings, and participatory training sessions, build trust and allow for immediate feedback and adaptation to local contexts. These approaches enhance the adoption of agricultural innovations by addressing specific challenges and cultural nuances through personalized communication.
Comparative Effectiveness in Knowledge Dissemination
ICT extension tools enhance agricultural knowledge dissemination through real-time updates, interactive multimedia, and wide-reaching platforms such as mobile apps and online forums, enabling rapid access to expert advice and best practices. Face-to-face extension remains indispensable for hands-on training, personalized guidance, and building trust, particularly in regions with limited digital literacy and connectivity. Combining ICT tools with traditional methods optimizes knowledge transfer efficacy, bridging gaps in access and engagement across diverse farming communities.
Accessibility and Digital Divide in Rural Areas
ICT Extension Tools enhance knowledge transfer by providing remote access to agricultural information, overcoming geographical barriers common in rural areas with limited extension services. However, the digital divide--characterized by disparities in internet connectivity, smartphone ownership, and digital literacy--restricts the effectiveness and reach of these tools among marginalized farming communities. Face-to-face extension remains crucial for inclusive accessibility, particularly where infrastructure deficits impede consistent ICT adoption and where personal interaction fosters trust and tailored guidance.
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: ICT vs. Face-to-Face
ICT extension tools significantly reduce operational costs by minimizing travel and lodging expenses associated with face-to-face extension services, leading to higher cost-efficiency per farmer reached. Studies show that mobile applications, SMS, and online platforms enable scalable knowledge transfer with lower marginal costs compared to traditional in-person visits. However, initial investment in ICT infrastructure and digital literacy training must be considered to optimize overall cost-effectiveness in agricultural extension.
Farmer Engagement and Trust Building
ICT extension tools, such as mobile apps and digital platforms, enhance farmer engagement by providing timely access to agricultural information and personalized advice, increasing convenience and scalability. Face-to-face extension fosters deeper trust through direct interpersonal interactions, enabling extension agents to build rapport, address specific farmer concerns, and demonstrate techniques hands-on. Combining ICT tools with face-to-face methods optimizes knowledge transfer, balancing the broad reach of digital solutions with the relational depth essential for sustained farmer trust and active participation.
Overcoming Language and Literacy Barriers
ICT Extension Tools leverage mobile apps, SMS, and interactive voice response systems to deliver agricultural knowledge in local languages, effectively overcoming literacy barriers. These digital platforms enable farmers with limited reading skills to access tailored, audio-visual content that enhances understanding and retention of complex farming techniques. Face-to-face extension, while valuable for personalized interaction, often struggles to bridge language gaps and reach illiterate farmers at scale compared to ICT-enabled methods.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Case studies reveal that ICT extension tools, such as mobile apps and online platforms, significantly enhance the reach and timeliness of agricultural knowledge transfer compared to traditional face-to-face methods. Success stories from regions like Kenya and India highlight improved farmer adoption rates and cost-effectiveness using digital channels, while lessons learned emphasize the need for digital literacy and infrastructure investment to maximize ICT impact. Combining ICT tools with targeted face-to-face extension ensures more comprehensive support, addressing both accessibility and personalized advice in agricultural knowledge dissemination.
Future Trends: Integrating ICT and Face-to-Face Extension
Integrating ICT extension tools with face-to-face methods enhances agricultural knowledge transfer by combining the scalability of digital platforms with the personalized support of direct interaction. Future trends emphasize hybrid models leveraging mobile apps, virtual reality, and AI-powered advisory services alongside traditional field visits to improve farmer engagement and learning outcomes. This integration fosters timely access to tailored information, supports real-time problem solving, and drives sustainable agricultural innovation.
Related Important Terms
Digital Knowledge Repositories
Digital knowledge repositories in ICT extension tools enhance agricultural knowledge transfer by providing farmers with immediate access to up-to-date information and best practices, outperforming traditional face-to-face methods in scalability and consistency. These repositories enable efficient dissemination of expert content, fostering data-driven decision-making and accelerating adoption of innovative farming techniques.
Augmented Reality Field Demonstrations
Augmented Reality Field Demonstrations in ICT extension tools offer immersive, interactive learning experiences that enhance farmers' understanding of complex agricultural practices compared to traditional face-to-face extension methods. These AR tools enable real-time visualization of crop management techniques, pest identification, and soil analysis, significantly improving knowledge retention and practical application in the field.
WhatsApp-Based Advisory Services
WhatsApp-based advisory services in agricultural extension leverage real-time communication, multimedia sharing, and group interactions to enhance farmer knowledge transfer more efficiently than traditional face-to-face methods. This ICT extension tool improves accessibility, reduces costs, and allows rapid dissemination of tailored agronomic advice, fostering timely decision-making and increasing adoption rates of best farming practices.
Tele-Extension Platforms
Tele-extension platforms leverage ICT tools to enhance agricultural knowledge transfer by providing real-time access to expert advice, remote diagnostics, and multimedia content, significantly expanding outreach and reducing costs compared to traditional face-to-face extension methods. These digital platforms facilitate interactive learning, timely updates on best practices, and scalability, addressing the limitations of in-person visits and improving farmer engagement and decision-making efficiency.
Microlearning Video Modules
Microlearning video modules in ICT extension tools enhance agricultural knowledge transfer by delivering concise, visually engaging content accessible anytime, increasing farmer engagement and retention compared to traditional face-to-face methods. These digital modules facilitate rapid dissemination of best practices and innovations, overcoming geographical barriers and enabling personalized learning at scale.
Artificial Intelligence Chatbots for Farmers
Artificial Intelligence chatbots in ICT extension tools enable personalized, instant responses to farmers' inquiries, enhancing knowledge transfer efficiency compared to traditional face-to-face extension methods. These AI-driven platforms analyze vast agricultural data to provide tailored advice on crop management, pest control, and market trends, increasing accessibility and scalability of agricultural extension services.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems in agricultural extension offer scalable, cost-effective solutions for knowledge transfer, enabling farmers to access real-time information and personalized advice without geographic constraints. Compared to face-to-face extension, IVR enhances continuous interaction and immediate feedback, significantly improving adoption rates of best practices and reducing dependence on limited extension personnel.
Remote Sensing-Driven Advisory
Remote sensing-driven advisory enhances ICT extension tools by providing real-time, spatially accurate data that enables precise agricultural decision-making, outperforming traditional face-to-face extension's limited reach and frequency. Integrating remote sensing with ICT platforms accelerates knowledge transfer, improves crop monitoring, and supports timely interventions for farmers in remote areas.
Farmer e-Communities
ICT extension tools enable real-time knowledge sharing and expert advice within farmer e-communities, enhancing accessibility and scalability of agricultural innovations. Face-to-face extension remains crucial for building trust, demonstrating techniques physically, and addressing context-specific challenges in localized farming systems.
Blended Extension Approaches
Blended extension approaches combine ICT extension tools such as mobile apps, SMS alerts, and online platforms with face-to-face extension methods to enhance agricultural knowledge transfer efficiency and accessibility. Integrating digital communication technologies with traditional interpersonal interactions improves farmer engagement, real-time feedback, and the contextual adaptation of advisory services.
ICT Extension Tools vs Face-to-Face Extension for Knowledge Transfer Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com