Supportive supervision fosters staff development by encouraging open communication, providing constructive feedback, and promoting problem-solving skills, which enhances motivation and professional growth. Directive supervision focuses on strict adherence to procedures and rules, ensuring compliance but potentially limiting employee autonomy and creativity. Balancing these approaches improves agricultural extension outcomes by combining clear guidance with empowerment and skill-building.
Table of Comparison
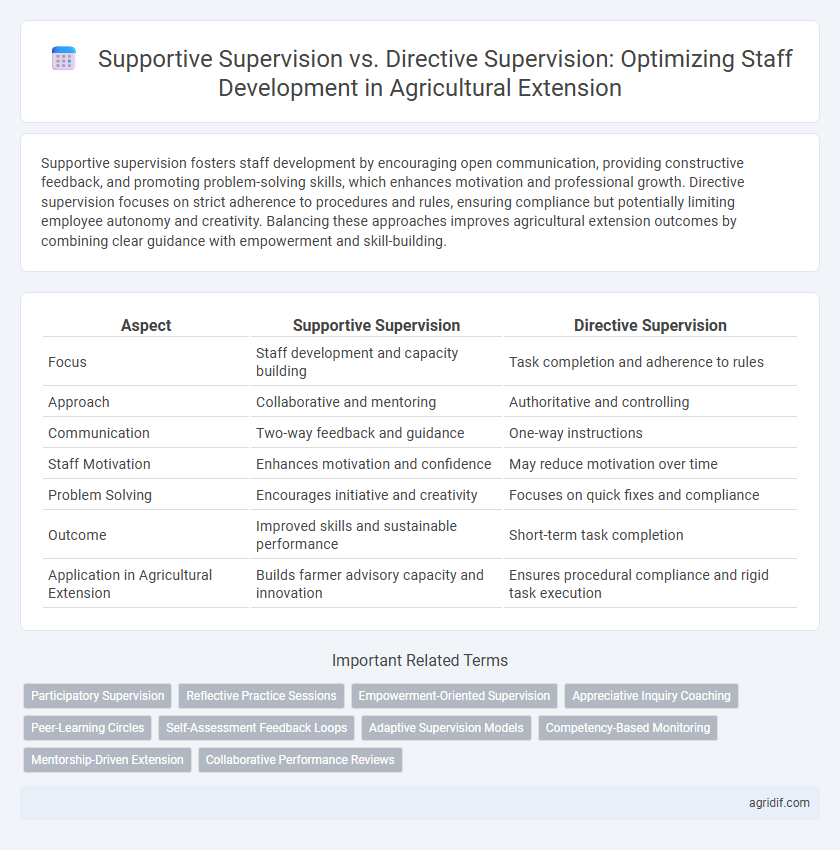
| Aspect | Supportive Supervision | Directive Supervision |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Staff development and capacity building | Task completion and adherence to rules |
| Approach | Collaborative and mentoring | Authoritative and controlling |
| Communication | Two-way feedback and guidance | One-way instructions |
| Staff Motivation | Enhances motivation and confidence | May reduce motivation over time |
| Problem Solving | Encourages initiative and creativity | Focuses on quick fixes and compliance |
| Outcome | Improved skills and sustainable performance | Short-term task completion |
| Application in Agricultural Extension | Builds farmer advisory capacity and innovation | Ensures procedural compliance and rigid task execution |
Understanding Supportive and Directive Supervision in Agricultural Extension
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes mentorship, collaborative problem-solving, and capacity building to enhance staff skills and motivation. Directive supervision focuses on clear instructions, task monitoring, and performance enforcement to ensure compliance and timely completion of activities. Understanding these approaches helps tailor staff development strategies, balancing guidance with accountability to improve agricultural service delivery.
Key Differences Between Supportive and Directive Supervisory Approaches
Supportive supervision emphasizes collaborative problem-solving, continuous feedback, and capacity building to enhance staff motivation and professional growth in agricultural extension. Directive supervision focuses on task-oriented guidance, strict adherence to procedures, and close monitoring to ensure compliance and immediate performance outcomes. The key differences lie in supportive supervision fostering autonomy and learning, while directive supervision enforces control and accountability through prescriptive instructions.
Impact of Supportive Supervision on Staff Motivation and Performance
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension enhances staff motivation by fostering open communication, providing constructive feedback, and encouraging problem-solving, which leads to improved performance and job satisfaction. Unlike directive supervision, which relies on strict control and task-oriented management, supportive supervision empowers employees, resulting in higher engagement and proactive innovation. Empirical studies demonstrate that supportive supervision significantly increases extension workers' commitment and effectiveness, ultimately boosting the quality of agricultural advisory services and farmer outcomes.
The Role of Directive Supervision in Staff Development
Directive supervision plays a crucial role in staff development within agricultural extension by providing clear instructions, structured guidance, and immediate feedback, which helps enhance technical skills and knowledge retention. This approach ensures compliance with specific agricultural protocols and accelerates the learning curve for less experienced staff, fostering accountability and consistent performance standards. Directive supervision is particularly effective in environments requiring strict adherence to established procedures and rapid skill acquisition.
Building Staff Capacity Through Supportive Supervision
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes ongoing mentorship, collaborative problem-solving, and capacity building to enhance staff skills and motivation. This approach fosters a positive learning environment, encouraging innovation and adaptive practices among extension workers. Directive supervision, while focused on compliance and task completion, often limits opportunities for professional growth and reduces staff engagement in capacity development.
Challenges of Implementing Supportive Supervision in Agricultural Extension
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension fosters staff development through mentoring and collaborative problem-solving, but faces challenges such as limited resources, inadequate training for supervisors, and resistance to change among field staff. The shift from directive to supportive supervision demands continuous capacity building and cultural adaptation within extension organizations. Overcoming these obstacles requires strategic investment in management training, improved communication systems, and organizational commitment to participatory leadership models.
Effectiveness of Directive Supervision in Achieving Extension Goals
Directive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes clear instructions and close monitoring, leading to higher task completion rates and improved adherence to extension protocols. Its effectiveness in achieving extension goals is demonstrated by enhanced staff performance, timely implementation of programs, and increased accountability. This supervision style helps maintain focus on specific targets, ensuring extension services are delivered efficiently and consistently.
Balancing Supportive and Directive Approaches for Optimal Staff Development
Balancing supportive and directive supervision in agricultural extension maximizes staff development by fostering empowerment and accountability simultaneously. Supportive supervision encourages continuous learning and problem-solving, while directive supervision ensures clarity in roles and adherence to standards. Integrating both approaches tailors development to individual needs, improving performance and extension outcomes effectively.
Case Studies: Supervision Models in Agricultural Extension Services
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension fosters collaboration, continuous learning, and problem-solving among staff, which enhances their skills and service quality. Directive supervision, characterized by top-down instructions and strict adherence to protocols, is effective in ensuring compliance but may limit creativity and adaptability. Case studies demonstrate that integrating supportive approaches within directive frameworks results in improved staff motivation and more responsive agricultural extension services.
Recommendations for Enhancing Staff Development Through Effective Supervision
Supportive supervision fosters a collaborative environment where agricultural extension staff receive guidance, motivation, and feedback, enhancing skill development and job satisfaction. Directive supervision, while structured and task-oriented, may limit opportunities for creativity and adaptive problem-solving among extension workers. Maximizing staff potential requires integrating supportive supervision practices with clear performance expectations, regular training, and constructive feedback mechanisms tailored to the unique challenges of agricultural extension services.
Related Important Terms
Participatory Supervision
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes collaborative problem-solving and capacity-building through participatory methods, fostering staff empowerment and continuous learning. Directive supervision, by contrast, relies on top-down instructions with limited feedback, often hindering staff development and engagement in participatory supervision approaches.
Reflective Practice Sessions
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes reflective practice sessions that foster staff development through collaborative problem-solving and continuous learning, enhancing adaptability and critical thinking. Directive supervision, by contrast, prioritizes task completion with top-down instructions, often limiting opportunities for reflection and tailored skill growth among extension staff.
Empowerment-Oriented Supervision
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes empowerment-oriented approaches that build staff capacity through collaborative problem-solving and continuous feedback, enhancing motivation and professional growth. Directive supervision, in contrast, relies on top-down instructions that may limit staff autonomy and innovation, potentially hindering long-term development and adaptive skills.
Appreciative Inquiry Coaching
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes Appreciative Inquiry Coaching to foster staff development by identifying strengths and encouraging collaborative problem-solving, thereby enhancing motivation and skill growth. Directive supervision, contrastingly, relies on top-down instructions that may limit creativity and engagement, potentially hindering long-term professional development of extension staff.
Peer-Learning Circles
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes collaborative feedback and problem-solving within peer-learning circles, fostering continuous staff development and knowledge exchange. Directive supervision, in contrast, relies on top-down instructions that may limit peer interaction, reducing opportunities for collective learning and innovation among extension workers.
Self-Assessment Feedback Loops
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension fosters staff development by encouraging self-assessment feedback loops that promote continuous learning and adaptation, while directive supervision tends to limit autonomy and reduce opportunities for reflective practice. Emphasizing feedback-driven self-evaluation enhances skill acquisition and motivation, leading to improved extension service delivery and farmer outcomes.
Adaptive Supervision Models
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension fosters staff development by emphasizing collaborative problem-solving, continuous feedback, and capacity building, promoting adaptability to diverse farming contexts. Directive supervision offers structured guidance and clear instructions, suitable for routine tasks but less effective in adaptive supervision models that require flexibility and responsiveness to farmers' evolving needs.
Competency-Based Monitoring
Supportive supervision emphasizes collaborative engagement and continuous feedback to enhance agricultural extension staff competencies, fostering skill development through mentoring and capacity-building activities. Directive supervision prioritizes compliance and task completion, often limiting opportunities for competency-based monitoring that nurtures adaptive problem-solving and professional growth.
Mentorship-Driven Extension
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension fosters staff development through mentorship-driven approaches that emphasize collaborative problem-solving, continuous feedback, and capacity building, enhancing extension workers' skills and confidence. Directive supervision, by contrast, relies on top-down instructions and compliance, which may limit adaptive learning and innovation critical for effective agricultural extension services.
Collaborative Performance Reviews
Supportive supervision in agricultural extension emphasizes collaborative performance reviews that foster continuous learning and motivation among staff, enhancing problem-solving skills and adaptability in the field. Directive supervision, by contrast, centers on top-down instructions with limited feedback, which may restrict staff development and hinder proactive engagement in improving extension services.
Supportive Supervision vs Directive Supervision for staff development Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com