Print media in agricultural extension offers tangible, easy-to-distribute materials such as brochures and manuals that are effective in areas with limited internet access. Digital media enables real-time updates, interactive content, and wider reach through platforms like social media and mobile apps, enhancing farmer engagement and knowledge sharing. Combining both media types maximizes outreach and adapts communication strategies to diverse audience needs and technological availability.
Table of Comparison
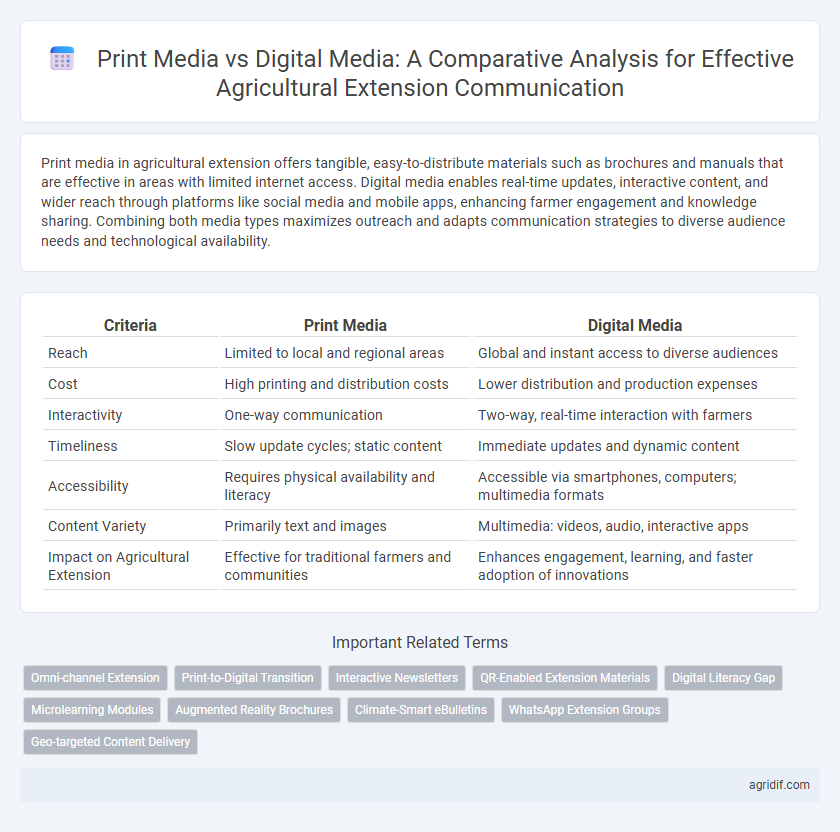
| Criteria | Print Media | Digital Media |
|---|---|---|
| Reach | Limited to local and regional areas | Global and instant access to diverse audiences |
| Cost | High printing and distribution costs | Lower distribution and production expenses |
| Interactivity | One-way communication | Two-way, real-time interaction with farmers |
| Timeliness | Slow update cycles; static content | Immediate updates and dynamic content |
| Accessibility | Requires physical availability and literacy | Accessible via smartphones, computers; multimedia formats |
| Content Variety | Primarily text and images | Multimedia: videos, audio, interactive apps |
| Impact on Agricultural Extension | Effective for traditional farmers and communities | Enhances engagement, learning, and faster adoption of innovations |
Overview of Print and Digital Media in Agricultural Extension
Print media in agricultural extension includes magazines, brochures, and newspapers, providing tangible, detailed, and locally relevant information to farmers with limited internet access. Digital media leverages mobile apps, social media platforms, and online videos, enabling rapid dissemination of updated agricultural practices and interactive farmer engagement. Both media types complement each other by addressing diverse literacy levels and accessibility, enhancing overall extension communication effectiveness.
Historical Evolution of Extension Communication Channels
Print media served as the foundational channel for agricultural extension communication, with newspapers, pamphlets, and bulletins widely used from the early 20th century to disseminate vital farming techniques and innovations. The advent of digital media in the late 20th century revolutionized extension communication by enabling rapid, interactive, and multimedia-rich information sharing through websites, social media, and mobile applications. This historical shift from print to digital media enhanced accessibility, real-time feedback, and personalized advisory services, significantly improving the reach and impact of agricultural extension programs.
Reach and Accessibility of Print Media
Print media in agricultural extension communication offers tangible, reliable resources that can reach farmers in remote areas with limited internet connectivity, ensuring accessibility regardless of digital infrastructure. Printed materials such as brochures, posters, and newsletters provide consistent messaging that can be easily shared and referred to multiple times without the need for electronic devices. The durability and ease of distribution in rural settings make print media a crucial tool for extending agricultural knowledge to underserved populations.
Digital Media Penetration in Rural Communities
Digital media penetration in rural communities has significantly transformed agricultural extension communication by providing timely access to weather updates, market prices, and best farming practices through mobile apps, social media, and SMS alerts. Studies show that smartphones and affordable internet packages have increased digital literacy and enabled farmers to interact directly with experts, thereby enhancing knowledge dissemination and adoption rates. Despite infrastructural challenges, digital platforms outperform print media in scalability and real-time information delivery, bridging the information gap in remote agricultural areas.
Cost-Effectiveness: Print vs. Digital Media
Digital media offers greater cost-effectiveness for agricultural extension communication, with lower production and distribution expenses compared to print media. While print materials entail costs for paper, printing, and physical delivery, digital platforms leverage internet connectivity to reach broader audiences instantaneously at minimal incremental costs. This scalability and reduced expenditure enhance the efficiency of disseminating agricultural knowledge through digital channels.
Content Customization and Interactivity
Print media in agricultural extension offers limited content customization and minimal interactivity, often providing standardized information that cannot be easily tailored to diverse farmer needs. Digital media allows dynamic content customization through multimedia formats, real-time updates, and interactive features such as feedback forms, quizzes, and discussion forums, enhancing farmer engagement and knowledge retention. The interactive nature of digital platforms facilitates personalized learning experiences, enabling extension agents to address specific agricultural challenges effectively.
Literacy and Language Considerations
Print media in agricultural extension communication often requires higher literacy levels and may be limited by language barriers, making accessibility challenging for diverse farmer populations. Digital media offers interactive, multimedia content that can overcome literacy constraints through audio-visual tools and supports multiple languages, enhancing comprehension and engagement. Tailoring extension materials to local dialects and literacy proficiency significantly improves the effectiveness of both print and digital communication channels.
Timeliness and Speed of Information Dissemination
Digital media significantly enhances timeliness and speed of information dissemination in agricultural extension, enabling real-time updates and instant access to critical data for farmers. Print media, while reliable for detailed guides and extended reading, lacks the immediacy required for rapid response to changing agricultural conditions such as pest outbreaks or weather alerts. Effective extension communication increasingly relies on digital platforms to deliver timely advice, improving decision-making and farm management practices.
Challenges in Adopting Digital Media for Extension
Challenges in adopting digital media for agricultural extension communication include limited internet connectivity and low digital literacy among rural farmers, restricting access to online resources and platforms. High costs of smartphones and data plans further hinder widespread usage, alongside concerns about misinformation and trustworthiness of digital content. Infrastructure gaps and language barriers also contribute to the slower integration of digital media compared to traditional print media in agricultural extension services.
Future Trends in Extension Communication Technologies
Digital media is rapidly transforming agricultural extension communication by enabling real-time data sharing, interactive platforms, and personalized advisory services, which print media cannot match in responsiveness or reach. Future trends emphasize the integration of AI-driven analytics, mobile apps, and multimedia tools to enhance farmer engagement and knowledge dissemination. While print media maintains relevance in low-connectivity areas, digital technologies dominate the trajectory of efficient, scalable, and cost-effective extension services.
Related Important Terms
Omni-channel Extension
Print media in agricultural extension provides trusted, accessible information through brochures, newsletters, and posters, effectively reaching farmers with limited internet access, while digital media enables real-time updates, interactive content, and broader dissemination via mobile apps, social media, and online platforms. An omni-channel extension approach integrates print and digital media to maximize outreach, ensuring consistent, multi-format communication tailored to diverse farmer preferences and technological capabilities.
Print-to-Digital Transition
The print-to-digital transition in agricultural extension communication enhances the accessibility and timeliness of information, leveraging digital platforms to reach diverse farmer demographics with multimedia content and real-time updates. Despite print media's enduring credibility, digital tools enable interactive engagement, rapid dissemination of innovations, and cost-effective scalability crucial for modern extension services.
Interactive Newsletters
Interactive newsletters in agricultural extension enhance farmer engagement by combining print media's tangible trustworthiness with digital media's real-time updates and multimedia integration. Leveraging clickable links, embedded videos, and personalized content in digital newsletters significantly improves knowledge retention and adoption of best practices compared to traditional print formats.
QR-Enabled Extension Materials
QR-enabled extension materials blend the traditional credibility of print media with the interactive capabilities of digital media, enhancing accessibility and engagement for farmers. By embedding QR codes in brochures, posters, and manuals, agricultural extension services facilitate instant access to updated videos, tutorials, and expert advice, bridging the gap between offline and online communication channels.
Digital Literacy Gap
Digital media in agricultural extension offers rapid information dissemination and interactive platforms but often faces challenges due to varying levels of digital literacy among farmers, limiting its effectiveness. Print media remains essential for reaching those with limited access to technology or lower digital skills, ensuring inclusive communication across diverse agricultural communities.
Microlearning Modules
Print media in agricultural extension offers tactile engagement and localized content but lacks the interactivity and real-time updates found in digital media. Digital platforms deliver microlearning modules with multimedia formats, instant feedback, and accessibility across devices, enhancing knowledge retention and farmer adoption rates.
Augmented Reality Brochures
Augmented Reality brochures in agricultural extension merge print media's tangibility with digital media's interactive capabilities, enhancing farmer engagement and knowledge retention through immersive 3D visuals and real-time data overlays. This hybrid approach enables precise demonstration of farming techniques and crop management practices, bridging traditional outreach with innovative technology for improved extension communication effectiveness.
Climate-Smart eBulletins
Climate-Smart eBulletins delivered through digital media enable rapid dissemination of up-to-date agricultural practices, enhancing farmers' adaptive capacity to climate variability more effectively than traditional print media. Digital platforms offer interactive content and real-time updates, improving access to critical climate-smart innovations and fostering sustainable agricultural resilience.
WhatsApp Extension Groups
WhatsApp extension groups enable real-time, cost-effective dissemination of agricultural advice, fostering interactive communication and quick problem-solving among farmers compared to traditional print media. These digital platforms enhance accessibility and engagement, driving timely adoption of innovative farming practices and improving overall extension service impact.
Geo-targeted Content Delivery
Geo-targeted content delivery enhances digital media's effectiveness in agricultural extension by providing location-specific advice, crop calendars, and weather alerts directly to farmers' devices, improving timely decision-making. Print media lacks this precision, often delivering generalized information that may not address local agricultural challenges or opportunities as effectively.
Print media vs Digital media for extension communication Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com