The auction system for produce selling allows real-time bidding, ensuring transparent price discovery and quick sales, benefiting farmers seeking immediate payment. The tender system involves submitting sealed bids, promoting competitive pricing but often extending the time before payment and delivery. Both systems impact market dynamics differently, with auctions fostering price fluctuations and tenders providing fixed timeframes for negotiations.
Table of Comparison
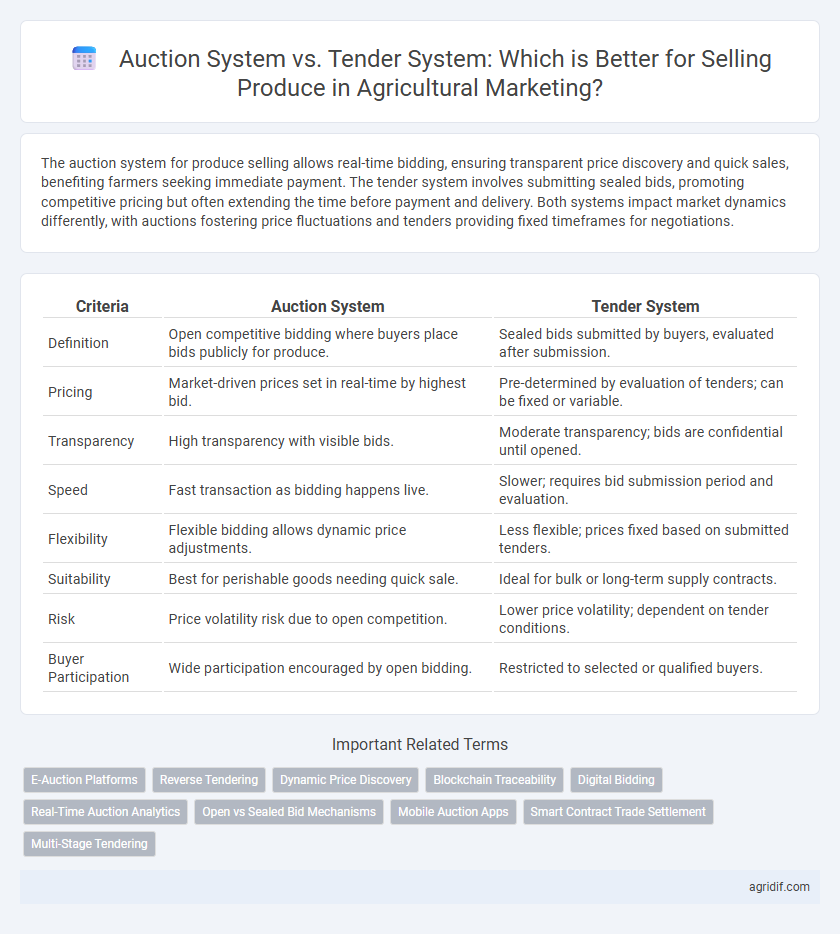
| Criteria | Auction System | Tender System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open competitive bidding where buyers place bids publicly for produce. | Sealed bids submitted by buyers, evaluated after submission. |
| Pricing | Market-driven prices set in real-time by highest bid. | Pre-determined by evaluation of tenders; can be fixed or variable. |
| Transparency | High transparency with visible bids. | Moderate transparency; bids are confidential until opened. |
| Speed | Fast transaction as bidding happens live. | Slower; requires bid submission period and evaluation. |
| Flexibility | Flexible bidding allows dynamic price adjustments. | Less flexible; prices fixed based on submitted tenders. |
| Suitability | Best for perishable goods needing quick sale. | Ideal for bulk or long-term supply contracts. |
| Risk | Price volatility risk due to open competition. | Lower price volatility; dependent on tender conditions. |
| Buyer Participation | Wide participation encouraged by open bidding. | Restricted to selected or qualified buyers. |
Overview of Auction and Tender Systems in Agricultural Marketing
The auction system in agricultural marketing involves competitive bidding where buyers place bids on produce, often resulting in real-time price discovery and transparency. The tender system requires sellers to invite sealed bids from buyers, allowing them to choose offers based on price and terms without public bidding. Both systems facilitate efficient produce selling but differ in price revelation and buyer competition mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Auction and Tender Methods
The auction system involves selling produce to the highest bidder in a transparent, real-time competitive environment, whereas the tender system requires buyers to submit sealed bids, with sales awarded based on predetermined criteria such as price and quality. Auctions typically offer faster sales and price discovery due to immediate buyer responses, while tenders provide a more controlled and confidential bidding process, often suitable for large or bulk transactions. The auction method fosters open competition and market-driven pricing, whereas the tender system emphasizes fairness and compliance through formal evaluation of bids.
Advantages of the Auction System for Farmers
The Auction System offers farmers real-time price discovery, ensuring they receive competitive bids that reflect current market demand. This transparent and competitive environment can lead to higher selling prices compared to fixed-rate tender systems. Immediate payment and reduced negotiation time further enhance liquidity and cash flow for farmers.
Benefits of the Tender System in Agri-Produce Sales
The Tender System enhances price transparency and competitive bidding, ensuring farmers receive fair market value for their produce. It streamlines the sales process by providing fixed timelines and reducing delays commonly seen in auction scenarios. This system also fosters trust between buyers and sellers through documented terms and minimized price fluctuations.
Transparency and Fairness: Auction vs Tender
The auction system in agricultural marketing enhances transparency by allowing multiple buyers to openly bid, ensuring fair price discovery based on real-time demand. The tender system relies on sealed bids, which may limit visibility and foster suspicion of favoritism or manipulation. Auctions provide a more impartial and competitive environment, promoting fairness in the sale of produce.
Pricing Mechanisms: Open Auctions Versus Sealed Tenders
The auction system employs open bidding, allowing real-time price discovery based on demand and competition, often resulting in higher prices for produce sellers. In contrast, the tender system uses sealed bids, where prices are submitted confidentially, emphasizing price certainty but potentially limiting price escalation due to lack of bidder interaction. Market participants benefit from the transparency and competitive environment of auctions, while tenders offer controlled pricing with reduced risk of price manipulation in agricultural produce sales.
Impact on Farmer Income: Auction System Compared to Tender System
The auction system often results in higher farmer income by promoting competitive bidding and transparent price discovery for agricultural produce. In contrast, the tender system can limit price competition as buyers submit sealed bids, sometimes leading to lower earnings for farmers due to reduced market signals. Studies indicate that auctions enhance farmers' bargaining power and market access, directly impacting their profitability and income stability.
Accessibility and Participation: Which System is More Inclusive?
The auction system offers greater accessibility by allowing multiple buyers to bid openly, increasing transparency and competition among farmers and traders. In contrast, the tender system limits participation to pre-qualified buyers, which can restrict access for smaller or new market entrants. Therefore, the auction system tends to be more inclusive, promoting diverse participation and fair price discovery in agricultural produce selling.
Challenges and Limitations of Auction and Tender Systems
Auction systems often face challenges such as price volatility and limited buyer participation, leading to inconsistent income for farmers. Tender systems encounter limitations like delayed payment processing and restricted market access due to stringent bidding criteria. Both methods can struggle with lack of transparency and inefficiencies in reflecting true produce value.
Choosing the Optimal Sales System for Agricultural Produce
Selecting the optimal sales system for agricultural produce depends on factors such as market demand, price transparency, and transaction speed. The auction system promotes competitive bidding, ensuring real-time price discovery and often higher returns for perishable goods. In contrast, the tender system offers structured offers and contract security, suitable for bulk produce with predefined quality standards and longer sales cycles.
Related Important Terms
E-Auction Platforms
E-auction platforms revolutionize the agricultural marketing landscape by providing transparent, real-time bidding environments that attract wider participation compared to traditional tender systems, ensuring competitive prices for produce. These digital systems reduce delays and human errors inherent in manual auctions and tenders, enhancing efficiency in price discovery and transaction security for farmers and buyers alike.
Reverse Tendering
The reverse tendering system in agricultural marketing offers producers a competitive platform where buyers submit decreasing bids, often leading to lower transaction costs and enhanced price discovery compared to traditional auction systems. This method increases transparency and efficiency by allowing farmers to select the best buyer offer, optimizing revenue while reducing dependence on intermediaries.
Dynamic Price Discovery
The auction system enables dynamic price discovery by allowing real-time bidding, reflecting immediate market demand and supply fluctuations for agricultural produce. In contrast, the tender system offers fixed-price bids submitted within deadlines, limiting price responsiveness and potentially delaying market equilibrium.
Blockchain Traceability
The auction system enables real-time bidding transparency and price discovery, while the tender system offers pre-set pricing with competitive offers; integrating blockchain traceability ensures immutable records of transactions, enhancing trust and product provenance in both methods. Blockchain's decentralized ledger provides secure, tamper-proof documentation from farm to buyer, improving accountability and reducing fraud in agricultural produce sales.
Digital Bidding
Digital bidding in agricultural marketing enhances the auction system by enabling real-time price discovery and transparent competition among buyers, leading to optimal pricing for produce. The tender system, while structured and secure, often lacks the dynamic interaction and immediate feedback of digital auctions, limiting price competitiveness and market efficiency.
Real-Time Auction Analytics
Real-time auction analytics in agricultural marketing enhances the auction system by providing instant price discovery, bid tracking, and market demand insights, enabling farmers to maximize profits through competitive bidding. In contrast, the tender system lacks dynamic data feedback, resulting in delayed pricing decisions and reduced transparency in produce selling.
Open vs Sealed Bid Mechanisms
The auction system uses an open bid mechanism where buyers openly compete by offering progressively higher prices, fostering transparency and real-time price discovery for agricultural produce. In contrast, the tender system employs a sealed bid mechanism, requiring buyers to submit confidential offers, which can encourage competitive pricing but may limit immediate market feedback and price visibility.
Mobile Auction Apps
Mobile auction apps revolutionize the agricultural marketing landscape by providing real-time bidding platforms that increase transparency and price discovery compared to traditional tender systems, which often involve delayed negotiations and limited bidder access. These apps enhance farmer profitability and market efficiency by enabling instantaneous, competitive offers from multiple buyers, reducing reliance on costly intermediaries.
Smart Contract Trade Settlement
The Auction System leverages real-time bidding to establish transparent price discovery, while the Tender System relies on sealed offers to ensure competitive, confidential procurement; integrating smart contract trade settlement automates payment execution and enforces contractual terms, significantly reducing disputes and settlement time. Blockchain-enabled smart contracts facilitate immutable transaction records and instant fund transfers, optimizing efficiency and trust in both auction and tender-based agricultural produce marketing.
Multi-Stage Tendering
Multi-stage tendering in agricultural produce selling enhances price transparency and competitive bidding by allowing successive rounds of offers, promoting better-quality bids compared to the instantaneous pricing of auction systems. This method mitigates price volatility and ensures rigorous evaluation of supplier capabilities, contributing to efficient market outcomes and reduced transactional risks.
Auction System vs Tender System for produce selling Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com