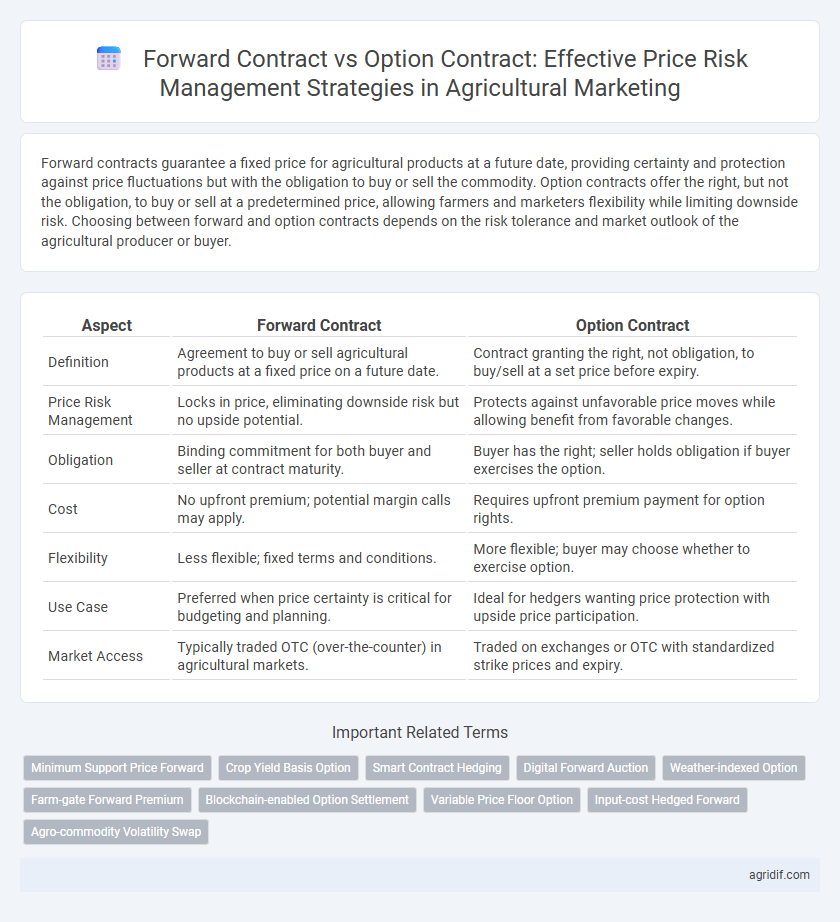
Forward contracts guarantee a fixed price for agricultural products at a future date, providing certainty and protection against price fluctuations but with the obligation to buy or sell the commodity. Option contracts offer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell at a predetermined price, allowing farmers and marketers flexibility while limiting downside risk. Choosing between forward and option contracts depends on the risk tolerance and market outlook of the agricultural producer or buyer.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Forward Contract | Option Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement to buy or sell agricultural products at a fixed price on a future date. | Contract granting the right, not obligation, to buy/sell at a set price before expiry. |
| Price Risk Management | Locks in price, eliminating downside risk but no upside potential. | Protects against unfavorable price moves while allowing benefit from favorable changes. |
| Obligation | Binding commitment for both buyer and seller at contract maturity. | Buyer has the right; seller holds obligation if buyer exercises the option. |
| Cost | No upfront premium; potential margin calls may apply. | Requires upfront premium payment for option rights. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; fixed terms and conditions. | More flexible; buyer may choose whether to exercise option. |
| Use Case | Preferred when price certainty is critical for budgeting and planning. | Ideal for hedgers wanting price protection with upside price participation. |
| Market Access | Typically traded OTC (over-the-counter) in agricultural markets. | Traded on exchanges or OTC with standardized strike prices and expiry. |
Introduction to Price Risk Management in Agriculture
Forward contracts enable farmers to lock in prices for their crops ahead of harvest, reducing uncertainty and securing predictable revenue streams. Option contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to sell or buy agricultural commodities at predetermined prices, offering flexibility to capitalize on favorable market movements while limiting downside risk. Both contracts serve as essential tools in agricultural marketing for managing price volatility and enhancing financial stability.
Understanding Forward Contracts in Agricultural Marketing
Forward contracts in agricultural marketing enable farmers and buyers to lock in prices for commodities before harvest, reducing exposure to price volatility. These agreements obligate both parties to transact at a predetermined price and date, providing certainty and mitigating financial risk. Unlike option contracts, forward contracts do not require a premium, but they carry the risk of missed opportunities if market prices move favorably.
Understanding Option Contracts in Agricultural Marketing
Option contracts in agricultural marketing provide farmers with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specified quantity of a commodity at a predetermined price before a certain date, offering flexibility in price risk management. This mechanism helps producers hedge against unfavorable price movements while retaining the potential to benefit from favorable price changes, unlike forward contracts which obligate parties to trade at a fixed price on a specific date. Understanding option premiums, strike prices, and expiration dates is crucial for effectively leveraging options to mitigate financial risks in volatile agricultural markets.
Key Differences Between Forward and Option Contracts
Forward contracts obligate the buyer and seller to complete a transaction at a predetermined price and date, ensuring price certainty but exposing both parties to potential losses if market prices move unfavorably. Option contracts provide the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an asset at a specified price before a set expiration date, allowing flexibility and limiting downside risk to the premium paid. The key differences lie in the level of obligation, risk exposure, and cost structure, with forwards requiring commitment while options offer strategic price risk management through selective execution.
Advantages of Using Forward Contracts for Farmers
Forward contracts offer farmers price certainty by locking in a sale price for their crops ahead of harvest, reducing exposure to volatile market fluctuations. These agreements facilitate precise financial planning and cash flow management, enabling farmers to mitigate losses from falling prices. By providing a guaranteed market and price, forward contracts enhance farmers' ability to secure loans and invest confidently in production inputs.
Benefits of Option Contracts in Price Risk Mitigation
Option contracts offer farmers the flexibility to protect against price declines while retaining the opportunity to benefit from favorable price increases in agricultural markets. These contracts provide a strategic advantage by limiting downside risk through a premium payment without obligating the seller or buyer to execute the contract. This risk management tool enhances income stability and allows for better financial planning amid volatile commodity prices.
Risks and Limitations of Forward Contracts in Agriculture
Forward contracts in agricultural marketing expose farmers to significant risks such as price volatility and lack of flexibility since prices are fixed at contract initiation, limiting the ability to benefit from favorable market movements. These agreements often lead to delivery risk, where unforeseen events like poor harvests or quality issues can result in contract penalties or enforcement challenges. Unlike options contracts, forward contracts do not provide a premium-based hedge, increasing the potential financial burden during adverse price shifts.
Risks and Limitations of Option Contracts for Producers
Option contracts in agricultural marketing expose producers to risks such as premium costs, which can reduce profit margins if market prices move favorably. Limited expiration periods may result in missed opportunities for price hedging beyond the contract term, while strike price selection can affect the effectiveness of risk mitigation. Furthermore, complex valuation and potential liquidity issues in options markets can restrict producers' ability to execute optimal price risk management strategies.
Practical Considerations in Choosing Forward or Option Contracts
Farmers managing price risk often prefer forward contracts for their certainty in locking a fixed price, which simplifies financial planning and budgeting. Option contracts offer flexibility by allowing producers to benefit from favorable market prices while limiting downside risk, though they involve paying a premium. Practical considerations include cash flow availability, market outlook, and risk tolerance, determining the optimal balance between guaranteed income and potential profit in agricultural marketing strategies.
Case Studies: Effective Use of Forward and Option Contracts in Agriculture
Forward contracts lock in a fixed price for agricultural products, as demonstrated by wheat farmers in Kansas who secured stable revenues despite market volatility in 2022. Option contracts provided corn growers in Iowa with the flexibility to benefit from favorable price movements while limiting downside risk during unpredictable harvest seasons. These case studies highlight how strategic use of forward and option contracts enhances price risk management and profitability in agriculture.
Related Important Terms
Minimum Support Price Forward
Minimum Support Price (MSP) forward contracts guarantee farmers a fixed price for their produce, reducing price volatility risk by setting a predetermined selling price before harvest. Option contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to sell at MSP, offering price risk protection while allowing farmers to benefit from favorable market price increases.
Crop Yield Basis Option
Forward contracts lock in a fixed price for crops, providing certainty but exposing farmers to basis risk if local prices diverge from national futures. Crop yield basis options offer flexible protection by allowing farmers to hedge against adverse basis movements while retaining potential upside from favorable price fluctuations.
Smart Contract Hedging
Forward contracts in agricultural marketing lock in a fixed price for future delivery, providing certainty but limited flexibility, whereas option contracts offer the right, without obligation, to buy or sell at a predetermined price, allowing farmers to capitalize on favorable market movements while managing downside risk. Smart contract hedging leverages blockchain technology to automate and enforce these contracts securely, enhancing transparency, reducing counterparty risk, and improving efficiency in price risk management for agricultural producers.
Digital Forward Auction
Digital forward auctions enhance price risk management by enabling transparent, competitive bidding in forward contracts for agricultural products, ensuring predetermined prices and reducing market uncertainty. Option contracts provide flexibility through the right, but not obligation, to buy or sell at a set price, complementing forward contracts by offering downside protection while allowing farmers to benefit from favorable price movements.
Weather-indexed Option
Weather-indexed options allow farmers to mitigate price risk linked to adverse weather conditions by providing payouts based on specific weather indices, contrasting with forward contracts that lock in prices regardless of weather variability. These options enhance flexibility and risk management in agricultural marketing by aligning contract performance with weather-driven yield fluctuations.
Farm-gate Forward Premium
A Forward Contract in agricultural marketing locks in a fixed price for farm produce, directly managing price risk by securing a farm-gate forward premium that guarantees revenue despite market fluctuations. In contrast, an Option Contract offers the right but not the obligation to sell at a predetermined price, allowing farmers to benefit from favorable price movements while paying a premium to protect against downside risks at the farm gate.
Blockchain-enabled Option Settlement
Forward contracts in agricultural marketing lock in prices for future delivery, reducing price risk but lacking flexibility, while option contracts provide price protections with the right, not obligation, to execute transactions. Blockchain-enabled option settlement enhances transparency, security, and efficiency by automating contract execution and verification, thus minimizing counterparty risk and settlement delays in agricultural commodity trading.
Variable Price Floor Option
A Variable Price Floor Option in agricultural marketing allows producers to set a minimum price level, protecting against downside risk while retaining upside potential by paying a premium for this price floor. This differs from a forward contract, which locks in a fixed price, eliminating price variability but also limiting any opportunity for price gains.
Input-cost Hedged Forward
Input-cost hedged forward contracts enable farmers to lock in input prices such as seeds and fertilizers, providing a fixed cost basis that reduces exposure to market volatility. Unlike option contracts that offer the right without obligation to buy or sell inputs, forward contracts guarantee execution at predetermined prices, ensuring more predictable input expenses and improved budgeting accuracy.
Agro-commodity Volatility Swap
Forward contracts lock in prices for agro-commodities, providing certainty but exposing producers to potential losses if market prices improve, whereas option contracts offer flexibility by allowing the right, without obligation, to buy or sell at a predetermined price, mitigating downside risk while enabling participation in favorable price movements. Agro-commodity volatility swaps specifically allow market participants to hedge against price volatility, enabling precise management of risk associated with unpredictable fluctuations in commodity prices beyond just the underlying price level.
Forward Contract vs Option Contract for price risk management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com