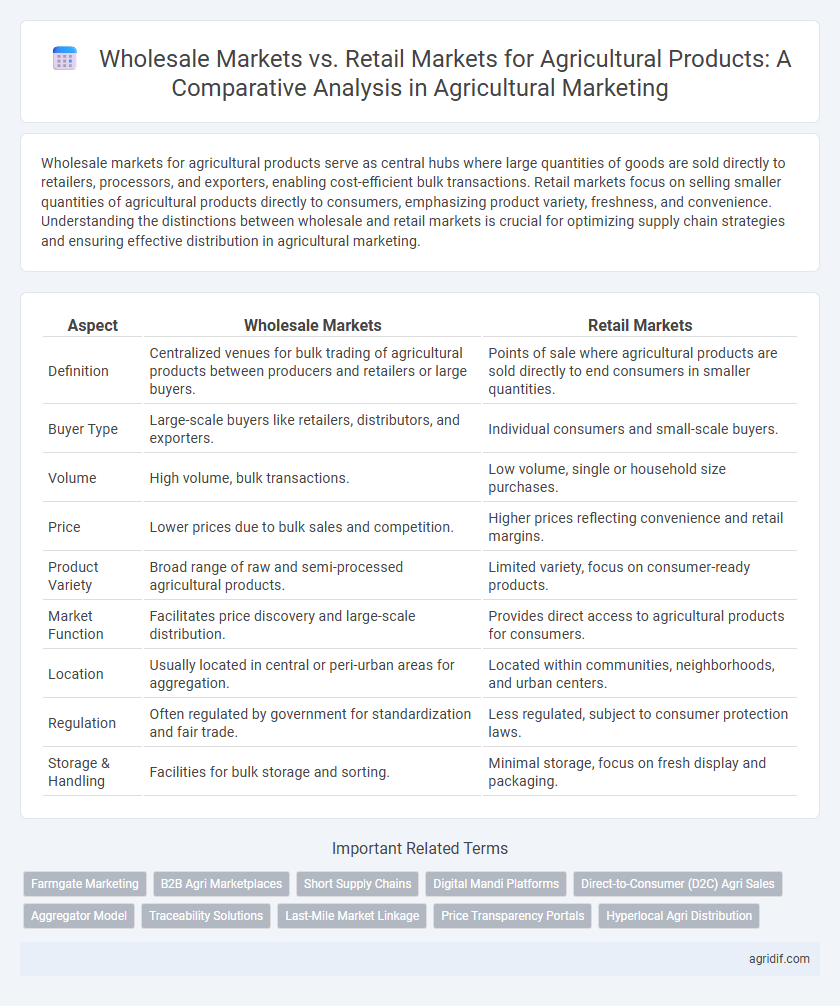
Wholesale markets for agricultural products serve as central hubs where large quantities of goods are sold directly to retailers, processors, and exporters, enabling cost-efficient bulk transactions. Retail markets focus on selling smaller quantities of agricultural products directly to consumers, emphasizing product variety, freshness, and convenience. Understanding the distinctions between wholesale and retail markets is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies and ensuring effective distribution in agricultural marketing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wholesale Markets | Retail Markets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized venues for bulk trading of agricultural products between producers and retailers or large buyers. | Points of sale where agricultural products are sold directly to end consumers in smaller quantities. |
| Buyer Type | Large-scale buyers like retailers, distributors, and exporters. | Individual consumers and small-scale buyers. |
| Volume | High volume, bulk transactions. | Low volume, single or household size purchases. |
| Price | Lower prices due to bulk sales and competition. | Higher prices reflecting convenience and retail margins. |
| Product Variety | Broad range of raw and semi-processed agricultural products. | Limited variety, focus on consumer-ready products. |
| Market Function | Facilitates price discovery and large-scale distribution. | Provides direct access to agricultural products for consumers. |
| Location | Usually located in central or peri-urban areas for aggregation. | Located within communities, neighborhoods, and urban centers. |
| Regulation | Often regulated by government for standardization and fair trade. | Less regulated, subject to consumer protection laws. |
| Storage & Handling | Facilities for bulk storage and sorting. | Minimal storage, focus on fresh display and packaging. |
Introduction to Wholesale and Retail Agricultural Markets
Wholesale markets for agricultural products operate as centralized hubs where bulk quantities are traded between producers, distributors, and retailers, emphasizing volume and price efficiencies. Retail markets focus on direct consumer sales, offering smaller quantities with greater product variety, freshness, and convenience. Understanding the distinctions aids in optimizing supply chains and pricing strategies within agricultural marketing.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Retail Markets
Wholesale markets for agricultural products facilitate bulk transactions between producers and intermediaries, emphasizing large volumes and lower prices per unit to support supply chain efficiency. Retail markets target end consumers, offering smaller quantities at higher prices, often emphasizing product variety, quality, and convenience. Key differences include transaction scale, pricing structures, and stakeholder roles, with wholesalers prioritizing distribution logistics and retailers focusing on customer experience.
Roles of Wholesale Markets in the Agri-Food Supply Chain
Wholesale markets serve as critical hubs in the agri-food supply chain by aggregating large volumes of agricultural products from multiple producers, enabling efficient distribution to various retail markets and food service providers. These markets facilitate price discovery through competitive bidding and reduce transaction costs by providing centralized trading platforms, which enhances market transparency and supply chain coordination. By managing bulk logistics and quality standards, wholesale markets help stabilize food supply, minimize post-harvest losses, and support the scalability of agricultural trade.
Retail Markets: Bridging Farmers and Consumers
Retail markets play a crucial role in agricultural marketing by directly connecting farmers with consumers, enabling farmers to receive better prices for their produce while ensuring fresh products reach end users. These markets reduce intermediaries, enhance transparency, and allow for immediate feedback on product quality and demand trends. As a result, retail markets foster local economic growth and support sustainable agricultural practices through direct farmer-consumer interactions.
Price Formation Mechanisms in Wholesale vs Retail
Wholesale markets for agricultural products typically exhibit price formation mechanisms driven by large volume transactions, where prices are influenced by supply-demand dynamics and competitive bidding among bulk buyers. In contrast, retail markets often reflect price setting based on consumer demand, convenience, and product quality, with added margins from intermediaries and retailers. Price fluctuations in wholesale markets tend to be more volatile due to immediate market supply changes, whereas retail prices remain relatively stable, incorporating fixed costs and retailing services.
Market Accessibility for Farmers: Wholesale vs Retail
Wholesale markets offer farmers greater market accessibility through bulk sales and direct connections to large buyers such as processors and exporters, reducing transaction costs and enabling faster movement of produce. Retail markets provide farmers access to end consumers but often involve intermediaries that limit direct negotiation and reduce farmers' profit margins. Efficient wholesale market infrastructure enhances farmers' ability to reach expansive networks, while retail markets primarily facilitate smaller-scale, localized sales with higher price variability.
Infrastructure and Logistics: Comparing Wholesale and Retail Markets
Wholesale markets for agricultural products feature extensive infrastructure designed to handle large volumes, including spacious warehouses, loading docks, and transportation hubs that facilitate bulk distribution. Retail markets prioritize smaller-scale infrastructure such as stalls, refrigeration units, and display areas optimized for consumer accessibility and product freshness. Efficient logistics in wholesale markets emphasize coordination of large shipments and supply chain management, while retail markets focus on timely replenishment and customer-oriented service.
Impact on Smallholder Farmers: Wholesale versus Retail
Wholesale markets offer smallholder farmers bulk sales opportunities, enabling higher volume transactions and access to regional buyers, which often results in better price stability and reduced marketing costs. Retail markets require farmers to engage in direct selling, typically involving smaller quantities with potentially higher profit margins but increased time investment and exposure to price fluctuations. Access to wholesale channels can enhance smallholders' bargaining power, while retail markets provide a platform for diversification and building local customer relationships.
Consumer Preferences in Wholesale and Retail Settings
Consumer preferences in wholesale markets for agricultural products tend to prioritize bulk purchasing, cost efficiency, and product variety suited for resale or large-scale use. Retail markets attract consumers seeking freshness, product quality, and convenience, often favoring local or organic options with direct producer interaction. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize supply chain strategies and tailor marketing efforts for different buyer segments in agricultural commerce.
Future Trends: Digitalization in Agricultural Marketing
Wholesale markets for agricultural products are increasingly adopting digital platforms to enhance supply chain transparency, improve price discovery, and facilitate real-time transactions between farmers and bulk buyers. Retail markets are also integrating e-commerce solutions and mobile apps to provide consumers with access to fresher produce, personalized offers, and seamless delivery options. The future of agricultural marketing lies in leveraging big data analytics, IoT, and blockchain technology to optimize market efficiency and ensure traceability from farm to table.
Related Important Terms
Farmgate Marketing
Wholesale markets centralize large volumes of agricultural products, enabling efficient bulk transactions between farmers and buyers, which reduces transportation costs and time from farm to market. Retail markets, operating at a smaller scale, focus on direct consumer sales, fostering higher prices but increased handling and distribution expenses, making farmgate marketing a crucial strategy for farmers to maximize revenue by selling directly at the source.
B2B Agri Marketplaces
Wholesale markets serve as crucial B2B agri marketplaces, facilitating large-volume transactions between farmers, distributors, and retailers, optimizing supply chains and reducing costs. Retail markets, by contrast, target end consumers with smaller quantities and higher prices, emphasizing direct sales and product variety over bulk trading efficiencies.
Short Supply Chains
Wholesale markets for agricultural products enable bulk transactions that reduce intermediaries and lower transaction costs, thereby supporting short supply chains by facilitating direct connections between farmers and retailers. In contrast, retail markets focus on end consumers, often involving multiple intermediaries, which can elongate supply chains and increase the final product price.
Digital Mandi Platforms
Wholesale markets for agricultural products aggregate large volumes from multiple farmers, offering bulk pricing and supply chain efficiencies, while retail markets cater directly to consumers with smaller quantities and personalized service. Digital Mandi platforms enhance both by providing real-time price discovery, transparent transactions, and expanded market access, bridging the gap between farmers, wholesalers, and retail buyers.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Agri Sales
Wholesale markets facilitate bulk transactions between farmers and retailers or processors, offering lower prices but limited consumer interaction. Retail markets and Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) agri sales enhance farmer profit margins by enabling direct access to end consumers, fostering transparency, freshness, and personalized marketing strategies.
Aggregator Model
Wholesale markets serve as central hubs where large quantities of agricultural products are aggregated from multiple farmers, enabling efficient bulk transactions and price discovery, while retail markets focus on direct sales to end consumers, often with higher prices and lower volume. The aggregator model streamlines supply chains by consolidating produce from smallholders, reducing transaction costs, enhancing market access, and providing better price realization compared to traditional fragmented wholesale and retail channels.
Traceability Solutions
Wholesale markets for agricultural products emphasize bulk transactions and require robust traceability solutions to track large volumes from multiple producers, ensuring food safety and quality at scale. Retail markets demand detailed traceability systems that provide end consumers with transparent origin, handling, and certification information to build trust and comply with regulatory standards.
Last-Mile Market Linkage
Wholesale markets serve as critical aggregation points for large volumes of agricultural products, enabling efficient distribution to multiple retail outlets and reducing transaction costs for farmers. Retail markets provide the essential last-mile linkage by offering direct access to consumers, ensuring product availability and freshness while supporting price discovery at the local level.
Price Transparency Portals
Wholesale markets for agricultural products typically feature price transparency portals that provide real-time data on bulk pricing, enabling farmers and distributors to make informed decisions, while retail markets often lack such comprehensive digital price access, resulting in higher price variability for end consumers. These portals enhance market efficiency by reducing information asymmetry and improving price discovery between producers and buyers at the wholesale level.
Hyperlocal Agri Distribution
Wholesale markets for agricultural products serve as bulk distribution hubs primarily supplying large quantities to retailers and institutional buyers, optimizing supply chains through economies of scale. Retail markets focus on direct consumer sales, emphasizing freshness and variety within a hyperlocal agri distribution network that reduces transportation time and preserves product quality.
Wholesale markets vs Retail markets for agricultural products Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com