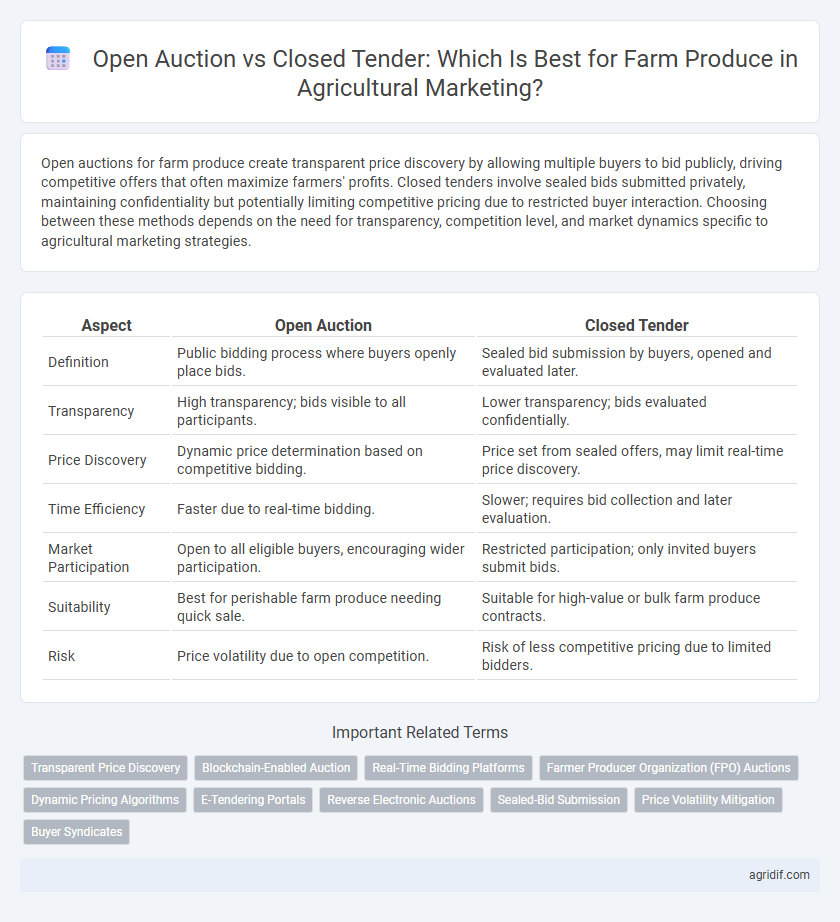
Open auctions for farm produce create transparent price discovery by allowing multiple buyers to bid publicly, driving competitive offers that often maximize farmers' profits. Closed tenders involve sealed bids submitted privately, maintaining confidentiality but potentially limiting competitive pricing due to restricted buyer interaction. Choosing between these methods depends on the need for transparency, competition level, and market dynamics specific to agricultural marketing strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open Auction | Closed Tender |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public bidding process where buyers openly place bids. | Sealed bid submission by buyers, opened and evaluated later. |
| Transparency | High transparency; bids visible to all participants. | Lower transparency; bids evaluated confidentially. |
| Price Discovery | Dynamic price determination based on competitive bidding. | Price set from sealed offers, may limit real-time price discovery. |
| Time Efficiency | Faster due to real-time bidding. | Slower; requires bid collection and later evaluation. |
| Market Participation | Open to all eligible buyers, encouraging wider participation. | Restricted participation; only invited buyers submit bids. |
| Suitability | Best for perishable farm produce needing quick sale. | Suitable for high-value or bulk farm produce contracts. |
| Risk | Price volatility due to open competition. | Risk of less competitive pricing due to limited bidders. |
Overview of Agricultural Marketing Methods
Open auction involves transparent bidding where farmers' produce is sold to the highest bidder in a public setting, ensuring price discovery and competitiveness. Closed tender requires buyers to submit sealed bids privately, often leading to negotiated prices without public disclosure. Both methods influence market efficiency and price realization, with open auctions promoting transparency and closed tenders offering confidentiality and potentially faster transactions.
Understanding Open Auctions in Agriculture
Open auctions in agriculture provide a transparent marketplace where farm produce is sold to the highest bidder, fostering price discovery based on real-time demand and supply. They enable farmers to achieve competitive prices and quickly adjust to market trends, unlike closed tenders that limit buyer participation. The dynamic bidding process in open auctions enhances price fairness and encourages wider market participation, benefiting both producers and buyers in agricultural marketing.
Exploring Closed Tenders for Farm Produce
Closed tenders for farm produce enhance price confidentiality and allow farmers to negotiate directly with selected buyers, reducing the risk of underbidding common in open auctions. This method encourages better quality control and contract customization, aligning buyer requirements with crop specifications. Efficient closed tender processes improve market stability by minimizing speculative price fluctuations typical in open auction systems.
Key Differences: Open Auction vs Closed Tender
Open Auction allows transparent, real-time bidding where farmers gain maximum price discovery for their produce, fostering competitive pricing and immediate sales. Closed Tender involves sealed bids submitted confidentially, promoting price security but potentially limiting market competition and price optimization. While Open Auctions enhance market transparency and farmer empowerment, Closed Tenders offer controlled negotiation and reduced exposure to price volatility.
Transparency and Fairness in Pricing
Open auctions in agricultural marketing ensure transparency by publicly displaying bids, allowing farmers to receive real-time market-driven prices that enhance fairness. Closed tenders limit competitive bidding to pre-selected buyers, often reducing price visibility and potentially compromising equitable price discovery for farm produce. Transparent pricing mechanisms in open auctions empower farmers by fostering trust and competition, whereas closed tenders may favor buyers with insider advantages, affecting market fairness.
Impact on Farmer Profitability
Open auction systems foster transparent price discovery by enabling competitive bidding among buyers, often resulting in better market prices for farmers. Closed tender processes may limit competition and reduce price transparency, potentially leading to lower profit margins for producers. Empirical studies show that farmers participating in open auctions frequently achieve higher profitability due to market-driven pricing mechanisms.
Buyer Participation and Competition
Open auctions for farm produce encourage greater buyer participation by allowing multiple bidders to compete transparently, often driving up prices through real-time bidding dynamics. Closed tenders restrict buyer access, limiting competition to pre-selected or invited parties, which can reduce price discovery and market efficiency. Higher buyer competition in open auctions typically results in better price realization for farmers compared to the more controlled environment of closed tenders.
Efficiency in Market Transactions
Open auctions provide a transparent platform where multiple buyers competitively bid for farm produce, often leading to higher price discovery and quicker transaction settlements. Closed tenders, while offering confidentiality, may delay market efficiency due to limited bidder participation and potential price underestimation. Efficient market transactions benefit from the dynamic pricing and immediate feedback inherent in open auctions, promoting fair value realization for farmers and buyers alike.
Risks and Challenges of Each Method
Open auctions for farm produce expose sellers to price volatility and potential collusion among bidders, increasing financial uncertainty. Closed tenders limit competition by restricting bidder access, which may result in lower price discovery and reduced market transparency. Both methods face risks of mispricing and logistical delays, impacting farmers' timely income realization and overall market efficiency.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Farm Produce
Open auction offers transparent price discovery for farm produce, attracting competitive bids that can maximize revenue, especially for perishable or high-demand crops. Closed tender ensures confidentiality and allows negotiation with pre-qualified buyers, ideal for bulk sales or specialized products requiring strict quality standards. Farmers should assess market conditions, crop type, and desired price certainty to choose between open auction and closed tender methods for optimal marketing outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Transparent Price Discovery
Open auction systems facilitate transparent price discovery by allowing multiple buyers to openly bid, revealing true market demand and value for farm produce. In contrast, closed tender processes often limit competitive visibility, potentially obscuring fair market prices and reducing transparency in agricultural marketing.
Blockchain-Enabled Auction
Blockchain-enabled open auctions for farm produce ensure transparent, tamper-proof bidding that enhances trust among buyers and sellers by recording all transactions on an immutable ledger. In contrast, closed tenders secured by blockchain maintain confidentiality and competitive fairness while providing verifiable audit trails that reduce fraud and disputes in agricultural marketing.
Real-Time Bidding Platforms
Real-time bidding platforms in agricultural marketing enable farmers to access dynamic open auctions, where transparent price discovery and immediate buyer competition maximize produce value. Closed tenders limit market reach by restricting bid visibility, often resulting in lower returns and reduced efficiency compared to the competitive and transparent environment fostered by open auction systems.
Farmer Producer Organization (FPO) Auctions
Farmer Producer Organization (FPO) auctions favor open auction methods for farm produce, as transparent bidding drives competitive pricing and maximizes farmer income. Closed tender systems often limit market access and price discovery, reducing the potential benefits for FPO members engaging in collective selling.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
Open auctions for farm produce leverage dynamic pricing algorithms that adjust bids in real-time, maximizing price discovery and reflecting current market demand fluctuations. Closed tenders rely on sealed bids submitted once, limiting price transparency and responsiveness, which can result in less optimal pricing compared to the continuous feedback loop provided by open auction platforms.
E-Tendering Portals
E-tendering portals for agricultural marketing enhance transparency and efficiency by enabling open auctions where multiple buyers compete, often resulting in better price discovery for farm produce. Closed tenders restrict participation to pre-qualified buyers, potentially limiting market competition but ensuring buyer credibility and streamlined transaction processes.
Reverse Electronic Auctions
Reverse electronic auctions for farm produce enable buyers to solicit competitive bids from multiple sellers, optimizing price discovery and transparency compared to traditional open auctions where sellers openly bid against each other. Closed tenders limit access and competition by restricting bid submissions to invited suppliers, whereas reverse electronic auctions expand market reach and encourage competitive pricing through real-time digital platforms.
Sealed-Bid Submission
Sealed-bid submission in closed tender processes enhances price transparency and competitiveness by requiring bidders to submit confidential offers, reducing the risk of collusion commonly seen in open auctions. This method promotes fair market values for farm produce by ensuring that bids are evaluated simultaneously, leading to more efficient price discovery and protecting farmers from underpricing.
Price Volatility Mitigation
Open auction systems enhance price transparency and competition among buyers, reducing extreme price fluctuations in farm produce markets. Closed tender processes, while potentially securing stable contracts, often limit market visibility and may contribute to higher price volatility due to restricted bid information.
Buyer Syndicates
Buyer syndicates in open auctions for farm produce benefit from transparent bidding that encourages competitive pricing, enhancing market efficiency and fair price discovery. In contrast, closed tenders limit syndicate participation due to restricted information flow, often resulting in less competitive outcomes and potential price manipulation.
Open Auction vs Closed Tender for Farm Produce Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com