Agrometeorological stations specialize in collecting data directly related to agricultural variables such as soil moisture, crop health, and evapotranspiration, providing precise insights for crop management and forecasting. Synoptic weather stations gather comprehensive meteorological data including temperature, humidity, wind, and atmospheric pressure, which are essential for broader weather prediction and climate monitoring. While both stations contribute valuable information, agrometeorological stations offer targeted data crucial for optimizing agricultural practices and improving yield predictions.
Table of Comparison
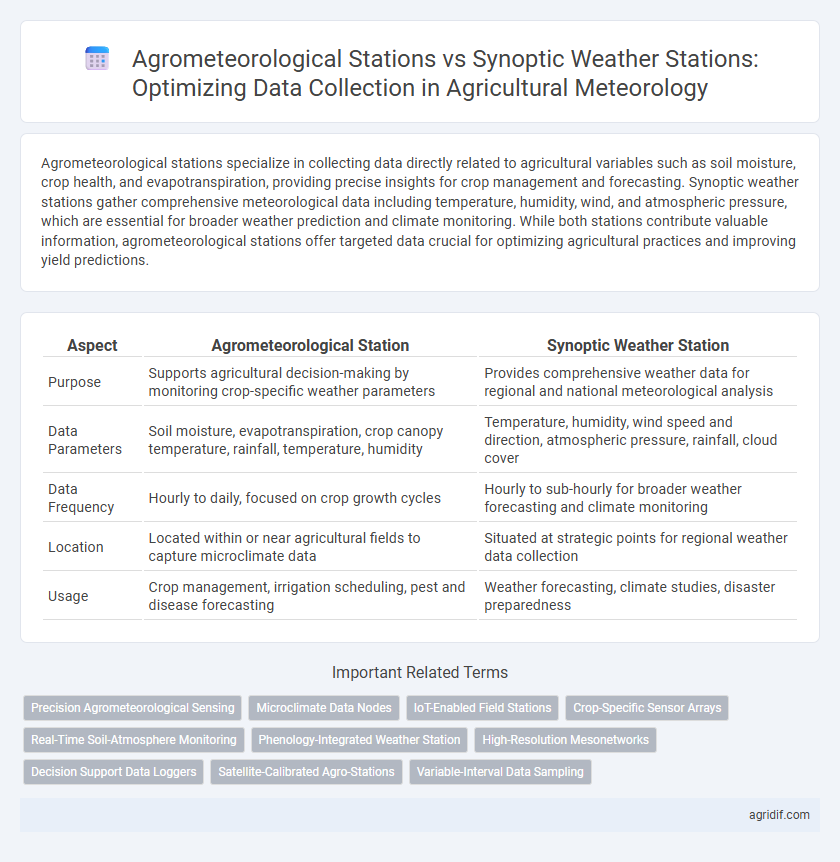
| Aspect | Agrometeorological Station | Synoptic Weather Station |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports agricultural decision-making by monitoring crop-specific weather parameters | Provides comprehensive weather data for regional and national meteorological analysis |
| Data Parameters | Soil moisture, evapotranspiration, crop canopy temperature, rainfall, temperature, humidity | Temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, atmospheric pressure, rainfall, cloud cover |
| Data Frequency | Hourly to daily, focused on crop growth cycles | Hourly to sub-hourly for broader weather forecasting and climate monitoring |
| Location | Located within or near agricultural fields to capture microclimate data | Situated at strategic points for regional weather data collection |
| Usage | Crop management, irrigation scheduling, pest and disease forecasting | Weather forecasting, climate studies, disaster preparedness |
Introduction to Agrometeorological and Synoptic Weather Stations
Agrometeorological stations specialize in collecting data directly related to crop growth, soil moisture, and microclimate conditions, essential for agricultural decision-making and risk management. Synoptic weather stations gather comprehensive atmospheric data such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure to analyze larger weather patterns and support meteorological forecasting. Both station types complement each other by providing localized agro-specific information and broader environmental context critical for agricultural meteorology.
Core Functions of Agrometeorological Stations
Agrometeorological stations specialize in monitoring microclimatic conditions such as soil moisture, evapotranspiration, and crop-specific weather parameters crucial for precise agricultural decision-making. These stations provide detailed data on temperature, humidity, solar radiation, wind speed, and precipitation tailored to optimize crop management and predict pest or disease outbreaks. Unlike synoptic weather stations that focus on broad atmospheric conditions for general weather forecasting, agrometeorological stations deliver localized, crop-oriented information essential for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Primary Roles of Synoptic Weather Stations
Synoptic weather stations primarily collect comprehensive atmospheric data, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure, to monitor weather patterns on a regional scale. These stations provide critical real-time information for forecasting and climate analysis, essential for large-scale agricultural planning and disaster preparedness. Unlike agrometeorological stations that focus on crop-specific microclimate data, synoptic stations support broader meteorological research and operational weather services.
Key Parameters Measured at Agrometeorological Stations
Agrometeorological stations primarily measure soil temperature, soil moisture, evapotranspiration rates, and crop-specific microclimatic factors, which are critical for precision farming and crop management. These stations provide detailed data on localized weather elements like solar radiation, rainfall, humidity, and wind speed tailored to agricultural needs. In contrast, synoptic weather stations focus on broader meteorological parameters such as atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, and wind patterns over larger areas, supporting general weather forecasting rather than targeted agricultural insights.
Data Collected at Synoptic Weather Stations
Synoptic weather stations collect comprehensive atmospheric data including temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, solar radiation, and precipitation, which are critical for large-scale weather analysis. These data points are recorded at standardized times globally, providing consistent temporal coverage essential for climate monitoring and forecasting. The integration of synoptic data supports agricultural decision-making by offering insights into regional weather patterns impacting crop growth and pest development.
Instrumentation Differences: Agrometeorological vs Synoptic Stations
Agrometeorological stations are equipped with specialized instruments such as soil moisture sensors, crop canopy temperature sensors, and evapotranspiration gauges tailored to monitor microclimatic conditions affecting agricultural productivity. Synoptic weather stations utilize standardized meteorological instruments including anemometers, barometers, hygrometers, and radiosondes designed for large-scale atmospheric observations and weather forecasting. The fundamental difference lies in agrometeorological stations focusing on parameters critical for crop management while synoptic stations emphasize broader atmospheric data for regional climate analysis.
Spatial Distribution and Network Coverage
Agrometeorological stations are strategically placed in agricultural zones to capture microclimatic data essential for crop management, offering dense spatial distribution tailored to local farming needs. Synoptic weather stations provide broader network coverage with standardized instruments, enabling regional and national-scale atmospheric observations crucial for general weather forecasting. The combination of both networks enhances data resolution and reliability, supporting precision agriculture and large-scale meteorological analysis.
Relevance of Data for Agricultural Decision-Making
Agrometeorological stations provide highly specialized data tailored to agricultural needs, such as soil moisture, crop-specific microclimate, and evapotranspiration rates crucial for irrigation scheduling and pest management. In contrast, synoptic weather stations collect broader atmospheric data like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, which support general weather forecasting but lack the granularity needed for precision agriculture. The targeted data from agrometeorological stations enhance crop yield predictions and optimize resource use, making them more relevant for timely and effective agricultural decision-making.
Data Accuracy and Temporal Frequency Comparisons
Agrometeorological stations provide high temporal frequency data tailored to crop-specific microclimates, enhancing data accuracy for agricultural decision-making through localized measurements of soil moisture, evapotranspiration, and crop temperature. Synoptic weather stations, while offering broader meteorological parameters, generally record data at coarser intervals, limiting their effectiveness in capturing rapid agro-environmental changes critical for precise farming practices. The detailed, continuous datasets from agrometeorological stations enable superior temporal resolution and predictive accuracy essential for optimizing irrigation, pest management, and harvest timing.
Future Prospects for Integrated Data Collection in Agriculture
Agrometeorological stations specialize in collecting hyper-local data such as soil moisture, crop growth stages, and microclimatic conditions critical for precision agriculture, while synoptic weather stations provide broader atmospheric data including temperature, humidity, and wind patterns essential for regional climate modeling. Future prospects emphasize integrated data collection platforms combining sensor networks from both station types with IoT and AI technologies to enhance predictive analytics for crop yield optimization and risk management. This synergy supports real-time decision-making, enabling adaptive farming practices that improve sustainability and resilience against climate variability.
Related Important Terms
Precision Agrometeorological Sensing
Agrometeorological stations are specifically designed for precision sensing of crop microclimates, offering high-resolution data on soil moisture, temperature, and evapotranspiration critical for targeted agricultural decision-making. Synoptic weather stations provide broader meteorological data such as large-scale temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure patterns but lack the granularity essential for precise agrometeorological applications.
Microclimate Data Nodes
Agrometeorological stations specialize in collecting microclimate data such as soil moisture, evapotranspiration, and crop-specific temperature, providing localized insights essential for precision agriculture. In contrast, synoptic weather stations offer broader-scale atmospheric data like temperature, humidity, and wind patterns, useful for regional weather forecasting but less detailed in capturing field-level microclimate variations.
IoT-Enabled Field Stations
IoT-enabled agrometeorological stations provide real-time, hyperlocal data on soil moisture, temperature, and microclimate conditions crucial for precision agriculture, surpassing the broader, less frequent synoptic weather station reports. The integration of IoT sensors facilitates continuous monitoring and automated data transmission, enhancing decision-making for crop management and resource optimization in smart farming.
Crop-Specific Sensor Arrays
Agrometeorological stations utilize crop-specific sensor arrays to provide precise microclimate data, including soil moisture, canopy temperature, and leaf wetness, essential for optimizing crop management. Synoptic weather stations primarily collect broader atmospheric data such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, offering less detailed information for targeted agriculture decisions.
Real-Time Soil-Atmosphere Monitoring
Agrometeorological stations provide specialized real-time soil-atmosphere monitoring by measuring soil moisture, temperature, and crop microclimate variables, crucial for precision agriculture and timely irrigation scheduling. Synoptic weather stations primarily offer broad-scale atmospheric data such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, essential for regional weather forecasting but less focused on granular agrometeorological parameters.
Phenology-Integrated Weather Station
Phenology-integrated weather stations at agrometeorological sites provide precise microclimate data essential for tracking crop development stages, unlike synoptic weather stations which offer broader atmospheric observations primarily for regional weather forecasting. The integration of phenological observations with localized meteorological data enhances decision-making in agricultural management by enabling timely interventions based on crop-specific environmental responses.
High-Resolution Mesonetworks
Agrometeorological stations provide high-resolution, site-specific data crucial for monitoring crop growth and microclimate variations, while synoptic weather stations offer broader-scale atmospheric observations necessary for regional weather forecasting. High-resolution mesonetworks comprising dense agrometeorological stations enhance precision in agricultural decision-making by capturing localized weather patterns that synoptic stations, spaced widely apart, often miss.
Decision Support Data Loggers
Agrometeorological stations utilize specialized data loggers designed for precise crop and soil monitoring, enabling tailored decision support for agricultural practices. Synoptic weather stations collect broader atmospheric data with general-purpose loggers, offering extensive climate information but less specificity for farm-level decision-making.
Satellite-Calibrated Agro-Stations
Satellite-calibrated agrometeorological stations provide precise, localized data by integrating satellite observations with ground-based sensors, enhancing crop-specific climate monitoring and risk assessment. Compared to synoptic weather stations that offer broader atmospheric data for general weather forecasting, these agro-stations deliver high-resolution, crop-relevant meteorological information crucial for optimizing agricultural management and improving yield predictions.
Variable-Interval Data Sampling
Agrometeorological stations employ variable-interval data sampling tailored to crop-specific growth stages and microclimatic conditions, enhancing precision in agricultural decision-making. In contrast, synoptic weather stations typically use fixed-interval sampling, providing standardized meteorological data primarily for broader weather forecasting rather than specialized agricultural applications.
Agrometeorological Station vs Synoptic Weather Station for Data Collection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com