Pesticides and herbicides are essential agrochemicals used for crop protection, with pesticides targeting a broad range of pests including insects, fungi, and rodents, while herbicides specifically control unwanted weeds that compete with crops for nutrients and sunlight. Effective use of pesticides ensures the reduction of crop damage caused by various pests, enhancing yield and quality, whereas herbicides improve crop growth by minimizing weed interference and soil nutrient depletion. Selecting the appropriate agrochemical depends on the pest type and crop requirements, optimizing plant health and maximizing agricultural productivity.
Table of Comparison
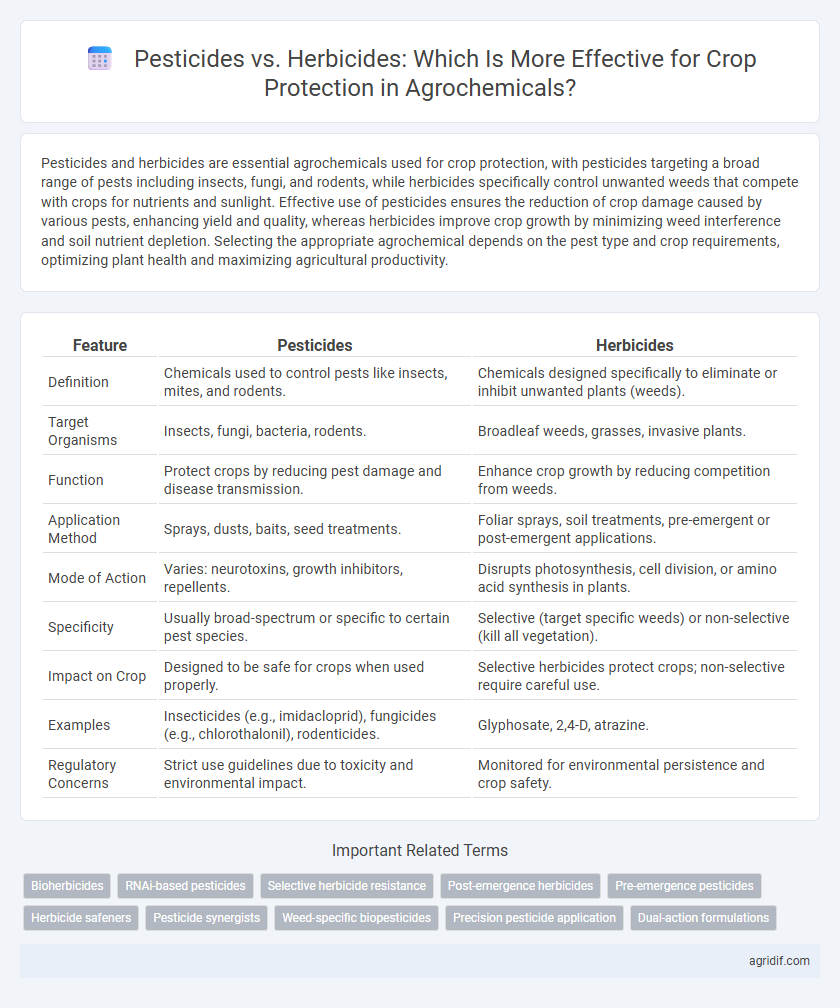
| Feature | Pesticides | Herbicides |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chemicals used to control pests like insects, mites, and rodents. | Chemicals designed specifically to eliminate or inhibit unwanted plants (weeds). |
| Target Organisms | Insects, fungi, bacteria, rodents. | Broadleaf weeds, grasses, invasive plants. |
| Function | Protect crops by reducing pest damage and disease transmission. | Enhance crop growth by reducing competition from weeds. |
| Application Method | Sprays, dusts, baits, seed treatments. | Foliar sprays, soil treatments, pre-emergent or post-emergent applications. |
| Mode of Action | Varies: neurotoxins, growth inhibitors, repellents. | Disrupts photosynthesis, cell division, or amino acid synthesis in plants. |
| Specificity | Usually broad-spectrum or specific to certain pest species. | Selective (target specific weeds) or non-selective (kill all vegetation). |
| Impact on Crop | Designed to be safe for crops when used properly. | Selective herbicides protect crops; non-selective require careful use. |
| Examples | Insecticides (e.g., imidacloprid), fungicides (e.g., chlorothalonil), rodenticides. | Glyphosate, 2,4-D, atrazine. |
| Regulatory Concerns | Strict use guidelines due to toxicity and environmental impact. | Monitored for environmental persistence and crop safety. |
Understanding Pesticides and Herbicides: Key Differences
Pesticides encompass a broad category of chemicals used to eliminate or control various pests, including insects, fungi, and weeds, ensuring crop health and productivity. Herbicides specifically target unwanted plants and weeds that compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, making them essential for effective weed management. Understanding the key differences between pesticides and herbicides helps optimize their use in integrated pest management strategies, minimizing crop damage while maximizing yield.
Modes of Action: How Pesticides and Herbicides Work
Pesticides protect crops by targeting and disrupting the vital biological functions of pests, including insects, fungi, and bacteria, through neurotoxins or enzyme inhibitors that interfere with nerve signals or metabolic pathways. Herbicides specifically control unwanted plant growth by inhibiting photosynthesis, cell division, or amino acid synthesis in weeds, effectively disrupting their growth and development. Understanding the distinct modes of action in pesticides and herbicides allows for more effective crop protection strategies and resistance management.
Target Organisms: Insects vs Weeds in Crop Protection
Pesticides specifically target insects and other pests that damage crops, effectively reducing pest populations to protect plant health and yield. Herbicides are formulated to control or eliminate weeds, which compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, thus enhancing crop growth and productivity. Both agrochemicals are vital for integrated pest management strategies, ensuring targeted intervention against insects or weeds for optimized crop protection.
Chemical Composition and Formulations
Pesticides encompass a broad range of chemical compounds designed to target various pests, including insects, fungi, and weeds, with active ingredients such as organophosphates, carbamates, and pyrethroids. Herbicides specifically target unwanted vegetation and are formulated using chemicals like glyphosate, atrazine, and 2,4-D, often delivered in liquid, granular, or emulsifiable concentrate forms. Formulation techniques optimize solubility, stability, and application efficiency, ensuring effective crop protection while minimizing environmental impact.
Effectiveness in Yield Improvement
Pesticides target a broad range of pests, including insects and fungi, effectively reducing crop damage and thereby enhancing yield potential. Herbicides specifically control unwanted weeds that compete with crops for nutrients, sunlight, and water, leading to significant improvements in crop growth and productivity. Studies show that integrating both pesticides and herbicides in crop management results in higher yield gains compared to using either alone.
Environmental Impact and Residue Concerns
Pesticides and herbicides serve distinct roles in crop protection, with pesticides targeting a broad spectrum of pests, while herbicides specifically control unwanted vegetation. Herbicides often contribute to soil and water contamination due to their persistence and potential to bioaccumulate, raising significant environmental impact concerns. Residue levels from both pesticides and herbicides on crops can pose health risks, necessitating stringent regulation and monitoring to minimize human and ecological exposure.
Resistance Development in Pests and Weeds
Pesticides and herbicides play crucial roles in crop protection by targeting pests and weeds, respectively, but both face challenges from resistance development. Pests often evolve resistance to pesticides through genetic mutations and selection pressure, leading to reduced efficacy and increased crop damage. Similarly, continuous herbicide application promotes the emergence of herbicide-resistant weeds, necessitating integrated management strategies to delay resistance and maintain sustainable agricultural productivity.
Safety Measures and Application Practices
Pesticides and herbicides require strict safety measures such as wearing protective clothing and using appropriate equipment to minimize exposure risks during application. Proper application practices include following label instructions precisely, applying at recommended rates, and avoiding application near water sources to prevent contamination. Integrated pest management strategies enhance crop protection while reducing chemical use and environmental impact.
Regulatory Guidelines for Use
Regulatory guidelines for pesticides and herbicides ensure their safe and effective use in crop protection by establishing maximum residue limits and application protocols based on toxicological assessments. Compliance with agencies such as the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) in the US and EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) in Europe mandates detailed labeling, usage restrictions, and environmental impact evaluations to mitigate risks to human health and biodiversity. These regulations require rigorous testing for both acute and chronic effects, promoting sustainable agrochemical practices to maintain crop yield while protecting ecosystems.
Integrated Pest and Weed Management Approaches
Pesticides and herbicides serve distinct roles in crop protection, targeting pests and weeds respectively to enhance agricultural productivity. Integrated Pest and Weed Management (IPWM) combines these chemical controls with cultural, biological, and mechanical strategies to reduce chemical reliance and minimize environmental impact. Employing IPWM optimizes crop health, sustainability, and resistance management by fostering ecological balance and preventing the development of pest and weed resistance.
Related Important Terms
Bioherbicides
Bioherbicides offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and herbicides by targeting specific weed species with natural pathogens, reducing chemical residues and environmental impact in crop protection. Their use supports sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil health and minimizing resistance development compared to synthetic herbicides.
RNAi-based pesticides
RNAi-based pesticides offer targeted gene silencing to protect crops from pests with minimal environmental impact, distinguishing them from traditional herbicides which primarily inhibit weed growth through chemical means. These innovative RNAi technologies enhance crop protection by specifically disrupting pest genetics, reducing pesticide resistance and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Selective herbicide resistance
Selective herbicide resistance enables crops to survive specific herbicides that target weeds, improving weed control without damaging the crop, whereas pesticides broadly include chemicals such as insecticides and fungicides used to manage various pests. Advances in genetic modification have accelerated the development of crops with selective herbicide resistance, enhancing crop protection efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Post-emergence herbicides
Post-emergence herbicides target weeds after crop germination, providing selective control to protect plant growth without harming the crops, unlike pesticides which include a broader range of chemical agents against pests and diseases. Applying post-emergence herbicides such as glyphosate and 2,4-D improves yield by eliminating competing weeds that emerge alongside crops during the growing season.
Pre-emergence pesticides
Pre-emergence pesticides, a subset of herbicides, target weed seeds and seedlings before they emerge from the soil, ensuring effective crop protection by preventing weed competition at early growth stages. These agrochemicals improve crop yield by reducing reliance on post-emergence treatments and minimizing herbicide resistance development in weed populations.
Herbicide safeners
Herbicide safeners enhance crop protection by reducing the phytotoxicity of herbicides, allowing higher selectivity and improved weed control without damaging the crop. These safeners stimulate detoxification enzymes in plants, safeguarding them against herbicide injury while maintaining effective pest management in agrochemical applications.
Pesticide synergists
Pesticide synergists enhance the effectiveness of both pesticides and herbicides by improving the active ingredient's absorption and reducing resistance in target pests and weeds. These compounds, such as piperonyl butoxide and enzyme inhibitors, optimize crop protection by increasing pesticidal potency without increasing chemical dosages.
Weed-specific biopesticides
Weed-specific biopesticides offer a targeted approach to crop protection by selectively inhibiting weed growth without harming crops, reducing environmental toxicity compared to broad-spectrum herbicides. These biopesticides leverage natural compounds or microorganisms to disrupt weed physiology, enhancing sustainable pest management and minimizing chemical residues in agricultural systems.
Precision pesticide application
Precision pesticide application enhances crop protection by targeting specific pests while minimizing environmental impact, in contrast to broader-spectrum herbicides that primarily control unwanted weeds. Utilizing GPS-guided sprayers and sensor technology, precision methods optimize pesticide use efficiency, reduce chemical runoff, and promote sustainable agrochemical management.
Dual-action formulations
Dual-action formulations combining pesticides and herbicides offer enhanced crop protection by simultaneously targeting insect pests and unwanted weeds, improving application efficiency and reducing overall chemical usage. These integrated solutions help maintain crop health and yield by delivering precise control over multiple threats while minimizing environmental impact and resistance development.
Pesticides vs Herbicides for crop protection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com