Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with annual crops, maximizing land use by providing shade, enhancing soil fertility, and reducing erosion while supporting crop diversity. Silvopasture combines trees with livestock grazing, promoting animal welfare through shelter, improving pasture quality, and increasing overall system productivity. Both methods optimize land utilization but differ in focus--alley cropping emphasizes crop-tree synergy, whereas silvopasture centers on harmonizing tree growth with livestock management.
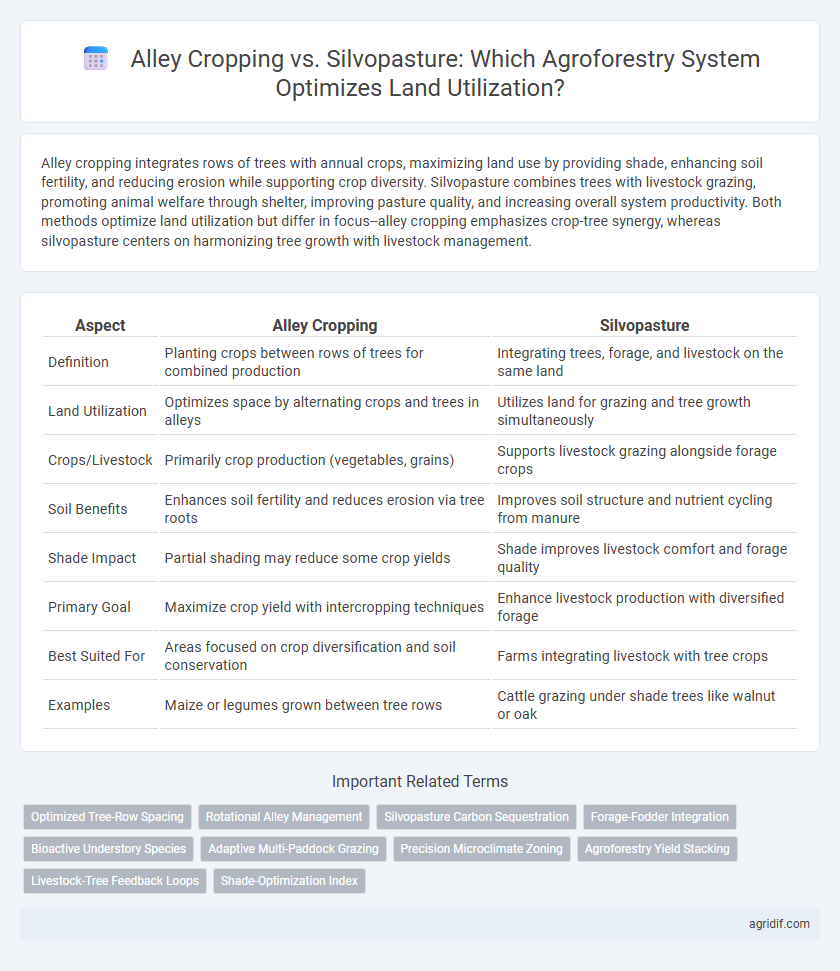
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alley Cropping | Silvopasture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planting crops between rows of trees for combined production | Integrating trees, forage, and livestock on the same land |
| Land Utilization | Optimizes space by alternating crops and trees in alleys | Utilizes land for grazing and tree growth simultaneously |
| Crops/Livestock | Primarily crop production (vegetables, grains) | Supports livestock grazing alongside forage crops |
| Soil Benefits | Enhances soil fertility and reduces erosion via tree roots | Improves soil structure and nutrient cycling from manure |
| Shade Impact | Partial shading may reduce some crop yields | Shade improves livestock comfort and forage quality |
| Primary Goal | Maximize crop yield with intercropping techniques | Enhance livestock production with diversified forage |
| Best Suited For | Areas focused on crop diversification and soil conservation | Farms integrating livestock with tree crops |
| Examples | Maize or legumes grown between tree rows | Cattle grazing under shade trees like walnut or oak |
Introduction to Agroforestry: Alley Cropping and Silvopasture
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops planted in the alleys to maximize sunlight and root space, enhancing nutrient cycling and soil health. Silvopasture combines trees with pastureland for grazing livestock, improving land productivity through diversified yields and microclimate regulation. Both systems optimize land utilization by blending woody perennials with annual or perennial crops, increasing biodiversity and providing multiple economic benefits.
Core Principles: Alley Cropping Versus Silvopasture
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with traditional crops planted in between, optimizing sunlight and nutrient use while promoting soil health through diversified root structures. Silvopasture combines trees with forage and livestock, emphasizing spatial arrangement to balance shade, shelter, and grazing areas for enhanced pasture productivity. Both systems prioritize multifunctional land use, but alley cropping focuses on crop-tree interactions, whereas silvopasture centers on livestock-tree-forage synergy.
Land Utilization Efficiency: Comparative Insights
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops, maximizing land use by allowing simultaneous cultivation of timber and agricultural produce on the same plot. Silvopasture combines trees with pastureland, optimizing land by supporting livestock grazing beneath tree canopies, enhancing biodiversity and soil health. Comparative studies show alley cropping often yields higher crop diversity per hectare, while silvopasture excels in improving overall ecosystem services and sustainable livestock productivity.
Crop and Livestock Integration in Agroforestry Systems
Alley cropping integrates rows of crops with tree alleys, optimizing land by enhancing crop diversity and soil health, while silvopasture combines trees with grazing livestock to improve pasture productivity and animal welfare. Both systems leverage spatial design to maximize resource use efficiency, with alley cropping focusing more on crop yield and silvopasture emphasizing livestock forage and shade. Effective integration of crops and livestock in agroforestry enhances biodiversity, improves carbon sequestration, and sustains long-term land productivity.
Soil Health and Fertility: Benefits in Both Systems
Alley cropping and silvopasture both enhance soil health by promoting nutrient cycling and reducing erosion through diverse root systems and increased organic matter. Alley cropping integrates crops between tree rows, improving soil structure and fertility by fostering microbial activity and nitrogen fixation. Silvopasture combines trees with pasture, boosting soil nutrients and moisture retention while supporting beneficial soil organisms for long-term land productivity.
Biodiversity Impact: Alley Cropping vs Silvopasture
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crop cultivation, enhancing plant diversity and providing habitat for beneficial insects, which supports pollination and pest control. Silvopasture combines trees with forage and livestock grazing, promoting diverse wildlife habitats and improving soil health through organic matter input from animals. Both systems increase biodiversity, but alley cropping primarily benefits plant and insect diversity, while silvopasture strengthens ecosystem complexity by supporting a wider range of animal species and soil organisms.
Economic Returns and Farmer Profitability
Alley cropping integrates high-value crops with tree rows, optimizing land use by producing diversified income streams through simultaneous harvests of crops and timber or nuts. Silvopasture combines forestry with livestock grazing, enhancing profitability by reducing feed costs and increasing forage productivity while generating timber revenue. Studies reveal silvopasture often leads to higher long-term economic returns due to lower input costs and synergistic land utilization, whereas alley cropping provides quicker cash flow but may require more intensive management.
Climate Resilience: Mitigating Environmental Risks
Alley cropping enhances climate resilience by integrating rows of trees with high-value crops, improving soil moisture retention and reducing erosion while providing windbreaks that mitigate drought impacts. Silvopasture combines trees with pastureland, promoting carbon sequestration and diversifying forage availability, which buffers livestock against extreme weather events. Both practices optimize land utilization by creating multifunctional landscapes that stabilize microclimates and enhance ecosystem services in agroforestry systems.
Suitability for Different Land Types and Climates
Alley cropping is highly suitable for fertile, well-drained soils in temperate climates, optimizing land with high agricultural productivity by integrating row crops between tree rows. Silvopasture thrives in diverse land types, including marginal or sloped terrains common in subtropical and tropical climates, combining trees with forage and livestock to enhance ecosystem resilience. Both systems improve land utilization but are selected based on soil fertility, climate conditions, and land topography for maximum agroecological benefits.
Practical Considerations for Implementation and Management
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops, optimizing land use by enhancing soil fertility and providing microclimate benefits, but requires careful spacing and crop-tree compatibility to avoid competition. Silvopasture combines trees with pastureland, supporting livestock grazing while improving biodiversity and soil health, demanding strategic management of tree density and forage species to balance shade and animal movement. Both systems necessitate tailored planning and ongoing monitoring to maximize productivity and ecological benefits based on site-specific conditions and management goals.
Related Important Terms
Optimized Tree-Row Spacing
Alley cropping optimizes land utilization by incorporating wide tree-row spacing that allows for crop cultivation between rows, maximizing sunlight and resource sharing for both crops and trees. Silvopasture utilizes narrower tree-row spacing to create shaded pastures that enhance forage quality and livestock comfort while maintaining efficient land use through integrated tree and animal production.
Rotational Alley Management
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with annual crops, optimizing land by enabling rotational alley management that enhances soil fertility and crop yields through periodic mowing and biomass incorporation. Silvopasture combines trees with livestock grazing, using rotational alley management to control forage availability and prevent overgrazing, promoting sustainable land use and improved biodiversity.
Silvopasture Carbon Sequestration
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock on the same land, enhancing carbon sequestration by promoting deeper root systems and increased biomass carbon storage compared to alley cropping, which primarily focuses on crops between tree rows. The holistic land utilization in silvopasture optimizes carbon capture while supporting sustainable livestock production and improving soil health.
Forage-Fodder Integration
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with forage crops, optimizing land by enhancing soil fertility and providing seasonal fodder, while silvopasture combines trees with grazing livestock, maximizing continuous forage production through tree shade and nutrient cycling. Both systems improve forage-fodder integration but alley cropping leans towards crop diversity and silvopasture emphasizes sustainable grazing management.
Bioactive Understory Species
Alley cropping integrates rows of high-value trees with bioactive understory crops such as herbs and legumes, enhancing soil fertility and pest resistance while maximizing land productivity. Silvopasture combines trees with pasture for livestock and includes bioactive understory species like medicinal plants and nutrient-rich forage, promoting animal health and improving land use efficiency through diversified ecological interactions.
Adaptive Multi-Paddock Grazing
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops, optimizing land by enhancing soil health and biodiversity, while silvopasture combines trees with adaptive multi-paddock grazing to improve pasture productivity and animal welfare through rotational grazing. Adaptive multi-paddock grazing in silvopasture maximizes forage growth and soil carbon sequestration, making land utilization more sustainable compared to alley cropping's crop-focused system.
Precision Microclimate Zoning
Alley cropping optimizes land utilization by integrating row crops within tree alleys, allowing precise microclimate zoning that enhances crop growth through targeted shading and wind protection. Silvopasture combines trees with grazing animals, using microclimate zones strategically to regulate forage quality and animal comfort, improving land efficiency and ecological balance.
Agroforestry Yield Stacking
Alley cropping integrates rows of crops between tree alleys, maximizing land use by combining agricultural and forestry yields, while silvopasture merges livestock grazing with tree cultivation, enhancing productivity through multifunctional land use. Yield stacking in agroforestry optimizes resource efficiency and increases overall farm revenue by diversifying outputs from the same land area.
Livestock-Tree Feedback Loops
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops, maximizing light and nutrient competition but limiting livestock integration, whereas silvopasture combines trees, forage, and livestock, creating dynamic feedback loops where animals enhance nutrient cycling through manure and grazing, while trees provide shade and shelter that improve livestock health and productivity. These reciprocal interactions in silvopasture optimize land utilization by boosting soil fertility and microclimate regulation, fostering sustainable agroecosystem resilience.
Shade-Optimization Index
Alley cropping enhances land utilization by strategically arranging crops between rows of trees to optimize light interception, thereby improving the Shade-Optimization Index through controlled shading that benefits understory plants. Silvopasture integrates trees with livestock grazing, where the Shade-Optimization Index plays a crucial role in balancing adequate shade for animal comfort while maintaining sufficient pasture growth.
Alley Cropping vs Silvopasture for Land Utilization Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com