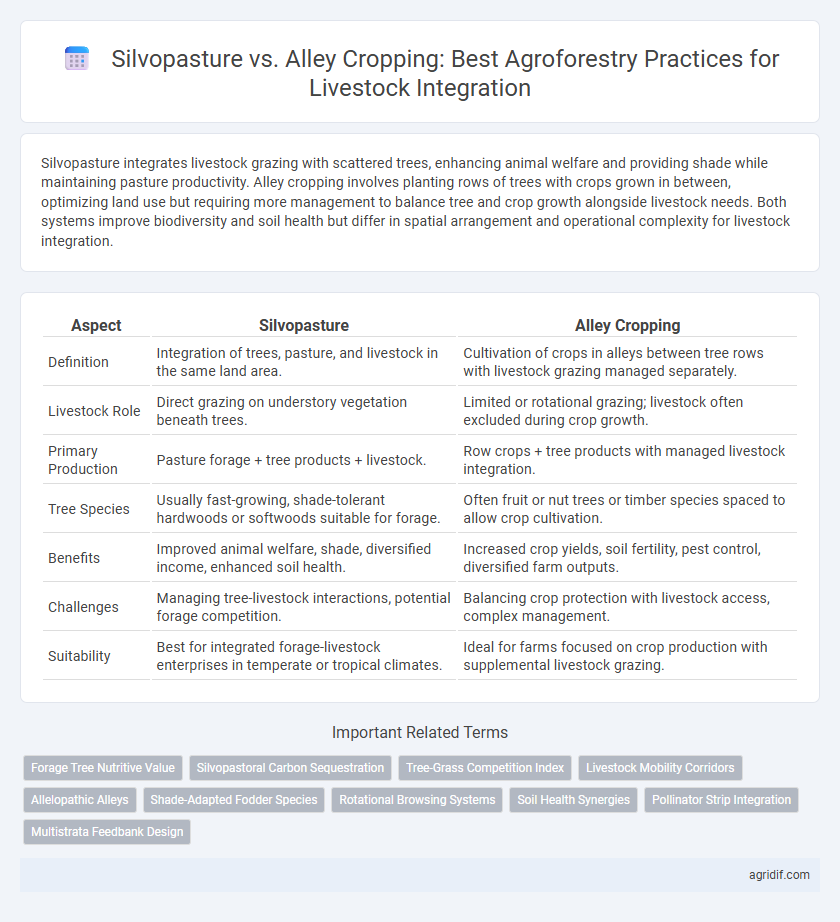
Silvopasture integrates livestock grazing with scattered trees, enhancing animal welfare and providing shade while maintaining pasture productivity. Alley cropping involves planting rows of trees with crops grown in between, optimizing land use but requiring more management to balance tree and crop growth alongside livestock needs. Both systems improve biodiversity and soil health but differ in spatial arrangement and operational complexity for livestock integration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Silvopasture | Alley Cropping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of trees, pasture, and livestock in the same land area. | Cultivation of crops in alleys between tree rows with livestock grazing managed separately. |
| Livestock Role | Direct grazing on understory vegetation beneath trees. | Limited or rotational grazing; livestock often excluded during crop growth. |
| Primary Production | Pasture forage + tree products + livestock. | Row crops + tree products with managed livestock integration. |
| Tree Species | Usually fast-growing, shade-tolerant hardwoods or softwoods suitable for forage. | Often fruit or nut trees or timber species spaced to allow crop cultivation. |
| Benefits | Improved animal welfare, shade, diversified income, enhanced soil health. | Increased crop yields, soil fertility, pest control, diversified farm outputs. |
| Challenges | Managing tree-livestock interactions, potential forage competition. | Balancing crop protection with livestock access, complex management. |
| Suitability | Best for integrated forage-livestock enterprises in temperate or tropical climates. | Ideal for farms focused on crop production with supplemental livestock grazing. |
Introduction to Livestock Integration in Agroforestry
Silvopasture integrates trees with livestock grazing, enhancing animal welfare through shade and diverse forage, while improving soil health and carbon sequestration. Alley cropping combines rows of trees or shrubs with pasture strips, maximizing land use efficiency and providing multiple products such as fodder, timber, and crops. Both systems increase biodiversity and nutrient cycling, but silvopasture emphasizes continuous grazing whereas alley cropping allows rotational grazing with crop production.
Overview of Silvopasture Systems
Silvopasture systems integrate trees, forage, and livestock on the same land, enhancing biodiversity and improving animal welfare by providing shade, shelter, and diversified nutrition. These systems optimize land use efficiency by combining timber production with grazing, reducing soil erosion and increasing carbon sequestration compared to traditional pasture systems. Key tree species used in silvopasture include nitrogen-fixing trees like Leucaena and timber species such as oak and pine, which support sustainable livestock integration.
Understanding Alley Cropping for Livestock
Alley cropping integrates livestock by planting rows of trees or shrubs with wide alleys for forage production, enhancing animal grazing options while preserving soil health and crop yield. This method optimizes land use by combining tree canopy benefits with nutrient-rich forage, supporting sustainable livestock growth and biodiversity. Compared to silvopasture, alley cropping provides structured forage areas, reducing competition between trees and animals and improving overall farm productivity.
Key Differences: Silvopasture vs Alley Cropping
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock simultaneously within the same land area, enhancing animal welfare and diversifying farm income by providing shade, shelter, and additional fodder. Alley cropping arranges crops or forage in alleys between rows of trees primarily for crop production, with livestock access typically limited or managed separately to prevent damage and to optimize crop yields. The key differences lie in livestock management intensity and spatial design, where silvopasture prioritizes continuous grazing under tree canopies, while alley cropping focuses on row crop cultivation with periodic livestock integration.
Benefits of Silvopasture for Livestock Producers
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock in a single system, improving animal welfare through shade and wind protection, which enhances livestock productivity and health. This practice increases land-use efficiency by combining timber and forage production, providing diversified income streams for farmers. The microclimate regulation and improved soil fertility in silvopasture systems contribute to sustainable livestock production and environmental resilience.
Advantages of Alley Cropping in Livestock Management
Alley cropping enhances livestock management by providing diverse forage options between rows of crops, improving animal nutrition while maintaining soil health through increased organic matter. This system reduces feed costs and supports rotational grazing, promoting sustainable land use and minimizing soil erosion. Additionally, alley cropping facilitates integrated pest management and maximizes land productivity by combining crop and livestock operations efficiently.
Environmental Impacts: Silvopasture vs Alley Cropping
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock in a single system, enhancing carbon sequestration and improving soil health through increased organic matter and reduced erosion. Alley cropping combines rows of trees with crops or pastures in alleys, promoting biodiversity and nutrient cycling but may have higher soil disturbance due to row management. Both systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional livestock farming, yet silvopasture typically offers greater microclimate regulation and habitat complexity for wildlife.
Economic Considerations for Farmers
Silvopasture offers farmers diversified income through timber, forage, and livestock sales, reducing economic risk by integrating multiple revenue streams on the same land. Alley cropping provides income from both crops and trees but may require higher initial investment and management complexity, impacting short-term profitability. Economic success depends on site-specific factors such as market access, production costs, and livestock compatibility with tree species in each system.
Best Practices for Successful Livestock Integration
Silvopasture and alley cropping both enhance livestock integration by combining tree cover with forage production, but silvopasture excels in providing shade and shelter, improving animal welfare and weight gain. Best practices include selecting compatible tree species that do not compete excessively with forage, maintaining proper stocking densities to prevent soil compaction, and implementing rotational grazing to optimize nutrient cycling and pasture recovery. Integrating livestock with alley cropping requires managing tree rows to allow sufficient light for crops while providing occasional browse for animals, balancing crop yields with grazing benefits.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Consider
Selecting between silvopasture and alley cropping for livestock integration hinges on key factors such as land size, animal type, and production goals. Silvopasture suits larger areas with grazing animals requiring extensive canopy cover, enhancing shade and forage diversity. Alley cropping fits smaller parcels emphasizing crop-livestock synergy, balancing tree rows with forage strips to optimize nutrient cycling and soil health.
Related Important Terms
Forage Tree Nutritive Value
Silvopasture integrates livestock with forage trees, enhancing protein-rich fodder like Leucaena and Gliricidia, which boost animal nutrition and weight gain; alley cropping combines crops with nitrogen-fixing trees, but forage quality varies by species, often lower in digestibility. Optimal forage tree nutritive value in silvopasture supports better rumen function and efficient nutrient uptake, while alley cropping's primary focus on crop yield may limit consistent high-quality fodder for livestock.
Silvopastoral Carbon Sequestration
Silvopasture systems integrate trees, forage, and livestock in a single area, enhancing carbon sequestration by increasing biomass productivity and soil organic carbon storage compared to alley cropping, which separates trees and crops into distinct rows. Silvopastoral practices promote deeper root systems and continuous ground cover, leading to higher carbon capture and improved soil health critical for mitigating climate change.
Tree-Grass Competition Index
Silvopasture integrates livestock with widely spaced trees to minimize Tree-Grass Competition Index, promoting optimal forage growth and animal productivity. Alley cropping involves planting rows of trees with forage crops in alleys, where higher Tree-Grass Competition Index often reduces forage yield but enhances overall land use efficiency.
Livestock Mobility Corridors
Livestock mobility corridors in silvopasture systems enable controlled grazing paths that improve pasture utilization and soil health by reducing animal trampling in sensitive areas. In contrast, alley cropping restricts livestock movement with narrow planting rows, limiting free-range access and potentially increasing soil compaction outside designated alleys.
Allelopathic Alleys
Alley cropping in agroforestry incorporates allelopathic alleys, where certain tree species release biochemicals that suppress weed growth, enhancing pasture quality for livestock without synthetic herbicides. Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock but typically avoids allelopathic species to prevent negative effects on forage and animal health.
Shade-Adapted Fodder Species
Silvopasture integrates shade-adapted fodder species like Desmanthus and Leucaena, providing high-quality nutrition for livestock while enhancing tree canopy benefits. Alley cropping, by contrast, supports fodder growth in systematic rows, optimizing light distribution for species such as Stylosanthes and Arachis, balancing forage production with crop yield.
Rotational Browsing Systems
Silvopasture integrates livestock with trees using rotational browsing systems that enhance forage diversity and soil health, optimizing animal nutrition and pasture productivity. Alley cropping allows livestock to graze between rows of crops, improving nutrient cycling and reducing pasture degradation through managed rotation, but typically supports less intensive browsing than silvopasture.
Soil Health Synergies
Silvopasture integrates trees, forage, and livestock by providing continuous ground cover that enhances soil organic matter and microbial activity, leading to improved nutrient cycling and reduced erosion. Alley cropping combines rows of trees with crops, allowing periodic tillage that may temporarily disrupt soil structure but increases biodiversity and promotes deeper root systems that stabilize soil and improve water infiltration.
Pollinator Strip Integration
Silvopasture combines trees, forage, and livestock grazing, enhancing biodiversity and providing shade while alley cropping integrates crops and trees in rows, facilitating pollinator strip inclusion between alleys to boost ecosystem services. Pollinator strips in alley cropping improve pollination efficiency and crop yield by creating habitat corridors for bees and beneficial insects, whereas silvopasture's scattered tree arrangement offers variable floral resources supporting diverse pollinator populations.
Multistrata Feedbank Design
Silvopasture integrates livestock with trees and pasture, enhancing forage quality through multistrata feedbank design that maximizes vertical space and nutrient cycling. Alley cropping arranges row crops between tree alleys, which can limit livestock movement and reduce continuous forage availability compared to the dynamic, multilayered forage systems in silvopasture.
Silvopasture vs alley cropping for livestock integration Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com