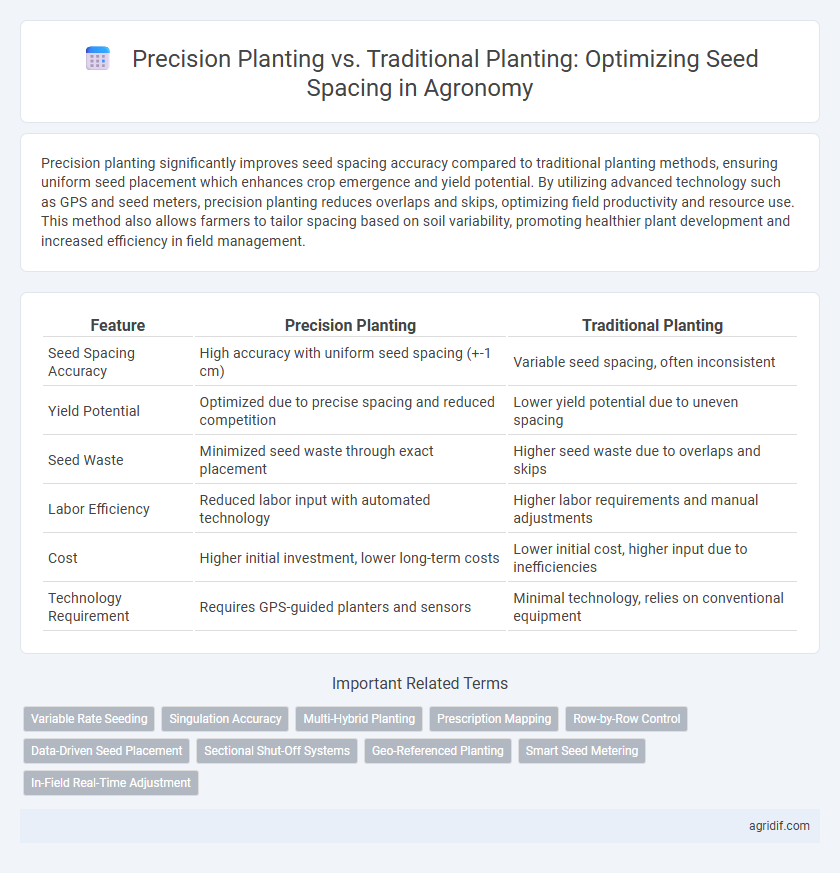
Precision planting significantly improves seed spacing accuracy compared to traditional planting methods, ensuring uniform seed placement which enhances crop emergence and yield potential. By utilizing advanced technology such as GPS and seed meters, precision planting reduces overlaps and skips, optimizing field productivity and resource use. This method also allows farmers to tailor spacing based on soil variability, promoting healthier plant development and increased efficiency in field management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Precision Planting | Traditional Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Spacing Accuracy | High accuracy with uniform seed spacing (+-1 cm) | Variable seed spacing, often inconsistent |
| Yield Potential | Optimized due to precise spacing and reduced competition | Lower yield potential due to uneven spacing |
| Seed Waste | Minimized seed waste through exact placement | Higher seed waste due to overlaps and skips |
| Labor Efficiency | Reduced labor input with automated technology | Higher labor requirements and manual adjustments |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs | Lower initial cost, higher input due to inefficiencies |
| Technology Requirement | Requires GPS-guided planters and sensors | Minimal technology, relies on conventional equipment |
Introduction to Seed Spacing in Agriculture
Precision planting technologies ensure accurate seed spacing by using advanced sensors and GPS guidance systems, leading to uniform crop emergence and optimized resource use. Traditional planting methods often rely on manual or mechanical spacing, which can result in irregular seed placement and variable plant density. Enhanced seed spacing through precision planting improves yield potential by maximizing light interception and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Defining Precision Planting and Traditional Planting
Precision planting utilizes advanced technology such as GPS, sensors, and variable rate seed meters to place seeds at exact intervals and depths, optimizing plant population and ensuring uniform emergence. Traditional planting relies on mechanical equipment with fixed seed spacing, often resulting in less precise seed placement and variable emergence rates. The use of precision planting improves seed spacing accuracy, maximizes yield potential, and reduces seed waste compared to traditional methods.
Importance of Accurate Seed Spacing
Accurate seed spacing in precision planting enhances crop uniformity, optimizes resource use, and increases yield potential compared to traditional planting methods that often result in uneven seed distribution. Precision planting technologies, such as GPS-guided equipment and variable rate seeders, ensure consistent in-row spacing that reduces competition among plants and improves nutrient uptake. Uniform seed placement directly impacts plant health and maximizes field profitability by enabling better emergence and growth management.
Technology Used in Precision Planting
Precision planting employs GPS-guided machinery and advanced sensors to ensure accurate seed spacing, optimizing plant population density and reducing seed wastage. Traditional planting relies on mechanical planters with fixed seed meters, resulting in less uniform spacing and potential yield variability. Technologies such as variable rate controllers, row-by-row monitoring, and real-time data analytics enhance precision planting's efficiency compared to conventional methods.
Seed Spacing Outcomes: Precision vs Traditional Methods
Precision planting technology delivers uniform seed spacing by utilizing GPS guidance and advanced sensors, optimizing row placement and reducing seed overlap or gaps. Traditional planting methods rely on mechanical planters that often result in inconsistent seed spacing due to human error and variable field conditions. Improved seed spacing through precision planting enhances germination rates, promotes even crop emergence, and maximizes yield potential.
Impact on Crop Yield and Uniformity
Precision planting technology significantly enhances seed spacing accuracy compared to traditional planting methods, leading to improved crop yield and uniform plant stands. By ensuring optimal seed placement and depth, precision planting reduces competition among plants and maximizes resource utilization, which directly boosts overall productivity. Traditional planting often results in uneven seed distribution, causing irregular growth and lower yield consistency across the field.
Resource Efficiency: Inputs and Cost Analysis
Precision planting enhances resource efficiency by optimizing seed spacing, reducing seed waste, and ensuring uniform plant emergence, which lowers overall input costs compared to traditional planting methods. Accurate seed placement minimizes overlapping and skips, improving nutrient and water use efficiency while reducing the need for herbicides and fertilizers. This targeted approach translates into significant cost savings and higher crop yields, making precision planting a financially advantageous option for modern agronomy.
Field Case Studies and Research Findings
Field case studies demonstrate that precision planting significantly improves seed spacing uniformity compared to traditional planting methods, leading to optimized plant population density. Research findings indicate that precision planters enhance yield potential by reducing seed placement errors and minimizing seed waste, resulting in more efficient resource utilization. Data from multiple agronomic trials confirm that precision planting boosts crop productivity and profitability by ensuring consistent seed-to-seed spacing tailored to specific field conditions.
Environmental Implications of Seed Spacing Strategies
Precision planting optimizes seed spacing by placing seeds at uniform, optimal distances, reducing seed wastage and minimizing soil disturbance compared to traditional planting methods. This targeted approach enhances resource use efficiency, decreases fertilizer runoff, and lowers the risk of soil erosion, contributing to improved environmental sustainability. In contrast, traditional planting often results in uneven seed distribution, which can lead to higher input demands and increased environmental strain.
Future Trends in Agronomic Planting Techniques
Precision planting utilizes GPS technology and variable rate seeding to optimize seed spacing, enhancing crop uniformity and yield potential compared to traditional planting methods that often result in irregular seed distribution. Emerging trends include integration of AI-driven analytics and real-time sensor data to dynamically adjust seed placement, minimizing seed wastage and improving resource efficiency. Future advancements in agronomic planting techniques emphasize automated machinery with machine learning capabilities for even more precise, adaptive seed spacing tailored to specific field conditions.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Seeding
Variable Rate Seeding in precision planting optimizes seed spacing by adjusting seeding rates based on soil variability, improving germination uniformity and crop yield compared to traditional uniform seed distribution. This technology leverages GPS and sensor data to dynamically modulate seed placement density, enhancing resource efficiency and minimizing seed waste.
Singulation Accuracy
Precision planting significantly improves singulation accuracy by placing seeds at exact intervals, reducing seed overlap and gaps compared to traditional planting methods. Enhanced singulation ensures uniform crop emergence, leading to optimal plant density and increased yield potential in agronomic practices.
Multi-Hybrid Planting
Precision planting technology enhances seed spacing accuracy by using GPS-guided systems and real-time sensor feedback, optimizing multi-hybrid planting to maximize yield potential and resource efficiency. Traditional planting methods often result in irregular seed distribution, which can reduce uniformity and limit the benefits of deploying multiple hybrids tailored to specific soil zones within a field.
Prescription Mapping
Precision planting utilizes prescription mapping to optimize seed spacing by analyzing soil variability and crop requirements, resulting in uniform seed distribution tailored to field-specific conditions. In contrast, traditional planting applies uniform seed spacing without accounting for field heterogeneity, often leading to suboptimal plant density and reduced yield potential.
Row-by-Row Control
Precision planting with row-by-row control enables highly accurate seed spacing, optimizing plant population and improving crop uniformity, while traditional planting often results in irregular spacing and suboptimal plant density. Enhanced precision reduces seed waste and maximizes yield potential by ensuring consistent seed placement tailored to soil variability and field conditions.
Data-Driven Seed Placement
Precision planting utilizes GPS technology and soil sensors to achieve highly accurate seed spacing, enhancing germination rates and crop uniformity compared to traditional planting methods. Data-driven seed placement optimizes input use, reduces seed waste, and increases overall yield potential by tailoring seed spacing to field variability.
Sectional Shut-Off Systems
Sectional shut-off systems in precision planting enable targeted seed placement by controlling individual planter sections, reducing seed overlap and skips compared to traditional planting methods with uniform seed spacing. This technology enhances seed use efficiency and crop uniformity by optimizing seed distribution based on field variability.
Geo-Referenced Planting
Geo-referenced precision planting leverages GPS technology to optimize seed spacing, enhancing uniformity and reducing seed overlap compared to traditional planting methods that rely on manual spacing and often result in irregular seed distribution. This spatial accuracy improves crop emergence rates and maximizes yield potential by ensuring each seed receives optimal resources.
Smart Seed Metering
Precision planting utilizes smart seed metering technology to ensure uniform seed spacing, resulting in optimized plant population and higher yield potential compared to traditional planting methods. Advanced sensors and real-time adjustments in precision systems minimize seed skips and doubles, enhancing overall field efficiency and reducing input waste.
In-Field Real-Time Adjustment
Precision planting utilizes advanced sensors and GPS technology to enable in-field real-time adjustment of seed spacing, resulting in optimal plant density and uniform crop emergence. Traditional planting methods lack this capability, often leading to uneven seed distribution and suboptimal yield potential.
Precision planting vs traditional planting for seed spacing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com