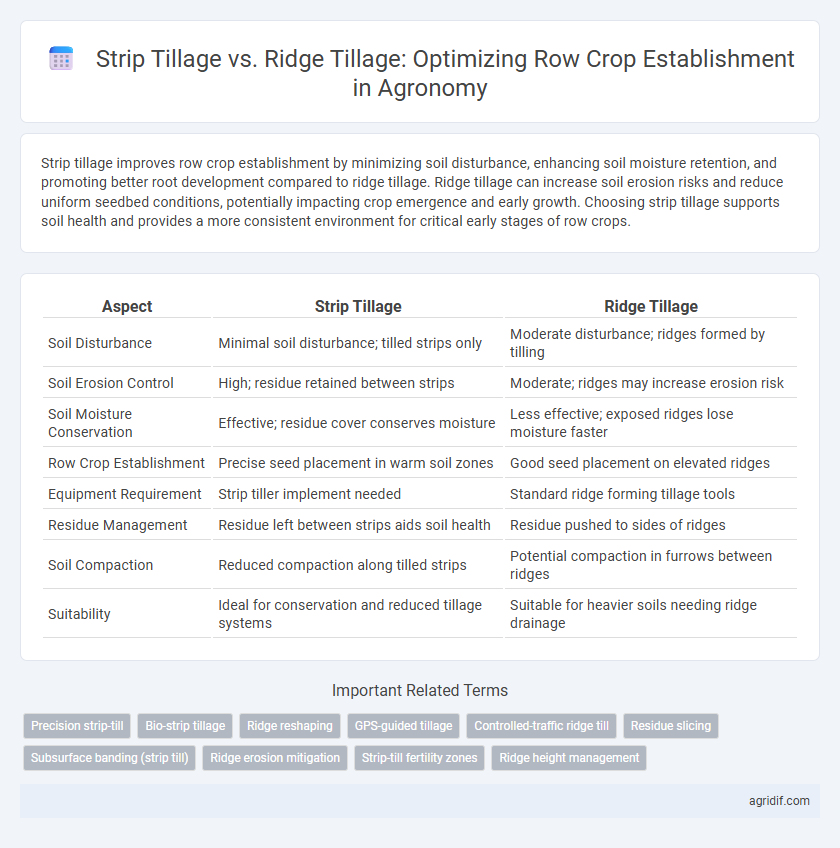
Strip tillage improves row crop establishment by minimizing soil disturbance, enhancing soil moisture retention, and promoting better root development compared to ridge tillage. Ridge tillage can increase soil erosion risks and reduce uniform seedbed conditions, potentially impacting crop emergence and early growth. Choosing strip tillage supports soil health and provides a more consistent environment for critical early stages of row crops.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Strip Tillage | Ridge Tillage |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Disturbance | Minimal soil disturbance; tilled strips only | Moderate disturbance; ridges formed by tilling |
| Soil Erosion Control | High; residue retained between strips | Moderate; ridges may increase erosion risk |
| Soil Moisture Conservation | Effective; residue cover conserves moisture | Less effective; exposed ridges lose moisture faster |
| Row Crop Establishment | Precise seed placement in warm soil zones | Good seed placement on elevated ridges |
| Equipment Requirement | Strip tiller implement needed | Standard ridge forming tillage tools |
| Residue Management | Residue left between strips aids soil health | Residue pushed to sides of ridges |
| Soil Compaction | Reduced compaction along tilled strips | Potential compaction in furrows between ridges |
| Suitability | Ideal for conservation and reduced tillage systems | Suitable for heavier soils needing ridge drainage |
Introduction to Row Crop Establishment Techniques
Strip tillage conserves soil structure by disturbing only narrow strips, promoting faster warming and improved root penetration for row crops. Ridge tillage creates raised beds that enhance drainage and soil aeration while reducing erosion, ideal for heavier soils. Selecting the appropriate tillage method depends on soil type, moisture conditions, and crop requirements to optimize early root development and yield potential.
Fundamentals of Strip Tillage in Modern Agronomy
Strip tillage conserves soil structure by tilling narrow strips while leaving inter-row areas undisturbed, promoting better water infiltration and reducing erosion. The practice enhances early root development and nutrient uptake by concentrating residue and nutrients in the tilled zone for row crops such as corn and soybeans. Modern agronomy emphasizes strip tillage as a sustainable alternative that balances soil health with effective seedbed preparation.
Ridge Tillage: Principles and Practices
Ridge tillage involves creating permanent raised rows that reduce soil disruption while improving moisture retention and root penetration, making it highly effective for row crop establishment. This practice enhances soil structure by maintaining crop residue on the ridges, which minimizes erosion and supports beneficial microbial activity. Adopting ridge tillage can lead to improved water infiltration and nutrient availability, promoting healthier crop growth compared to conventional tillage methods.
Comparative Benefits: Strip Tillage vs Ridge Tillage
Strip tillage reduces soil disturbance while preserving residue cover, which enhances moisture retention and minimizes erosion compared to ridge tillage. Ridge tillage improves early soil warming and drainage by forming elevated rows, benefiting crops in cooler, wetter conditions. Both methods optimize seedbed conditions, but strip tillage offers superior soil conservation, whereas ridge tillage provides better root zone aeration and temperature management.
Impacts on Soil Structure and Health
Strip tillage preserves soil structure by minimizing disturbance to the undisturbed zones between rows, enhancing water infiltration, and promoting root development, which improves soil health over time. Ridge tillage alters surface soil by forming elevated crop beds, which can increase soil aeration but may also lead to greater erosion risks if not managed properly. Both methods influence microbial activity and organic matter dynamics, with strip tillage generally fostering more stable soil aggregates and higher biological diversity compared to ridge tillage.
Effects on Soil Moisture and Temperature Management
Strip tillage conserves soil moisture by minimizing soil disturbance, creating narrow tilled zones that retain more water compared to ridge tillage's raised beds which can dry out faster due to increased surface exposure. Soil temperature in strip tillage tends to warm more quickly in early spring, enhancing seed germination and early root development, whereas ridge tillage may exhibit greater temperature fluctuations due to elevated and exposed soil surfaces. Effective management of soil moisture and temperature through strip tillage can improve crop emergence uniformity and overall yield potential in row crop systems.
Weed Control Efficiency: Strip vs Ridge Tillage
Strip tillage offers enhanced weed control efficiency by disturbing only narrow soil bands where seeds are planted, minimizing weed seed germination in undisturbed zones. Ridge tillage reduces weed pressure by creating elevated seedbeds that expose weed seeds to desiccation and predation but may require more herbicide use compared to strip tillage. Research shows strip tillage can lower overall weed emergence and herbicide dependence, promoting sustainable row crop establishment.
Equipment and Implementation Considerations
Strip tillage requires specialized narrow-width coulters and residue managers to prepare seedbeds only in the row zone, allowing no-till in inter-rows, whereas ridge tillage employs ridge builders and trash whippers to form raised beds with cleared planting zones. Equipment calibration for strip tillage demands precise control to avoid soil compaction and maintain residue cover, while ridge tillage systems emphasize maintaining ridge structure and erosion control during planting. Implementation considerations include terrain suitability, with strip tillage better for rolling fields due to residue preservation and ridge tillage favored in areas requiring improved drainage and soil warming for early planting.
Crop Yield and Economic Outcomes
Strip tillage enhances soil structure by minimizing disturbance, leading to improved moisture retention and root development that can increase crop yield by up to 15% compared to ridge tillage. Ridge tillage often reduces initial costs through lower fuel and labor requirements but may result in lower yields due to increased soil erosion and variable seed placement. Economic outcomes favor strip tillage over multiple seasons as higher yields and improved soil health translate to greater profitability despite slightly elevated upfront costs.
Environmental Implications and Sustainability
Strip tillage reduces soil erosion and promotes water infiltration by disturbing only narrow strips, enhancing soil structure and organic matter retention compared to ridge tillage, which can increase runoff and soil compaction. Ridge tillage may lead to uneven moisture distribution and higher susceptibility to nutrient leaching, impacting long-term soil fertility and environmental health. Sustainable row crop establishment benefits from strip tillage's ability to balance residue management with conservation efforts, improving carbon sequestration and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Related Important Terms
Precision strip-till
Precision strip-till combines the soil disturbance benefits of strip tillage with exact seed placement, enhancing root development and water infiltration for row crops. Compared to ridge tillage, precision strip-till improves nutrient management and reduces soil erosion by maintaining residue cover while preparing narrow strips for planting.
Bio-strip tillage
Bio-strip tillage enhances soil health and moisture retention by combining minimal soil disturbance with organic residue management, promoting optimal root development in row crops. Compared to ridge tillage, this method reduces erosion and improves nutrient availability, leading to increased yield potential and sustainable crop establishment.
Ridge reshaping
Ridge reshaping in ridge tillage enhances soil structure by maintaining optimal moisture levels and improving root zone aeration, which leads to better crop emergence and yield consistency compared to strip tillage. This practice also reduces soil erosion and compaction while facilitating nutrient retention specifically in row crop establishment.
GPS-guided tillage
GPS-guided strip tillage enhances row crop establishment by precisely cultivating narrow strips, reducing soil disturbance and optimizing seed placement for improved root development and moisture retention. Ridge tillage, guided by GPS technology, creates raised seedbeds that improve drainage and soil warming but may increase erosion risk compared to the minimal disturbance approach of strip tillage.
Controlled-traffic ridge till
Controlled-traffic ridge tillage enhances soil structure by confining machinery traffic to permanent lanes, reducing compaction and promoting better root development for row crops compared to strip tillage. This method improves water infiltration and residue management, leading to increased yield potential and sustainable soil health in row crop establishment.
Residue slicing
Strip tillage effectively slices crop residue, enhancing soil warming and seedbed preparation for row crops, while ridge tillage tends to leave more residue intact, which can reduce soil temperature but improve moisture retention. The precision of residue slicing in strip tillage supports better seed-to-soil contact, promoting more uniform germination compared to ridge tillage methods.
Subsurface banding (strip till)
Subsurface banding in strip tillage enhances nutrient placement directly in the root zone, improving fertilizer efficiency and early root development compared to ridge tillage. This method reduces soil disturbance and preserves soil structure, promoting better moisture retention and reducing erosion risks during row crop establishment.
Ridge erosion mitigation
Ridge tillage significantly reduces ridge erosion by maintaining permanent raised beds that enhance soil structure and minimize surface runoff compared to strip tillage, which disturbs the soil more extensively between rows. This conservation practice promotes better moisture retention and root development while protecting against soil loss in row crop establishment.
Strip-till fertility zones
Strip-till fertility zones concentrate nutrients within narrow bands, enhancing root development and improving nutrient use efficiency compared to ridge tillage, which distributes inputs more broadly but less precisely. This targeted placement in strip-till systems supports higher yields and enables reduced fertilizer rates by optimizing nutrient availability at the seed zone in row crop establishment.
Ridge height management
Ridge tillage offers precise ridge height management, maintaining optimal soil temperature and moisture levels critical for uniform row crop establishment. Consistent ridge height enhances root development and reduces soil compaction compared to variable ridge heights seen in strip tillage systems.
Strip tillage vs ridge tillage for row crop establishment Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com