Crossbred livestock exhibit enhanced hybrid vigor, leading to improved growth rates, disease resistance, and overall productivity compared to purebred animals. While purebreds offer uniformity and predictable traits for specific breeding goals, crossbreeding combines desirable characteristics from different breeds, optimizing adaptability and performance in varied environmental conditions. Effective livestock improvement programs leverage crossbreeding strategies to balance genetic diversity with targeted trait enhancement for sustainable production.
Table of Comparison
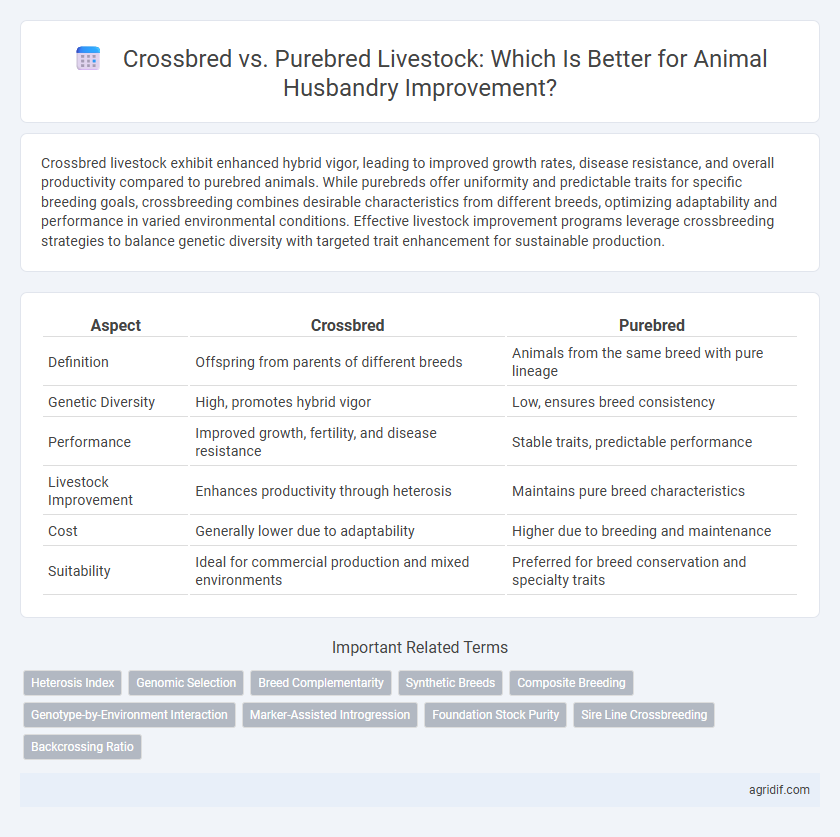
| Aspect | Crossbred | Purebred |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offspring from parents of different breeds | Animals from the same breed with pure lineage |
| Genetic Diversity | High, promotes hybrid vigor | Low, ensures breed consistency |
| Performance | Improved growth, fertility, and disease resistance | Stable traits, predictable performance |
| Livestock Improvement | Enhances productivity through heterosis | Maintains pure breed characteristics |
| Cost | Generally lower due to adaptability | Higher due to breeding and maintenance |
| Suitability | Ideal for commercial production and mixed environments | Preferred for breed conservation and specialty traits |
Introduction to Livestock Breeding Strategies
Crossbred livestock combine desirable traits from two or more breeds, enhancing hybrid vigor, disease resistance, and productivity compared to purebred animals. Purebred breeding maintains genetic consistency and allows for the preservation of specific breed characteristics important for specialized production. Selecting an optimal breeding strategy involves balancing genetic diversity, adaptation to local environments, and overall herd improvement goals in livestock management.
Defining Crossbred and Purebred Livestock
Crossbred livestock result from mating animals of two or more different breeds, combining desirable traits such as disease resistance, growth rate, and adaptability for enhanced productivity. Purebred livestock refer to animals bred within a single breed lineage, preserving specific genetic characteristics and breed standards for consistency in traits like appearance, temperament, and performance. Both breeding strategies play crucial roles in livestock improvement, with crossbreeding enhancing hybrid vigor and purebreeding maintaining breed purity and predictability.
Genetic Diversity: Crossbred vs Purebred
Crossbred livestock exhibit higher genetic diversity compared to purebred animals, leading to enhanced hybrid vigor and improved resilience against diseases. Purebred animals maintain uniformity in traits but often face increased risks of inbreeding depression and genetic disorders. Emphasizing crossbreeding strategies can optimize livestock improvement by balancing productivity and genetic health.
Production Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Crossbred livestock exhibit enhanced production efficiency by combining the superior traits of two or more breeds, resulting in higher growth rates, improved fertility, and greater disease resistance compared to purebreds. Performance comparison reveals that crossbreds often outperform purebreds in feed conversion ratios and adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, which directly impacts profitability. However, purebred animals maintain genetic consistency and predictable trait inheritance, making them essential for breeding programs aiming to preserve specific breed characteristics.
Disease Resistance: Which Type Prevails?
Crossbred livestock often exhibit enhanced disease resistance due to heterosis, which boosts immune system variability and resilience against pathogens. Purebred animals may possess specific genetic traits but typically have reduced genetic diversity, making them more susceptible to certain diseases. For sustainable livestock improvement, crossbreeding strategies are favored to enhance overall herd health and reduce morbidity rates.
Adaptability to Environmental Conditions
Crossbred livestock demonstrate superior adaptability to diverse environmental conditions compared to purebred animals, benefiting from hybrid vigor that enhances resistance to diseases and climatic stress. This adaptability leads to improved survival rates and productivity in regions with fluctuating temperatures, humidity, and feed availability. Farmers often prefer crossbreds to optimize livestock performance in challenging environments, ensuring sustainable production outcomes.
Economic Benefits: Cost and Profitability
Crossbred livestock often yield higher profitability due to improved growth rates, disease resistance, and feed efficiency compared to purebred animals, reducing overall production costs. While purebreds require higher initial investment and maintenance expenses, crossbreeding enhances economic returns by increasing output and lowering veterinary costs. Farmers adopting crossbreeding strategies benefit from better adaptability and market demand, resulting in enhanced cost-effectiveness and sustainable income growth.
Breeding Programs and Management Practices
Crossbred livestock often exhibit hybrid vigor, leading to improved growth rates, disease resistance, and reproductive efficiency compared to purebred animals, making them advantageous in breeding programs aimed at enhancing productivity. Breeding programs integrating crossbreeding strategies require tailored management practices, including precise nutrition plans and health monitoring, to maximize genetic potential and maintain genetic diversity. Purebred breeding focuses on preserving specific genetic traits, demanding rigorous selection criteria and controlled mating, while crossbred programs emphasize heterosis benefits through systematic breed combination and rotational mating systems.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Crossbred livestock often face challenges with genetic inconsistency, leading to unpredictable performance traits and potential health issues, whereas purebred animals may suffer from reduced genetic diversity, increasing susceptibility to hereditary diseases. Crossbreeding requires careful management and selection to maintain hybrid vigor, but improper breeding can result in loss of desired characteristics and adaptation problems. Purebreeding limits adaptability and can slow genetic progress due to inbreeding depression, posing significant constraints for livestock improvement programs.
Future Trends in Livestock Breeding
Crossbred livestock combines the desirable traits of different breeds, enhancing hybrid vigor and disease resistance, which accelerates productivity improvements compared to purebred animals. Future trends emphasize genomic selection and precision breeding technologies to optimize crossbreeding strategies, ensuring sustainable growth and better adaptability to climate change. Integration of CRISPR gene editing and big data analytics will further revolutionize livestock improvement by tailoring genetic profiles for enhanced yield and robustness.
Related Important Terms
Heterosis Index
Crossbred livestock exhibit a higher Heterosis Index compared to purebred animals, leading to enhanced traits such as growth rate, fertility, and disease resistance crucial for livestock improvement. This genetic advantage in crossbreeding accelerates productivity and sustainability in animal husbandry by maximizing hybrid vigor.
Genomic Selection
Crossbred livestock exhibit increased genetic diversity and heterosis, enhancing traits such as growth rate, disease resistance, and fertility, while purebred lines maintain genetic uniformity essential for predictable performance. Genomic selection accelerates improvement by identifying superior breeding candidates based on genome-wide markers, enabling precise enhancement of both crossbred and purebred livestock for optimal productivity and sustainability.
Breed Complementarity
Crossbred livestock combine traits from purebred parents to enhance breed complementarity, resulting in improved growth rates, disease resistance, and fertility compared to purebreds. Utilizing crossbreeding strategies optimizes genetic diversity and performance, maximizing productivity and sustainability in animal husbandry.
Synthetic Breeds
Synthetic breeds combine desirable traits from multiple purebred lines to enhance livestock productivity, adaptability, and disease resistance, outperforming purebreds in various environmental conditions. Crossbreeding strategies incorporated in synthetic breed development optimize heterosis effects, resulting in improved growth rates, fertility, and overall herd performance.
Composite Breeding
Composite breeding combines desirable traits from multiple purebred livestock to enhance productivity, disease resistance, and adaptability in diverse environments. Crossbred animals generated through this method often outperform purebreds by exhibiting hybrid vigor, resulting in higher growth rates, better feed efficiency, and improved reproductive performance.
Genotype-by-Environment Interaction
Crossbred livestock exhibit enhanced adaptability and performance across diverse environmental conditions due to favorable Genotype-by-Environment Interaction, leading to improved productivity and resilience compared to purebred animals. Purebreds often perform optimally in stable, controlled environments but may show reduced efficiency in variable or stress-prone settings, limiting genetic potential in heterogeneous farming systems.
Marker-Assisted Introgression
Marker-assisted introgression leverages molecular markers to precisely transfer desirable genes from purebred to crossbred livestock, enhancing traits such as disease resistance and productivity. This technique accelerates genetic improvement by enabling targeted breeding, maintaining hybrid vigor while incorporating superior alleles from purebred lines.
Foundation Stock Purity
Foundation stock purity ensures the genetic stability and desired traits in purebred livestock, maintaining breed standards crucial for consistent performance. Crossbred animals enhance hybrid vigor and adaptability, but relying heavily on crossbreeding can dilute foundation stock purity, potentially compromising long-term genetic improvement goals.
Sire Line Crossbreeding
Sire line crossbreeding enhances livestock improvement by combining superior genetic traits from purebred sires with diverse dam lines, resulting in offspring with improved growth rates, disease resistance, and overall productivity. This method optimizes heterosis while maintaining desirable breed characteristics, making it a strategic approach for sustainable animal husbandry.
Backcrossing Ratio
Backcrossing ratio plays a crucial role in livestock improvement by combining the desirable traits of purebred animals with the hybrid vigor of crossbreds, enhancing productivity and disease resistance. Optimizing backcrossing ratios helps achieve a balanced genetic makeup, maintaining breed purity while introducing superior performance characteristics.
Crossbred vs Purebred for livestock improvement Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com