Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors and improve welfare by allowing chickens to roam freely and engage in dust bathing, while also supporting better air quality through the decomposition of litter. Battery cages, although space-efficient and easier to manage, restrict movement and contribute to stress and health issues among chickens due to confinement. Choosing between deep litter and battery cage systems depends on balancing animal welfare with production efficiency and management capabilities.
Table of Comparison
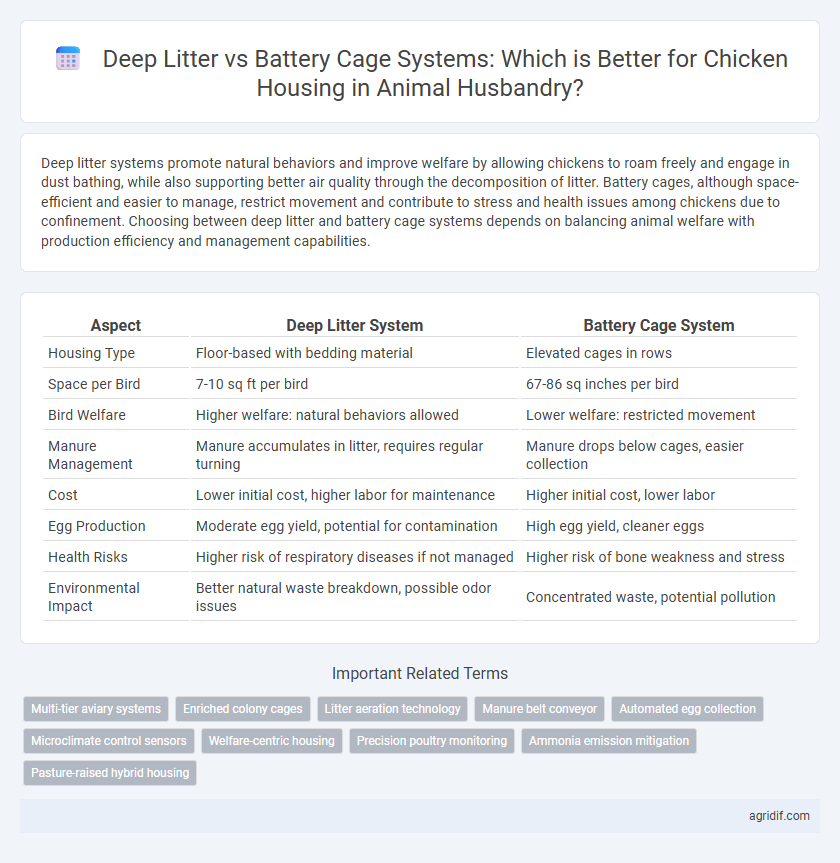
| Aspect | Deep Litter System | Battery Cage System |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Floor-based with bedding material | Elevated cages in rows |
| Space per Bird | 7-10 sq ft per bird | 67-86 sq inches per bird |
| Bird Welfare | Higher welfare: natural behaviors allowed | Lower welfare: restricted movement |
| Manure Management | Manure accumulates in litter, requires regular turning | Manure drops below cages, easier collection |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher labor for maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower labor |
| Egg Production | Moderate egg yield, potential for contamination | High egg yield, cleaner eggs |
| Health Risks | Higher risk of respiratory diseases if not managed | Higher risk of bone weakness and stress |
| Environmental Impact | Better natural waste breakdown, possible odor issues | Concentrated waste, potential pollution |
Introduction to Chicken Housing Systems
Chicken housing systems significantly influence poultry health, productivity, and welfare, with deep litter and battery cage being the two predominant methods. Deep litter systems use a layered floor covered with bedding materials like straw or wood shavings, promoting natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing. In contrast, battery cages confine chickens in individual wire cages, optimizing space and feed efficiency but often raising animal welfare concerns due to restricted movement.
Overview of Deep Litter System
The Deep Litter System for chicken housing involves spreading a thick bedding layer of materials such as wood shavings, straw, or sawdust on the floor, which absorbs moisture and manure while promoting natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing. This system supports better ventilation and microbial activity, improving litter decomposition and reducing ammonia emissions compared to battery cages. Deep litter offers a more humane and sustainable environment by enhancing bird welfare, reducing disease incidence, and lowering construction and maintenance costs.
Overview of Battery Cage System
The battery cage system in poultry farming involves housing chickens in rows of small, individual cages made of wire mesh, designed for space efficiency and ease of egg collection. This method allows for controlled feeding, waste management, and minimizes aggression among birds, leading to higher productivity per square meter. However, it raises animal welfare concerns due to restricted movement and limited natural behaviors.
Space Requirements: Deep Litter vs Battery Cage
Deep litter systems require significantly more space per chicken, typically around 1 to 1.5 square feet, allowing birds to move freely and exhibit natural behaviors. Battery cages confine chickens to much smaller areas, often less than 200 square inches per bird, prioritizing space efficiency but limiting movement. This difference impacts animal welfare, with deep litter supporting better physical health and natural activity compared to the restricted environment of battery cages.
Health and Welfare of Chickens
Deep litter systems promote better health and welfare for chickens by allowing natural behaviors like dust bathing and foraging, reducing stress and respiratory issues. Battery cages restrict movement, leading to osteoporosis, feather pecking, and increased susceptibility to disease due to overcrowding and poor air quality. Research from poultry welfare organizations indicates that deep litter housing significantly improves immune function and overall well-being compared to battery cage environments.
Feed and Water Management
Deep litter systems promote natural foraging behavior, which can reduce feed waste and improve nutrient absorption by allowing chickens to engage in scratching and pecking. Battery cages streamline feed and water delivery through automated systems, ensuring precise rationing and minimizing contamination but often limit birds' natural behaviors that may influence feed intake. Effective feed and water management in deep litter requires regular monitoring to prevent spoilage and maintain hygiene, while battery cage systems demand rigorous maintenance of equipment to sustain consistent feed and water quality.
Disease Control and Biosecurity
Deep litter systems promote natural chicken behaviors but require rigorous management to prevent buildup of pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli, increasing disease risk if litter becomes damp or soiled. Battery cages enable easier cleaning and reduce exposure to feces, lowering the incidence of diseases such as coccidiosis and avian influenza. Biosecurity measures in battery cages are generally more effective due to confined spaces, limiting contact with wild birds and pests that can transmit infections.
Egg Production and Quality Comparison
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors and reduce stress in chickens, leading to improved egg shell strength and overall egg quality compared to battery cages. Battery cages, while optimizing space and feed efficiency for higher egg production rates, often result in lower egg shell quality and increased prevalence of cracked eggs due to restricted movement. Studies indicate that eggs from deep litter systems have higher nutrient content and better consumer acceptance, balancing quantity with enhanced product quality.
Economic Considerations for Farmers
Deep litter systems reduce initial infrastructure costs and lower long-term expenses by minimizing waste disposal and providing natural insulation, resulting in economic efficiency for small to medium-scale farmers. Battery cage systems demand higher upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs but offer increased egg production per unit area, enhancing profitability in large-scale commercial operations. Farmers must weigh the balance between capital expenditure, labor requirements, and production output when selecting between deep litter and battery cage housing for optimal economic returns.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Deep litter systems reduce environmental pollution by promoting natural waste decomposition and enhancing soil fertility through nutrient recycling, while battery cages generate concentrated waste that requires costly management to prevent contamination. Deep litter housing supports sustainable poultry farming by minimizing ammonia emissions and enabling organic manure production, which improves farm ecology. Battery cages, although efficient in production, pose significant sustainability challenges due to high energy use and limited waste biodegradation.
Related Important Terms
Multi-tier aviary systems
Multi-tier aviary systems offer a dynamic alternative to deep litter and battery cage methods by maximizing vertical space, promoting natural behaviors such as perching and nesting for improved welfare. These systems enhance egg production efficiency and reduce environmental impact through better manure management and ventilation.
Enriched colony cages
Enriched colony cages offer improved welfare over traditional battery cages by providing more space, perches, and nesting areas, allowing chickens to express natural behaviors while maintaining efficient production. Compared to deep litter systems, enriched colony cages reduce exposure to pathogens and litter management issues, enhancing flock health and egg quality.
Litter aeration technology
Deep litter systems enhance poultry welfare by promoting natural behaviors and improving manure decomposition through advanced litter aeration technology, which maintains optimal oxygen levels and reduces ammonia buildup. In contrast, battery cages restrict movement and limit airflow, often leading to poor air quality and increased health risks for chickens.
Manure belt conveyor
Deep litter systems enhance manure management by allowing natural decomposition within bedding materials, reducing ammonia levels and improving bird welfare. Manure belt conveyor systems in battery cages efficiently remove waste, minimizing disease risk and labor but may compromise natural behaviors and increase stress in chickens.
Automated egg collection
Deep litter systems allow chickens to roam freely on bedding material, reducing labor costs and promoting natural behaviors, but often lack efficient automated egg collection mechanisms. Battery cage housing facilitates automated egg collection through conveyor belts and mechanized systems, increasing productivity and hygiene but may compromise animal welfare due to restricted movement.
Microclimate control sensors
Deep litter systems utilize microclimate control sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and ammonia levels, promoting a healthier environment by maintaining optimal conditions for chicken welfare. In contrast, battery cage systems rely on more limited sensor integration, often resulting in less effective air quality management and increased stress for the birds.
Welfare-centric housing
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, enhancing chicken welfare by providing a more enriching environment compared to battery cages. Battery cages restrict movement and prevent expression of innate behaviors, often leading to increased stress and health issues in poultry.
Precision poultry monitoring
Deep litter systems enable precision poultry monitoring through improved natural behaviors and environmental interactions, enhancing welfare and reducing stress indicators measurable by sensors. Battery cage systems offer controlled conditions but limit behavioral data, requiring advanced monitoring technology to detect health and productivity metrics accurately.
Ammonia emission mitigation
Deep litter systems reduce ammonia emissions by allowing better absorption and microbial breakdown of nitrogenous waste, whereas battery cages concentrate manure and increase ammonia volatilization due to limited ventilation. Implementing deep litter bedding with proper management practices significantly lowers airborne ammonia levels, improving air quality and poultry welfare in chicken housing.
Pasture-raised hybrid housing
Pasture-raised hybrid chickens benefit from deep litter systems that enhance natural behaviors, improve air quality through organic waste decomposition, and reduce stress compared to battery cages. Deep litter housing supports sustainable manure management and encourages foraging, crucial for optimal health and productivity in hybrid breeds raised on pasture.
Deep litter vs Battery cage for chicken housing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com