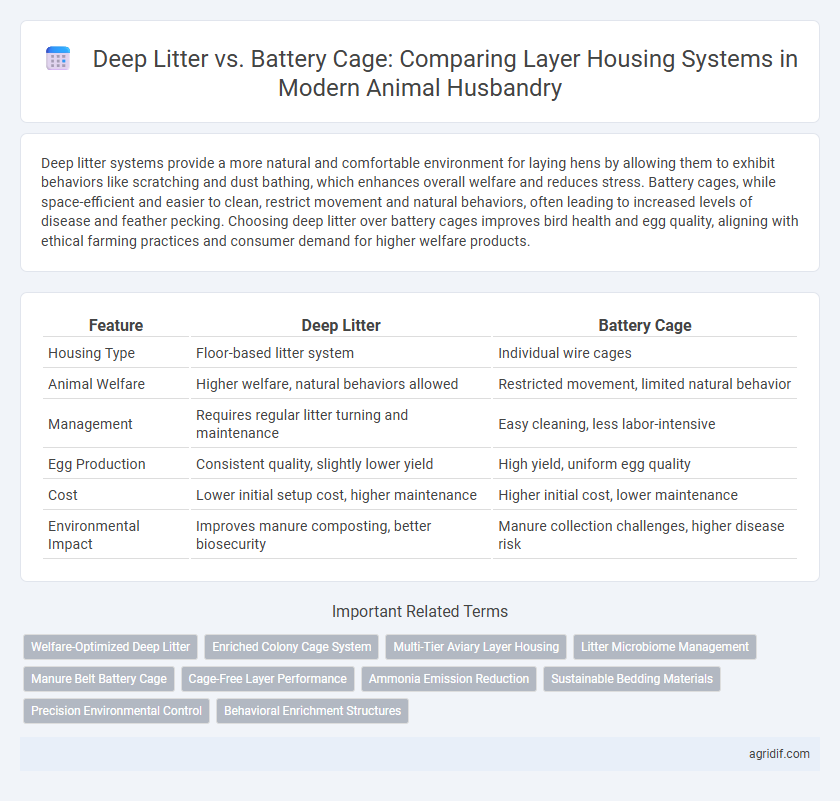
Deep litter systems provide a more natural and comfortable environment for laying hens by allowing them to exhibit behaviors like scratching and dust bathing, which enhances overall welfare and reduces stress. Battery cages, while space-efficient and easier to clean, restrict movement and natural behaviors, often leading to increased levels of disease and feather pecking. Choosing deep litter over battery cages improves bird health and egg quality, aligning with ethical farming practices and consumer demand for higher welfare products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Deep Litter | Battery Cage |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Floor-based litter system | Individual wire cages |
| Animal Welfare | Higher welfare, natural behaviors allowed | Restricted movement, limited natural behavior |
| Management | Requires regular litter turning and maintenance | Easy cleaning, less labor-intensive |
| Egg Production | Consistent quality, slightly lower yield | High yield, uniform egg quality |
| Cost | Lower initial setup cost, higher maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Improves manure composting, better biosecurity | Manure collection challenges, higher disease risk |
Introduction to Layer Housing Systems
Layer housing systems in animal husbandry encompass various methods like deep litter and battery cage systems to optimize egg production in poultry farming. Deep litter systems provide a more natural environment with bedding material that absorbs waste, promoting bird welfare and natural behaviors. Battery cages, conversely, maximize space efficiency and egg collection but often raise concerns about bird welfare due to restricted movement.
Overview of Deep Litter System
The deep litter system for layer housing involves maintaining a thick layer of absorbent bedding materials such as wood shavings or straw on the floor, which is regularly stirred to promote microbial decomposition of manure and reduce odor. This method enhances bird welfare by allowing natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing, improving air quality, and providing better insulation compared to conventional battery cages. Deep litter systems also contribute to sustainable waste management by converting manure into valuable compost, reducing environmental impact associated with intensive poultry farming.
Battery Cage System Explained
The battery cage system for layer housing involves housing hens in small, individual wire cages arranged in rows and tiers, maximizing space efficiency and facilitating egg collection. This method improves flock management and hygiene by reducing contact with droppings but raises concerns about animal welfare due to restricted movement and natural behavior expression. Despite criticism, battery cages remain widely used in commercial egg production for their cost-effectiveness and productivity benefits.
Space and Comfort for Laying Hens
Deep litter systems provide significantly more space per hen compared to battery cages, allowing natural behaviors such as scratching, dust bathing, and nesting. Enhanced comfort in deep litter housing reduces stress and promotes better health and egg production, while battery cages restrict movement leading to increased behavioral restrictions and potential welfare issues. Space allocation in deep litter setups typically ranges from 1 to 2 square feet per hen, far exceeding the 67 to 86 square inches provided in conventional battery cages.
Productivity and Egg Yield Comparisons
Deep litter systems enhance poultry welfare by allowing natural behaviors, leading to improved layer productivity and higher egg yield compared to battery cages. Battery cages, while space-efficient, often restrict movement and can increase stress, negatively impacting egg production rates and shell quality. Studies indicate that hens in deep litter housing consistently produce more eggs with better overall health metrics than those confined in battery cages.
Health and Disease Management
Deep litter systems promote healthier respiratory function and lower stress levels in layers by providing better ventilation and natural behavior expression, thereby reducing disease incidence. Battery cages often increase susceptibility to respiratory infections and foot lesions due to limited movement and poor air quality. Effective health and disease management requires balancing welfare benefits of deep litter with rigorous hygiene protocols.
Economic Considerations and Cost Analysis
Deep litter systems for layer housing often result in lower operational costs due to reduced equipment expenses and less frequent manure removal compared to battery cages. Battery cages require significant initial investment for cage installation and maintenance, alongside higher energy costs for ventilation and lighting. Economic analyses show deep litter promotes better welfare and productivity, potentially increasing profitability despite slightly higher labor inputs.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
Deep litter systems in layer housing promote better environmental sustainability by facilitating natural decomposition of manure, reducing ammonia emissions, and enhancing soil fertility through composted waste reuse. Battery cages generate concentrated waste that requires complex management to prevent groundwater contamination and high levels of ammonia, posing greater environmental risks. Effective waste management in deep litter setups supports a circular nutrient cycle, making it a more eco-friendly choice compared to conventional battery cage systems.
Animal Welfare and Ethical Perspectives
Deep litter housing for layer hens promotes natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, enhancing animal welfare compared to the restricted movement in battery cages. Battery cages, associated with stress and higher mortality rates, face ethical criticism for confining birds in small spaces with limited freedom. Emphasizing welfare, many countries are phasing out battery cages in favor of deep litter or free-range systems to meet ethical standards and consumer demand.
Choosing the Best Housing System for Layers
Deep litter systems promote improved welfare by allowing layers to express natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, reducing stress and associated health issues. Battery cages, while space-efficient and cost-effective, restrict movement and increase the risk of skeletal problems and feather pecking among hens. Optimal layer housing balances welfare, productivity, and management efficiency, often favoring deep litter or enriched cage systems to enhance egg quality and hen well-being.
Related Important Terms
Welfare-Optimized Deep Litter
Welfare-optimized deep litter systems for layer housing significantly enhance bird comfort and natural behaviors by providing ample space, substrate for dust bathing, and increased environmental enrichment compared to restrictive battery cages. This method reduces stress-related issues and improves overall health and egg quality by promoting better air quality, lower ammonia levels, and minimized skeletal disorders.
Enriched Colony Cage System
The Enriched Colony Cage System offers improved welfare by providing layers with perches, nesting areas, and more space compared to traditional battery cages, enhancing natural behaviors and productivity. This system balances biosecurity and management ease while promoting better bone strength and reduced stress, making it a viable alternative to deep litter and conventional cage methods.
Multi-Tier Aviary Layer Housing
Multi-tier aviary layer housing offers enhanced welfare by allowing hens to express natural behaviors like perching, nesting, and dust bathing, contrasting with the restrictive environment of battery cages. Deep litter systems combined with multi-tier aviaries improve manure management and air quality, promoting better health and productivity in layer hens.
Litter Microbiome Management
Effective litter microbiome management in deep litter systems enhances pathogen suppression and promotes beneficial microbial diversity, improving layer health and egg quality compared to battery cage housing. Battery cages limit microbial interaction, increasing disease susceptibility and reducing the natural microbial balance that supports immune function in layers.
Manure Belt Battery Cage
Manure belt battery cages in layer housing offer improved waste management by efficiently removing droppings via conveyor belts, significantly reducing ammonia levels and enhancing bird hygiene compared to deep litter systems. This system promotes better egg quality and bird health through consistent cleanliness and reduced pathogen exposure, making it a superior choice for sustainable poultry production.
Cage-Free Layer Performance
Cage-free layer performance in deep litter systems demonstrates improved hen welfare, higher natural behaviors, and increased egg quality compared to battery cage systems, which restrict movement and cause stress. Research indicates that deep litter housing enhances productivity and reduces mortality rates, aligning with consumer demand for ethically produced eggs.
Ammonia Emission Reduction
Deep litter systems in layer housing significantly reduce ammonia emissions by promoting microbial breakdown of manure within the bedding material, enhancing nitrogen retention and minimizing volatile ammonia release. In contrast, battery cages concentrate waste beneath the birds, leading to rapid ammonia volatilization and poorer air quality, negatively impacting both bird welfare and worker health.
Sustainable Bedding Materials
Sustainable bedding materials in deep litter systems for layer housing, such as rice hulls and wood shavings, improve moisture absorption and reduce ammonia emissions compared to battery cages, enhancing bird welfare and environmental impact. Battery cages lack sustainable bedding options, leading to poor waste management and increased ecological pollution in poultry farms.
Precision Environmental Control
Deep litter systems enable more precise environmental control by naturally regulating temperature and humidity through bedding materials and microbial activity, reducing the need for mechanical ventilation. Battery cages offer easier monitoring and control of individual bird environments but often require complex systems to manage heat, airflow, and waste removal effectively.
Behavioral Enrichment Structures
Deep litter systems provide hens with natural substrates that encourage foraging, dust bathing, and scratching behaviors, promoting improved welfare and reduced stress. Battery cages restrict movement, limiting behavioral enrichment opportunities and often resulting in increased stereotypic behaviors and poor physical condition.
Deep Litter vs Battery Cage for Layer Housing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com