Langstroth hives offer standardized, modular frames that simplify honey extraction and hive management, making them ideal for commercial beekeepers and beginners seeking efficiency. Top-bar hives provide a more natural environment for bees with horizontal bars and allow for less invasive inspections, appealing to hobbyists who prioritize bee health and sustainable practices. Choosing between Langstroth and Top-bar hives depends on goals such as ease of harvest, colony observation, and personal preference in apiculture methods.
Table of Comparison
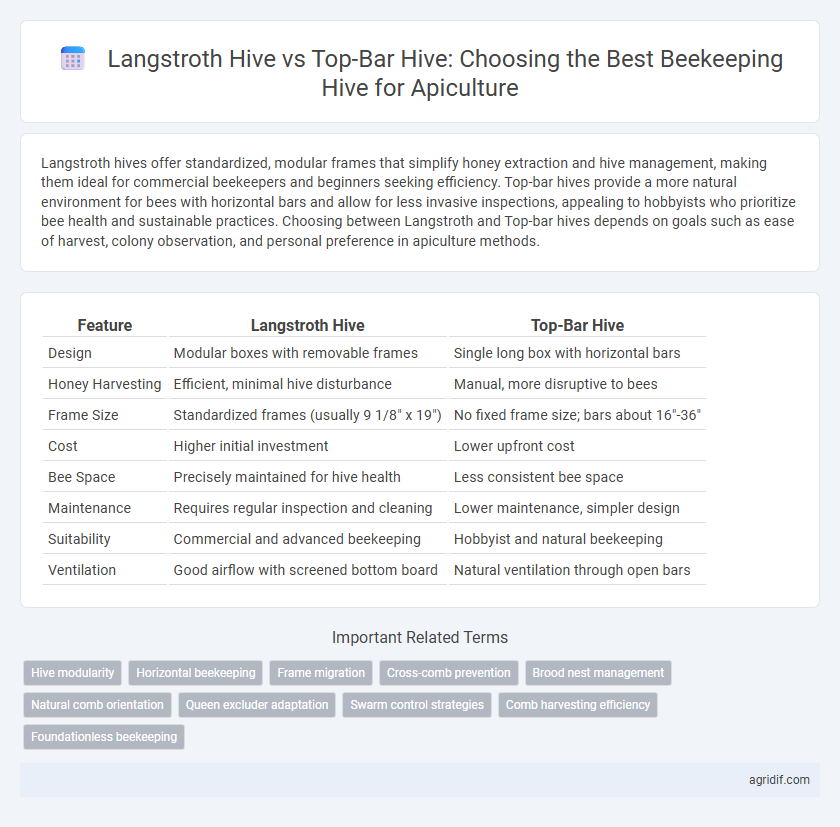
| Feature | Langstroth Hive | Top-Bar Hive |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Modular boxes with removable frames | Single long box with horizontal bars |
| Honey Harvesting | Efficient, minimal hive disturbance | Manual, more disruptive to bees |
| Frame Size | Standardized frames (usually 9 1/8" x 19") | No fixed frame size; bars about 16"-36" |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Bee Space | Precisely maintained for hive health | Less consistent bee space |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and cleaning | Lower maintenance, simpler design |
| Suitability | Commercial and advanced beekeeping | Hobbyist and natural beekeeping |
| Ventilation | Good airflow with screened bottom board | Natural ventilation through open bars |
Introduction to Beehive Types: Langstroth vs Top-bar
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked rectangular boxes with removable frames, optimizing honey production and ease of inspection for commercial beekeepers. Top-bar hives utilize horizontal bars across a single box, promoting natural comb construction and simplified management favored by hobbyists and small-scale apiculturists. Both hive types influence colony health, honey yield, and beekeeper intervention methods in diverse apiculture practices.
Structural Design Differences
The Langstroth hive features vertically stacked rectangular boxes with removable frames designed for optimal honeycomb management and efficient honey extraction. In contrast, the Top-bar hive consists of a single horizontal box with bars across the top, allowing bees to build natural comb without foundation, promoting a more natural colony behavior. Structural differences impact hive ventilation, accessibility, and maintenance, influencing beekeepers' choice based on management style and environmental conditions.
Hive Management and Handling
Langstroth hives offer modular frames that simplify hive management by allowing easy inspection and honey extraction without destroying the comb, enhancing efficiency in handling and disease control. Top-bar hives promote natural comb building and gentle handling, suitable for small-scale or hobbyist beekeepers who prioritize low-impact management and minimal equipment. The choice between Langstroth and Top-bar significantly impacts labor intensity, hive manipulation techniques, and overall colony health monitoring.
Honey Production and Harvesting
Langstroth hives maximize honey production through removable frames that allow efficient inspection and honey extraction without damaging the comb, leading to higher yields and less colony disruption. Top-bar hives promote natural comb building and are often preferred for sustainable beekeeping, but honey harvesting is more labor-intensive and yields tend to be lower compared to Langstroth models. Beekeepers prioritizing maximum honey output and ease of harvesting typically favor Langstroth hives, while those emphasizing natural bee behavior may choose top-bar hives despite the reduced honey volume.
Suitability for Beginners and Experienced Beekeepers
Langstroth hives, with their standardized frames and ease of inspection, are highly suitable for beginners seeking structured guidance and scalability in beekeeping. Top-bar hives appeal more to experienced beekeepers prioritizing natural hive behavior observation and sustainable practices through non-invasive honey harvesting. Skill levels influence hive choice, as Langstroth demands technical management while top-bar hives require advanced hands-on expertise.
Bee Health and Colony Strength
Langstroth hives offer superior ventilation and standardized frames that reduce stress and disease risk, promoting stronger colony health. Top-bar hives encourage natural comb building, which can enhance bee behavior but requires more management to prevent pests and structural weaknesses. Colony strength is often higher in Langstroth hives due to easier inspection and treatment, while top-bar hives support natural instincts that may improve resilience.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
The Langstroth hive generally incurs higher initial costs due to its standardized design and need for specialized equipment, making it a pricier option for commercial beekeepers. In contrast, the Top-bar hive offers greater affordability and accessibility for beginners and hobbyists, often constructed from locally available materials with minimal tools. Cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance make the Top-bar hive a practical choice in regions with limited resources or for small-scale apiculture ventures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Langstroth hives, with their standardized, removable frames, support sustainable beekeeping by facilitating hive inspections and disease management, reducing colony stress and promoting healthier bee populations. Top-bar hives, constructed from natural materials and requiring fewer man-made components, offer lower environmental impact through reduced resource use and simpler maintenance, aligning with eco-friendly beekeeping practices. Both hive types contribute to sustainability by supporting pollinator health but differ in material consumption and management intensity.
Seasonal Maintenance Requirements
Langstroth hives require regular seasonal inspections to manage brood chambers, replace honey supers, and check for pest infestations like Varroa mites, ensuring colony health and productivity. Top-bar hives demand consistent comb inspection and removal during warmer months to prevent comb damage and support colony expansion, with less need for heavy equipment manipulation. Effective seasonal maintenance in both hive types is crucial for optimal honey yield and bee welfare.
Choosing the Ideal Hive for Your Apiary
Langstroth hives offer standardized, removable frames that facilitate honey extraction and hive inspection, making them ideal for commercial beekeeping and maximizing honey yield. Top-bar hives promote natural comb building without frames, appealing to sustainable and hobbyist beekeepers interested in minimal intervention and bee health. Selecting the ideal hive depends on apiary goals, available space, and management preferences, with Langstroth suited for productivity and Top-bar favoring natural colony behavior.
Related Important Terms
Hive modularity
Langstroth hives offer superior modularity with standardized, stackable frames that allow easy expansion and hive management, enhancing honey production efficiency. In contrast, top-bar hives feature a simpler, single-box design with non-interchangeable bars, providing less modular flexibility but easier access for natural comb construction.
Horizontal beekeeping
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked frames promoting efficient honey extraction and colony inspection, while top-bar hives emphasize horizontal beekeeping with a single-level design that mimics natural bee comb building, enhancing colony health and reducing stress. The horizontal structure of top-bar hives allows for easier manipulation of combs and less disturbance to bees compared to the complex vertical arrangement of Langstroth systems.
Frame migration
Frame migration in Langstroth hives often leads to bees building burr comb between frames, causing reduced hive inspection efficiency and potential damage to brood patterns. Top-bar hives, with their single bars and movable comb, minimize frame migration, allowing natural comb construction and easier management of bee space.
Cross-comb prevention
Langstroth hives utilize removable frames that maintain consistent spacing, effectively preventing cross-comb formation and facilitating easier inspections. Top-bar hives, while more natural in design, require diligent spacing control by the beekeeper to minimize cross-comb development, which can complicate hive management.
Brood nest management
Langstroth hives provide structured brood nest management through standardized frames that allow easy inspection and manipulation of brood combs, promoting efficient colony health monitoring and disease control. In contrast, top-bar hives offer a more natural brood nest environment with horizontal comb growth, which can be less disruptive to the bees but requires more experience to effectively manage brood expansion and prevent hive overcrowding.
Natural comb orientation
The Langstroth hive uses removable frames that encourage bees to build uniform combs aligned with the vertical structure of the hive, promoting easier inspection and honey extraction. In contrast, the Top-bar hive allows bees to build natural combs oriented horizontally, closely mimicking wild bee behavior and reducing hive disturbance during management.
Queen excluder adaptation
The Langstroth hive, featuring removable frames and a queen excluder, allows beekeepers to restrict the queen's access to honey supers, preventing brood contamination and facilitating honey harvest. In contrast, the top-bar hive typically lacks a queen excluder, relying on natural nesting behavior, which may result in mixed brood and honey combs, complicating harvest and hive management.
Swarm control strategies
Langstroth hives facilitate swarm control through movable frames, allowing beekeepers to inspect and manipulate brood patterns to prevent congestion. Top-bar hives rely on less structured comb management, making proactive swarm prevention more dependent on frequent hive monitoring and manual intervention.
Comb harvesting efficiency
Langstroth hives offer superior comb harvesting efficiency due to their removable frames that allow easy extraction without destroying the comb, promoting rapid honey collection and hive maintenance. In contrast, top-bar hives require more manual comb cutting which can damage the comb and reduce harvesting speed, making them less efficient for high-volume honey production.
Foundationless beekeeping
Langstroth hives, widely used for their modular frames and ease of honey extraction, typically require foundation sheets to guide bees in comb building, whereas top-bar hives support foundationless beekeeping by allowing bees to naturally create comb on wooden bars. Foundationless top-bar hives promote natural bee behavior and increase colony health by reducing chemical exposure and structural constraints inherent in Langstroth systems.
Langstroth hive vs Top-bar hive for beekeeping Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com