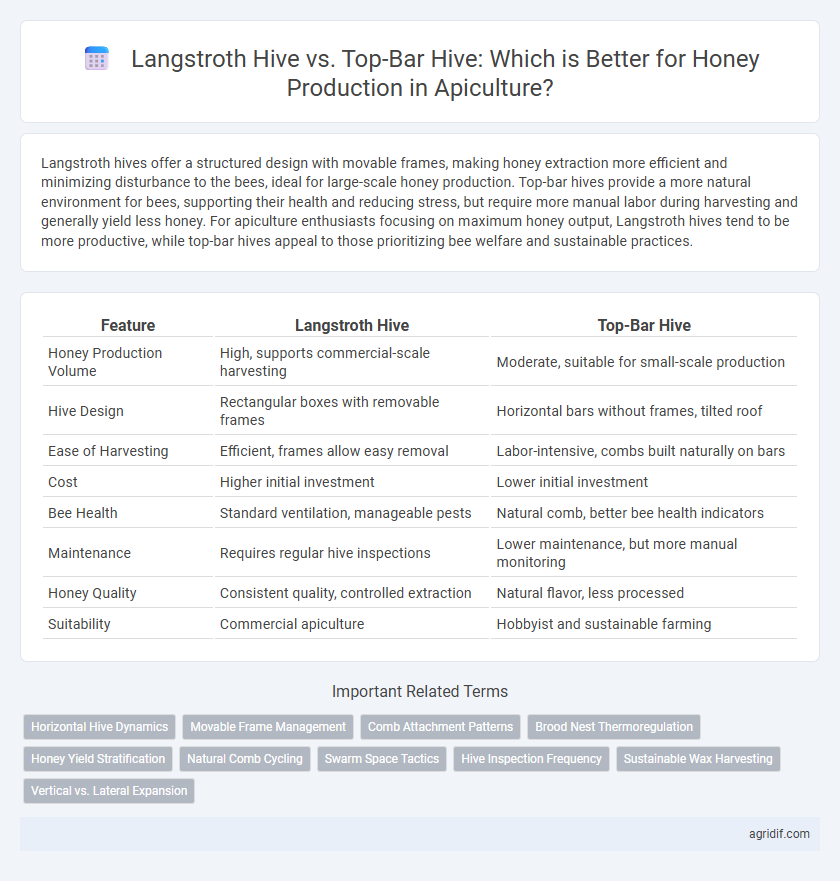
Langstroth hives offer a structured design with movable frames, making honey extraction more efficient and minimizing disturbance to the bees, ideal for large-scale honey production. Top-bar hives provide a more natural environment for bees, supporting their health and reducing stress, but require more manual labor during harvesting and generally yield less honey. For apiculture enthusiasts focusing on maximum honey output, Langstroth hives tend to be more productive, while top-bar hives appeal to those prioritizing bee welfare and sustainable practices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Langstroth Hive | Top-Bar Hive |
|---|---|---|
| Honey Production Volume | High, supports commercial-scale harvesting | Moderate, suitable for small-scale production |
| Hive Design | Rectangular boxes with removable frames | Horizontal bars without frames, tilted roof |
| Ease of Harvesting | Efficient, frames allow easy removal | Labor-intensive, combs built naturally on bars |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Bee Health | Standard ventilation, manageable pests | Natural comb, better bee health indicators |
| Maintenance | Requires regular hive inspections | Lower maintenance, but more manual monitoring |
| Honey Quality | Consistent quality, controlled extraction | Natural flavor, less processed |
| Suitability | Commercial apiculture | Hobbyist and sustainable farming |
Introduction to Hive Types in Apiculture
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked rectangular boxes with removable frames, allowing efficient honey extraction and hive inspections. Top-bar hives have horizontal bars where bees build natural combs, promoting a more natural environment but often yielding less honey. Both hive types support apiculture practices but differ in management style and productivity outcomes.
Design Overview: Langstroth vs Top-Bar Hives
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked removable frames designed for easy inspection and honey extraction, optimizing hive management and maximizing honey yield. Top-bar hives consist of horizontal bars without frames, promoting natural comb building which reduces equipment costs but may limit honey harvest efficiency. The Langstroth design supports mechanized honey production, while top-bar hives favor traditional, low-maintenance beekeeping methods.
Materials and Construction Differences
Langstroth hives are typically constructed from kiln-dried pine or cedar wood with standardized, rectangular boxes and removable frames designed for efficient honey extraction and hive inspection. Top-bar hives often use simpler materials like untreated wood or bamboo, featuring horizontal bars across a single long box, which encourages bees to build natural comb without frames but limits mechanized honey harvesting. The rigid frame design of Langstroth hives supports higher productivity and easier maintenance, whereas top-bar hives emphasize eco-friendliness and traditional beekeeping methods.
Honey Production Efficiency Comparison
Langstroth hives typically offer higher honey production efficiency due to their vertically stacked frames, enabling better colony expansion and easier honey extraction without destroying combs. Top-bar hives allow natural comb building but generally yield less honey per colony because of smaller storage capacity and manual harvesting techniques. The modular design of Langstroth hives supports systematic hive management and maximizes honey output, making them preferred for commercial-scale apiculture.
Ease of Hive Management
The Langstroth hive offers modular frames that simplify inspection and honey extraction, making hive management more efficient for beekeepers. In contrast, the Top-bar hive allows a natural comb-building process but requires more manual skill and experience to handle without damaging the combs. Beekeepers seeking ease of management often prefer Langstroth hives due to their standardized design and compatibility with commercial equipment.
Impact on Bee Health and Colony Strength
Langstroth hives promote strong bee health by offering removable frames that facilitate regular inspections and disease management, reducing stress on the colony. Top-bar hives encourage natural comb-building behavior, which may enhance colony strength but can complicate hive inspections and treatment. Optimal hive choice balances ease of management with supporting bee vitality and robust colony development.
Suitability for Small vs Large Scale Beekeeping
The Langstroth hive, with its modular design and standardized frame sizes, is highly suitable for large-scale beekeeping operations aiming for efficient honey production and ease of hive management. Top-bar hives, characterized by their simplicity and lower cost, are ideal for small-scale or hobbyist beekeepers who prioritize natural beekeeping methods and want less intensive hive management. Large-scale apiculture benefits from Langstroth's compatibility with mechanized extraction, whereas top-bar hives are preferred in sustainable and low-intervention environments.
Honey Harvesting Methods
Langstroth hives utilize removable frames that allow for efficient honey extraction with minimal disturbance to the colony, using centrifugal extractors to separate honey from the comb. Top-bar hives rely on manually cutting honeycombs from bars, which often results in comb destruction and lower honey yields but offers a more natural beekeeping approach. The Langstroth system's standardized frames and extraction technology generally provide higher honey production compared to the labor-intensive, comb-sacrificing methods of the Top-bar hive.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Langstroth hives typically require a higher initial investment due to standardized materials and modular design, while top-bar hives offer a lower-cost alternative with simpler construction. Maintenance of Langstroth hives involves regular inspection of removable frames and potential component replacement, whereas top-bar hives demand less frequent, though more manual, hive management with horizontal bars. Cost efficiency in honey production favors top-bar hives for small-scale or hobbyist beekeepers, whereas Langstroth hives suit commercial operations seeking scalability and streamlined maintenance.
Environmental Adaptability and Climate Resilience
Langstroth hives offer standardized, modular frames that facilitate hive inspection and honey extraction, making them widely adaptable across diverse environments but potentially less suited for extreme climates due to rigid structural design. Top-bar hives provide greater environmental adaptability through their horizontal structure, allowing better natural ventilation and temperature regulation, which enhances climate resilience in tropical and variable weather conditions. Beekeepers seeking optimal honey production under fluctuating environmental factors often prefer top-bar hives for their capacity to support bees' natural brood patterns and reduce stress from harsh climates.
Related Important Terms
Horizontal Hive Dynamics
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked frames promoting efficient honeycomb management and higher honey yield through enhanced airflow and brood inspection; in contrast, top-bar hives utilize horizontal bars allowing natural comb building with minimal disruption but may result in lower honey production and more manual labor. Horizontal hive dynamics in top-bar hives encourage natural bee behavior and provide better thermal regulation, while Langstroth's vertical design optimizes space and honey extraction efficiency for commercial apiculture.
Movable Frame Management
Langstroth hives feature removable frames that allow precise inspection and management of honeycomb, facilitating efficient pest control and honey extraction while preserving colony health. Top-bar hives use fixed bars without movable frames, limiting hive manipulation but promoting natural comb-building and reducing disturbance to the bees during honey harvests.
Comb Attachment Patterns
Langstroth hives utilize removable frames with standardized comb attachment patterns, allowing uniform, vertically oriented beeswax comb that simplifies honey extraction and hive inspection. Top-bar hives feature free-hanging combs attached to horizontal bars, promoting natural comb shapes but requiring careful handling during harvesting to avoid damage and maintain colony health.
Brood Nest Thermoregulation
Langstroth hives provide superior brood nest thermoregulation due to their standardized hive boxes and removable frames, which enable efficient airflow and temperature control essential for optimal bee development. In contrast, top-bar hives rely on bees' natural cluster positioning and hive shape, which may result in less consistent temperature maintenance during brood rearing.
Honey Yield Stratification
Langstroth hives typically produce higher honey yields due to their vertically stacked frames allowing for better hive management and expansion, optimizing space for honey storage. Top-bar hives, while promoting natural bee behavior with horizontal bars, often result in lower honey yield stratification as comb construction is less uniform and harder to manage for peak honey extraction.
Natural Comb Cycling
Langstroth hives promote structured honey production with removable frames, facilitating easier inspection and honey extraction, whereas Top-bar hives support natural comb cycling by allowing bees to build combs freely, enhancing colony health and resilience. Natural comb cycling in Top-bar hives reduces stress on bees during brood rearing and seasonal transitions, potentially increasing overall honey yield through improved colony vitality.
Swarm Space Tactics
Langstroth hives utilize movable frames that optimize swarm space control by allowing beekeepers to manage brood and honey storage areas precisely, reducing swarming tendencies and enhancing honey yield. In contrast, top-bar hives offer a more natural comb-building environment with less manipulation, relying on bee behavior and hive design to manage swarm space, which can lead to variable honey production outcomes.
Hive Inspection Frequency
Langstroth hives require more frequent inspections, typically every 7 to 10 days, to monitor frame health and prevent swarming, supporting consistent honey production. Top-bar hives allow for less intrusive inspections every 2 to 3 weeks, promoting natural colony behavior but potentially risking delayed issue detection.
Sustainable Wax Harvesting
Langstroth hives enable sustainable wax harvesting through removable frames that minimize comb damage, preserving hive structure and promoting colony health. Top-bar hives allow natural comb building, supporting organic wax production but may require more careful comb removal to maintain hive sustainability.
Vertical vs. Lateral Expansion
Langstroth hives support vertical expansion by allowing beekeepers to add multiple stacked supers, increasing honey production space efficiently and supporting large-scale honey harvesting. In contrast, top-bar hives expand laterally with a single horizontal box where bees build comb side-to-side, favoring natural comb growth but limiting scalability and total honey yield.
Langstroth hive vs Top-bar hive for honey production Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com