Effective Varroa mite control involves targeted use of miticides and regular hive inspections to prevent weakening of bee colonies, whereas Small hive beetle control relies more on maintaining hive cleanliness and deploying traps to reduce beetle populations. Integrating both strategies enhances overall pest management by addressing the unique life cycles and behaviors of these pests. Sustainable approaches focus on minimizing chemical use while promoting colony health through vigilant monitoring and timely interventions.
Table of Comparison
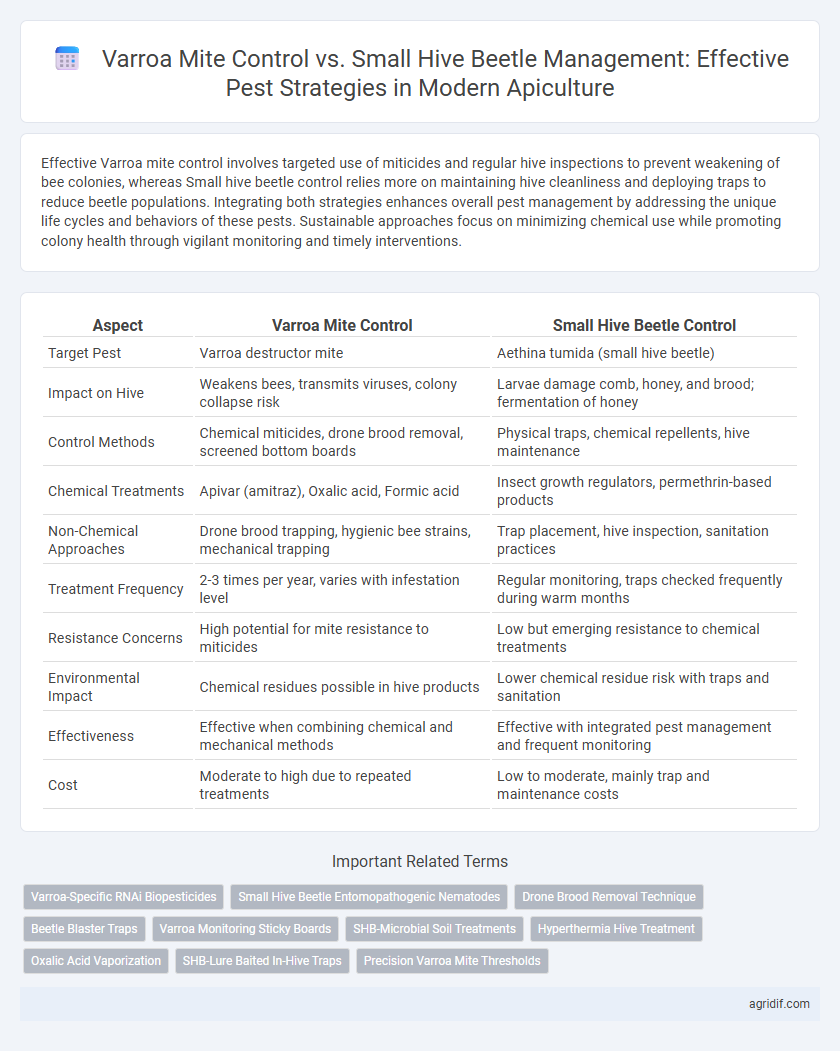
| Aspect | Varroa Mite Control | Small Hive Beetle Control |
|---|---|---|
| Target Pest | Varroa destructor mite | Aethina tumida (small hive beetle) |
| Impact on Hive | Weakens bees, transmits viruses, colony collapse risk | Larvae damage comb, honey, and brood; fermentation of honey |
| Control Methods | Chemical miticides, drone brood removal, screened bottom boards | Physical traps, chemical repellents, hive maintenance |
| Chemical Treatments | Apivar (amitraz), Oxalic acid, Formic acid | Insect growth regulators, permethrin-based products |
| Non-Chemical Approaches | Drone brood trapping, hygienic bee strains, mechanical trapping | Trap placement, hive inspection, sanitation practices |
| Treatment Frequency | 2-3 times per year, varies with infestation level | Regular monitoring, traps checked frequently during warm months |
| Resistance Concerns | High potential for mite resistance to miticides | Low but emerging resistance to chemical treatments |
| Environmental Impact | Chemical residues possible in hive products | Lower chemical residue risk with traps and sanitation |
| Effectiveness | Effective when combining chemical and mechanical methods | Effective with integrated pest management and frequent monitoring |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to repeated treatments | Low to moderate, mainly trap and maintenance costs |
Introduction to Key Pests: Varroa Mite and Small Hive Beetle
Varroa mites (Varroa destructor) and small hive beetles (Aethina tumida) rank among the most destructive pests affecting honey bee colonies worldwide. Varroa mites feed on bee hemolymph, weakening individual bees and transmitting viral pathogens, while small hive beetles damage comb, stored honey, and pollen through larval tunneling, causing fermentation and hive collapse. Effective pest management strategies require targeted control measures, including miticides for Varroa and traps or bio-control agents for small hive beetles, to maintain colony health and productivity.
Life Cycles: Varroa Mite vs Small Hive Beetle
Varroa mites complete their reproductive cycle within honey bee brood cells, where females enter and lay eggs on developing larvae, leading to rapid population growth synchronized with bee brood availability. Small hive beetles have a more complex life cycle involving adult beetles that infiltrate hives to lay eggs, with larvae developing in brood comb or stored honey before pupating in soil outside the hive, enabling multiple generations per year depending on environmental conditions. Effective pest management requires understanding Varroa's close brood-dependent reproduction versus Small hive beetle's soil pupation stage for targeted interventions.
Damage to Hives: Comparative Impact on Bee Colonies
Varroa mite infestations critically weaken bee colonies by feeding on bee hemolymph, transmitting viral pathogens, and causing brood mortality, leading to significant hive population declines and impaired immunity. Small hive beetles primarily damage hives by contaminating honey, causing fermentation, and structural damage through tunneling, which disrupts brood development and hive hygiene but generally results in less direct bee mortality compared to Varroa mites. Effective pest management necessitates targeting Varroa mites due to their profound impact on colony health and productivity, while controlling small hive beetles remains essential to preserve hive integrity and prevent resource loss.
Early Detection Methods for Each Pest
Varroa mite early detection relies on methods such as sugar shake, alcohol wash, and sticky boards to accurately assess mite infestation levels in bee colonies. Small hive beetle early detection involves the use of beetle traps, visual inspections for larvae and adult beetles, and monitoring hive cleanliness to identify infestations. Effective pest management hinges on timely identification through these species-specific detection techniques to minimize colony damage.
Varroa Mite Control Strategies
Varroa mite control strategies in apiculture primarily involve integrated pest management techniques such as chemical treatments with miticides like amitraz and oxalic acid, along with mechanical methods including drone brood removal and screen bottom boards to disrupt mite reproduction. Effective monitoring tools like the sugar shake and alcohol wash enable timely detection and assessment of Varroa infestation levels, guiding precise treatment applications. In contrast to small hive beetle control, which emphasizes physical traps and hive sanitation, Varroa mite management requires targeted interventions to preserve bee colony health and minimize resistance development.
Small Hive Beetle Management Techniques
Small hive beetle management focuses on integrated pest control techniques including maintaining colony strength, using beetle traps, and applying approved chemical treatments such as permethrin-based insecticides. Cultural practices like reducing hive debris, regular hive inspections, and eliminating beetle breeding sites significantly reduce infestations. These methods contrast with Varroa mite control, which primarily relies on miticides and biotechnical controls targeting mite populations specifically.
Chemical Control: Efficacy and Risks
Chemical control of Varroa mites primarily involves the use of miticides such as amitraz, fluvalinate, and coumaphos, which demonstrate high efficacy but pose risks of resistance development and honeybee toxicity. In contrast, chemical treatments for Small hive beetle management often include insecticides like permethrin and fipronil, which effectively reduce beetle populations but carry concerns about contaminating hive products and harming beneficial insects. Balancing efficacy and minimizing chemical residues remains critical for sustainable pest management in apiculture.
Biological and Cultural Control Approaches
Biological control of Varroa mites often involves the use of predatory mites or entomopathogenic fungi that specifically target Varroa populations without harming honey bees, while small hive beetle control benefits from nematodes and beneficial beetle predators that disrupt their life cycle. Cultural control strategies for Varroa include drone brood removal and brood interruption techniques to reduce mite reproduction, whereas small hive beetle management emphasizes maintaining strong, populous colonies alongside hive sanitation and traps to prevent beetle infestation. Both pest management approaches integrate these biological and cultural methods to sustainably reduce pest populations and enhance colony health.
Integrated Pest Management for Sustainable Beekeeping
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for sustainable beekeeping prioritizes targeted strategies for controlling Varroa mites and Small hive beetles to maintain colony health. Techniques include biological controls such as predatory beetle larvae management, mechanical traps for beetles, and chemical treatments like miticides carefully applied to minimize resistance and residue. Monitoring pest populations through regular hive inspections and adopting cultural practices like hive sanitation and genetic selection for resistant bees optimize pest suppression while supporting long-term apiary sustainability.
Future Trends in Apiculture Pest Control
Emerging trends in apiculture pest control emphasize integrated pest management strategies combining biological controls, such as predatory beetles or entomopathogenic fungi, with targeted chemical treatments to combat Varroa destructor and Aethina tumida infestations. Advances in genetic technologies, including selective breeding for mite-resistant honeybee strains and CRISPR-based gene drives, offer promising avenues for sustainable Varroa mite suppression. Digital monitoring tools employing AI and IoT sensors enable precise hive health tracking, facilitating early detection and localized treatment of both Varroa mites and small hive beetles, enhancing colony resilience and productivity.
Related Important Terms
Varroa-Specific RNAi Biopesticides
Varroa-specific RNAi biopesticides target the Varroa destructor mite by silencing essential genes, offering a highly precise and environmentally safe pest management strategy compared to conventional treatments used for small hive beetle control. This RNA interference approach reduces Varroa populations without harming honey bees or beneficial microbes, addressing resistance issues common in chemical miticides and improving overall colony health in apiculture.
Small Hive Beetle Entomopathogenic Nematodes
Entomopathogenic nematodes offer a targeted biological control method against Small Hive Beetles by penetrating and killing larvae in the soil, reducing hive infestation without harming bees. Unlike Varroa mite control, which often relies on chemical miticides, nematodes provide an eco-friendly alternative that disrupts Small Hive Beetle populations in apiary environments.
Drone Brood Removal Technique
Drone brood removal technique targets Varroa mite control by exploiting mites' preference for drone cells, significantly reducing mite populations without chemicals. This method is less effective against Small hive beetle control, which requires different strategies like traps and hive sanitation to manage beetle infestations.
Beetle Blaster Traps
Varroa mite control primarily involves miticides and integrated pest management strategies, whereas Small hive beetle control benefits significantly from Beetle Blaster Traps, which effectively lure and eliminate beetles using attractants like fruit oil and pheromones. These traps minimize beetle infestations without chemical residue risks, promoting healthier hive environments and improved colony productivity.
Varroa Monitoring Sticky Boards
Varroa mite control relies heavily on precise Varroa monitoring sticky boards, which effectively capture fallen mites to assess infestation levels and inform targeted treatment decisions. Unlike small hive beetle control, which may require bait traps and hive sanitation, Varroa monitoring boards provide quantifiable data critical for optimizing acaricide application and maintaining colony health.
SHB-Microbial Soil Treatments
Varroa mite control primarily relies on acaricides and integrated pest management techniques targeting mite reproduction within bee colonies, whereas Small hive beetle (SHB) control benefits significantly from microbial soil treatments that disrupt SHB pupation in the soil environment. Utilizing entomopathogenic fungi and bacteria specifically tailored to degrade SHB larvae in the soil enhances pest management by reducing SHB populations without harming honeybee colonies.
Hyperthermia Hive Treatment
Hyperthermia hive treatment effectively targets Varroa mite infestations by exposing hives to controlled high temperatures that disrupt mite reproduction without harming bees; however, this method is less effective against Small hive beetle larvae which require different environmental conditions for control. Combining hyperthermia with integrated pest management strategies, such as beetle traps and hive sanitation, optimizes overall colony health by addressing the distinct biological vulnerabilities of Varroa mites and Small hive beetles.
Oxalic Acid Vaporization
Oxalic acid vaporization effectively targets Varroa mite infestations by disrupting their reproductive cycle within capped brood, offering a highly efficient control method compared to treatments for small hive beetles, which typically require bait traps and soil interventions. While oxalic acid shows minimal efficacy against Small hive Beetle larvae and adults, its rapid mite mortality rate and low residue profile make it a preferred choice for integrated Varroa mite pest management in apiculture.
SHB-Lure Baited In-Hive Traps
SHB-Lure baited in-hive traps target Small Hive Beetle infestation by attracting and capturing adult beetles, reducing colony stress and preventing larval buildup that damages comb and honey. Varroa mite control requires integrated strategies such as miticides and drone brood removal, as SHB traps specifically do not affect Varroa populations, highlighting the need for combined pest management approaches in apiculture.
Precision Varroa Mite Thresholds
Precision Varroa mite thresholds enable beekeepers to implement targeted treatments that minimize colony stress and reduce chemical resistance, contrasting with Small hive beetle control which relies more on physical traps and hive management strategies. Utilizing calibrated mite infestation levels, apiarists optimize intervention timing for Varroa destructor, enhancing colony health and honey production efficiency compared to the generalized approaches used for Aethina tumida containment.
Varroa mite control vs Small hive beetle control for pest management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com