Certified disease-free seed ensures higher germination rates and reduces the risk of crop diseases, leading to improved overall yield and crop quality. Saved farm seed, while cost-effective, often carries a higher risk of seed-borne pathogens and genetic degradation, which can compromise plant health and productivity over time. Choosing certified seed enhances crop resilience and supports sustainable agricultural practices by maintaining seed purity and vigor.
Table of Comparison
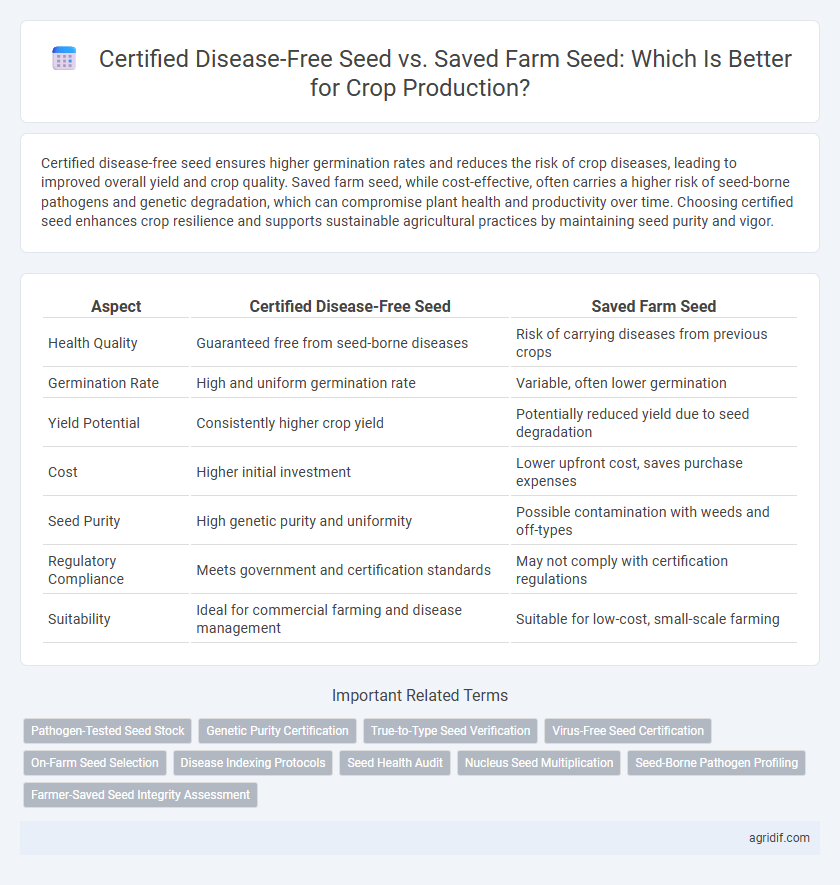
| Aspect | Certified Disease-Free Seed | Saved Farm Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Health Quality | Guaranteed free from seed-borne diseases | Risk of carrying diseases from previous crops |
| Germination Rate | High and uniform germination rate | Variable, often lower germination |
| Yield Potential | Consistently higher crop yield | Potentially reduced yield due to seed degradation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost, saves purchase expenses |
| Seed Purity | High genetic purity and uniformity | Possible contamination with weeds and off-types |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets government and certification standards | May not comply with certification regulations |
| Suitability | Ideal for commercial farming and disease management | Suitable for low-cost, small-scale farming |
Understanding Certified Disease-Free Seed
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure it is free from pathogens, significantly reducing the risk of crop diseases and improving yield quality. This seed type is produced under strict regulatory standards that guarantee genetic purity and health, offering farmers reliable planting material compared to saved farm seed, which may carry diseases or genetic variability. Utilizing certified disease-free seed enhances crop resilience, promotes sustainable production, and minimizes losses caused by seed-borne diseases.
Characteristics of Saved Farm Seed
Saved farm seed often exhibits greater genetic variability compared to certified disease-free seed, which can lead to inconsistent crop performance. This seed type may carry latent diseases or pests, increasing the risk of crop loss and reduced yield quality. Farmers frequently save seed to reduce input costs, but this practice requires careful selection and management to maintain seed viability and health.
Seed Purity and Genetic Integrity
Certified disease-free seed ensures higher seed purity and maintains genetic integrity by undergoing rigorous testing and strict quality control protocols, reducing the risk of pathogen transmission. Saved farm seed often has lower purity due to potential contamination and genetic drift caused by repeated use without proper selection and certification processes. Using certified seed enhances crop uniformity, yield stability, and resistance traits, which are critical for sustainable crop production.
Disease Risk: Certified vs. Saved Seed
Certified disease-free seed significantly reduces the risk of introducing pathogens compared to saved farm seed, which often carries latent infections from previous crops. The use of certified seed ensures higher germination rates and healthier plants due to rigorous testing and treatments that eliminate seed-borne diseases. Relying on saved seed increases the likelihood of disease buildup in the field, potentially leading to lower yields and increased need for chemical control measures.
Yield Potential Comparison
Certified disease-free seed often results in higher yield potential compared to saved farm seed due to its guaranteed genetic purity and absence of pathogens that can reduce crop vigor. Studies indicate crops grown from certified seed can produce up to 20-30% more yield than those from saved seeds, which may carry accumulated diseases and inferior genetic traits. Using certified seed enhances uniformity and crop health, directly improving overall productivity and farm profitability.
Economic Considerations and Cost Analysis
Certified disease-free seed ensures higher yield potential and reduces crop loss due to disease, justifying its higher initial cost through increased economic returns. Saved farm seed, while lower in upfront expense, risks diminished germination rates and potential disease transmission, which can lead to greater long-term costs and reduced profitability. Investment in certified seeds enhances crop quality and market value, outweighing the short-term savings associated with saved seed use.
Crop Uniformity and Quality
Certified disease-free seed ensures superior crop uniformity and quality due to rigorous testing and hygiene standards that eliminate pathogens. Saved farm seed often carries a higher risk of disease, leading to inconsistent germination rates and variable plant vigor, which compromises overall crop performance. Using certified seed promotes reliable yields and market-grade produce by maintaining genetic purity and health.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Certified disease-free seed complies with stringent regulatory standards ensuring high-quality, pathogen-free planting material that meets national and international agricultural requirements. Saved farm seed often lacks formal inspection and certification, posing risks of disease transmission and inconsistent crop performance due to limited compliance with regulatory frameworks. Adoption of certified seed supports adherence to plant health regulations, enhances crop yield reliability, and mitigates the spread of seed-borne diseases.
Impact on Pest and Disease Management
Certified disease-free seed significantly reduces the incidence of pests and diseases by providing clean, pathogen-free planting material that enhances crop health and yield. Saved farm seed often carries latent infections and pest infestations from previous seasons, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks and pest infestations. Using certified seed supports integrated pest management strategies by minimizing initial pathogen load and reducing reliance on chemical controls.
Long-Term Sustainability and Farm Productivity
Certified disease-free seed ensures higher germination rates and reduces disease incidence, directly enhancing long-term farm productivity and crop yield consistency. Saved farm seed may carry pathogens or low vigor due to repeated planting cycles, potentially diminishing sustainability by increasing vulnerability to crop failure. Investing in certified seed supports stable production systems, promotes soil health, and secures farmer income over multiple growing seasons.
Related Important Terms
Pathogen-Tested Seed Stock
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous pathogen testing to ensure the absence of viruses, fungi, and bacteria, significantly reducing disease incidence and improving crop yield compared to saved farm seed. Pathogen-tested seed stock is crucial for sustainable crop production, enhancing seed quality and crop health by minimizing the risk of seed-borne infections that can persist in saved farm seed.
Genetic Purity Certification
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous testing to ensure genetic purity and freedom from pathogens, enhancing crop uniformity and yield potential. In contrast, saved farm seed lacks formal genetic purity certification, increasing the risk of genetic drift and seed-borne diseases that can reduce crop performance and quality.
True-to-Type Seed Verification
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous testing and verification to ensure true-to-type genetic purity, minimizing the risk of disease transmission and enhancing crop uniformity. In contrast, saved farm seed often lacks formal true-to-type seed verification, increasing variability and potential contamination that can compromise yield quality and crop performance.
Virus-Free Seed Certification
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous virus-free seed certification processes to ensure high germination rates and minimize viral pathogen transmission, enhancing crop yield and quality. In contrast, saved farm seed often carries a higher risk of virus contamination, reducing plant vigor, increasing disease susceptibility, and potentially leading to significant economic losses.
On-Farm Seed Selection
Certified disease-free seed ensures higher germination rates and reduces the risk of disease transmission, significantly improving crop yield and quality compared to saved farm seed. On-farm seed selection requires rigorous inspection and knowledge of seed health to minimize pathogen presence, though it may carry more risk of contamination and lower uniformity than certified seeds.
Disease Indexing Protocols
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous disease indexing protocols, including laboratory testing and field inspections, ensuring minimal pathogen presence and higher crop yield potential. Saved farm seed lacks standardized disease indexing procedures, increasing the risk of pathogen carryover, reduced seed quality, and potential crop losses.
Seed Health Audit
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous Seed Health Audits ensuring minimal pathogen presence and higher germination rates, significantly reducing crop losses and promoting uniform growth. Saved farm seed, while cost-effective, often lacks systematic health assessments, increasing risks of disease transmission and variable crop performance.
Nucleus Seed Multiplication
Certified disease-free seed ensures higher germination rates and reduced pathogen risks, crucial for Nucleus Seed Multiplication in maintaining genetic purity and enhancing crop yields. In contrast, saved farm seed often carries accumulated diseases and genetic drift, compromising seed quality and production efficiency in subsequent planting cycles.
Seed-Borne Pathogen Profiling
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous pathogen profiling using advanced molecular diagnostics to ensure the absence of seed-borne pathogens, significantly reducing the risk of disease transmission in crop production. In contrast, saved farm seed lacks comprehensive pathogen testing, often harboring latent infections that compromise seed health and yield potential.
Farmer-Saved Seed Integrity Assessment
Certified disease-free seed undergoes rigorous laboratory testing and field inspections to ensure high germination rates and minimal pathogen presence, significantly reducing crop losses and improving yield quality. Farmer-saved seed often lacks formal quality assessments, increasing risks of disease transmission and genetic degradation, making regular Farmer-Saved Seed Integrity Assessment crucial for sustainable crop production.
Certified disease-free seed vs Saved farm seed for planting material Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com