Certified seed ensures higher yield consistency due to rigorous quality control, genetic purity, and disease-free standards maintained during production. In contrast, saved seed often shows variability in germination rates and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases, leading to unpredictable crop performance. Farmers relying on certified seeds benefit from uniform crop stands and optimized yield potential, enhancing overall farm productivity.
Table of Comparison
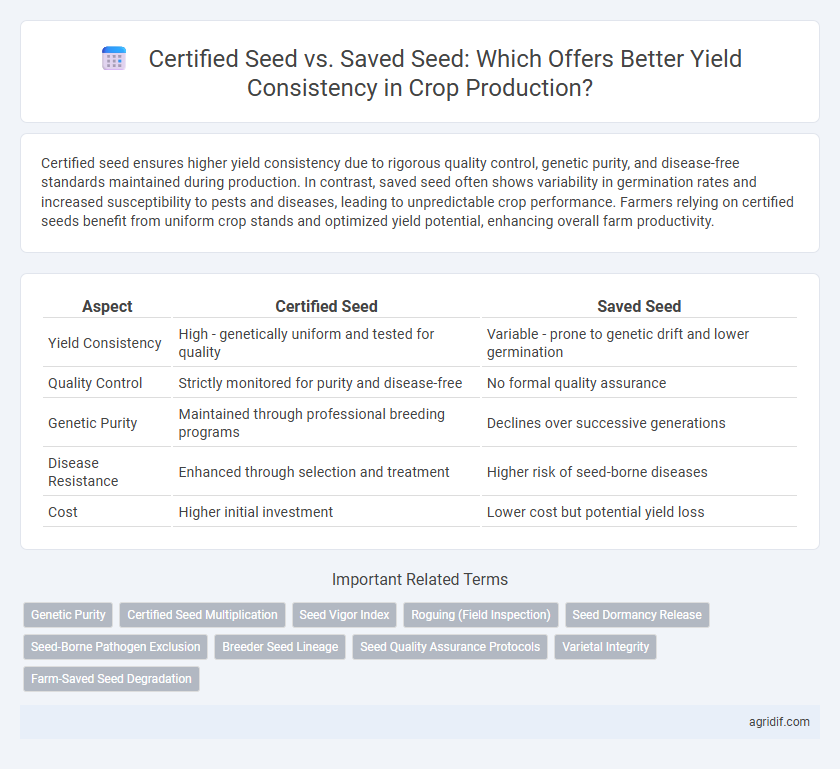
| Aspect | Certified Seed | Saved Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Consistency | High - genetically uniform and tested for quality | Variable - prone to genetic drift and lower germination |
| Quality Control | Strictly monitored for purity and disease-free | No formal quality assurance |
| Genetic Purity | Maintained through professional breeding programs | Declines over successive generations |
| Disease Resistance | Enhanced through selection and treatment | Higher risk of seed-borne diseases |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost but potential yield loss |
Introduction to Certified Seed and Saved Seed
Certified seed undergoes rigorous quality control, including genetic purity and germination testing, ensuring consistent crop yield and uniformity. Saved seed, harvested from previous crops without formal certification, carries higher risks of genetic drift and reduced vigor, which can lead to yield variability. Farmers prioritizing yield consistency often prefer certified seed for its proven reliability and enhanced disease resistance.
Defining Yield Consistency in Crop Production
Yield consistency in crop production refers to the ability of seeds to produce stable and reliable crop outputs across different growing seasons and environmental conditions. Certified seed, which undergoes rigorous quality control and genetic purity testing, ensures uniform germination rates and disease resistance, leading to more predictable yields. In contrast, saved seed often presents variability in genetic traits and vigor, resulting in inconsistent crop performance and lower overall yield stability.
Genetic Purity: Certified vs Saved Seed
Certified seed guarantees high genetic purity through rigorous selection and testing processes, ensuring uniform crop growth and optimal yield consistency. In contrast, saved seed often suffers from genetic drift and contamination, leading to variable plant performance and reduced overall productivity. Maintaining genetic purity in certified seed directly supports enhanced yield stability and crop quality.
Seed Health and Disease Control
Certified seed undergoes rigorous testing to ensure high seed health standards and minimize disease presence, leading to more consistent crop yields. Saved seed is more prone to carry pathogens and genetic variability, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks and yield fluctuations. Utilizing certified seed enhances disease control measures and promotes uniform plant development across the field.
Impact on Crop Uniformity
Certified seed ensures higher crop uniformity by meeting strict quality standards and genetic purity, leading to consistent plant growth and development. Saved seed often results in variable crop uniformity due to genetic drift, pest infestation, and disease accumulation over multiple planting cycles. Uniformity in crops directly influences yield stability, as homogeneous plants respond similarly to inputs and environmental conditions.
Yield Potential: Evidence from Field Trials
Certified seed demonstrates significantly higher yield potential compared to saved seed, as evidenced by multiple field trials showing consistent performance across diverse environmental conditions. The genetic purity and rigorous quality control in certified seed result in improved germination rates, uniformity, and disease resistance, directly contributing to enhanced crop yields. Conversely, saved seed often exhibits genetic drift and contamination, leading to yield variability and reduced overall productivity.
Economic Considerations: Cost vs Return
Certified seed generally incurs higher upfront costs but delivers greater yield consistency and disease resistance, resulting in improved economic returns for farmers. Saved seed, while cheaper initially, often leads to variable yields and increased risks of pest and disease exposure, which can reduce overall profitability. Investing in certified seed optimizes long-term economic gains by enhancing crop quality and minimizing production risks.
Regulatory and Quality Assurance Factors
Certified seed undergoes rigorous regulatory inspection and quality assurance protocols to ensure genetic purity, disease-free status, and uniform germination rates, directly contributing to yield consistency. In contrast, saved seed often lacks standardized testing and may harbor seed-borne diseases or genetic variability, increasing the risk of inconsistent crop performance. Regulatory frameworks mandate certified seed labeling and traceability, providing farmers with reliable quality assurance that supports stable and predictable yields.
Farmer Experiences and Case Studies
Farmers using certified seed report up to 20% higher yield consistency compared to saved seed across multiple case studies in maize and wheat production. Certified seed ensures genetic purity and disease resistance, reducing yield variability and improving crop uniformity. Field trials in diverse agro-climatic zones demonstrate that certified seed significantly enhances farm profitability through stable performance and reduced input costs.
Recommendations for Maximizing Yield Consistency
Utilize certified seed to ensure genetic purity, disease resistance, and improved germination rates, leading to more consistent and higher crop yields. Avoid using saved seed repeatedly, as it may degrade in quality due to pest accumulation, seed-borne diseases, and genetic drift. Regularly purchasing certified seeds combined with proper field management practices maximizes yield consistency and enhances overall crop production efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Genetic Purity
Certified seed ensures high genetic purity by undergoing rigorous quality control measures, leading to consistent yield performance in crop production. In contrast, saved seed often experiences genetic drift and contamination, resulting in variable yields and reduced reliability.
Certified Seed Multiplication
Certified seed multiplication ensures higher yield consistency by maintaining genetic purity, rigorous quality checks, and minimizing disease incidence compared to saved seed. This systematic process boosts crop productivity and farmer income through reliable seed performance and uniform crop stands.
Seed Vigor Index
Certified seed demonstrates a higher Seed Vigor Index compared to saved seed, directly contributing to improved yield consistency and crop uniformity. This enhanced vigor ensures stronger seedling emergence and better resilience against environmental stresses, optimizing overall production outcomes.
Roguing (Field Inspection)
Certified seed undergoes rigorous roguing during field inspections to eliminate off-type plants and ensure genetic purity, resulting in higher yield consistency compared to saved seed. Saved seed often carries mixed genetics and higher disease presence due to lack of systematic roguing, leading to variable crop performance and reduced uniformity in production.
Seed Dormancy Release
Certified seed ensures uniform seed dormancy release due to controlled conditioning processes, leading to consistent germination rates and higher yield stability compared to saved seed. Saved seed often exhibits irregular dormancy patterns caused by environmental stress during seed development, resulting in uneven crop emergence and variable production outcomes.
Seed-Borne Pathogen Exclusion
Certified seeds undergo rigorous testing and treatment processes that effectively exclude seed-borne pathogens, ensuring higher yield consistency and reducing crop losses compared to saved seeds. Saved seeds often carry latent infections of seed-borne pathogens, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks and variability in crop performance.
Breeder Seed Lineage
Certified seed, derived from a rigorously maintained breeder seed lineage, ensures genetic purity and uniformity, resulting in consistent and higher crop yields compared to saved seed, which may suffer from genetic degradation and variability. Utilizing certified seed supports stable production by preserving the integrity of elite breeder lines essential for optimal agronomic performance.
Seed Quality Assurance Protocols
Certified seed undergoes rigorous Seed Quality Assurance Protocols including genetic purity testing, germination rate analysis, and disease screening, ensuring consistent high yields and crop performance. In contrast, saved seed often lacks systematic quality controls, leading to variable germination, increased disease risk, and lower yield consistency in subsequent planting cycles.
Varietal Integrity
Certified seed ensures varietal integrity through rigorous quality control and genetic purity standards, leading to consistent and higher crop yields compared to saved seed, which often suffers from genetic drift and contamination. Maintaining varietal integrity with certified seed is crucial for predictable performance, pest resistance, and optimal yield stability in crop production.
Farm-Saved Seed Degradation
Farm-saved seed often suffers from genetic drift and increased pest and disease load, leading to yield inconsistency compared to certified seed, which undergoes rigorous quality control and genetic purity tests. Continuous use of farm-saved seed accelerates degradation, reducing crop vigor and productivity over successive planting cycles.
Certified seed vs saved seed for yield consistency Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com