Manual planting ensures precise seedling placement and higher initial survival rates, making it ideal for complex terrains and species requiring careful handling. Aerial seeding offers rapid coverage over large or inaccessible areas but may result in uneven seed distribution and lower germination success. Choosing between these methods depends on site conditions, project scale, and desired establishment speed in afforestation efforts.
Table of Comparison
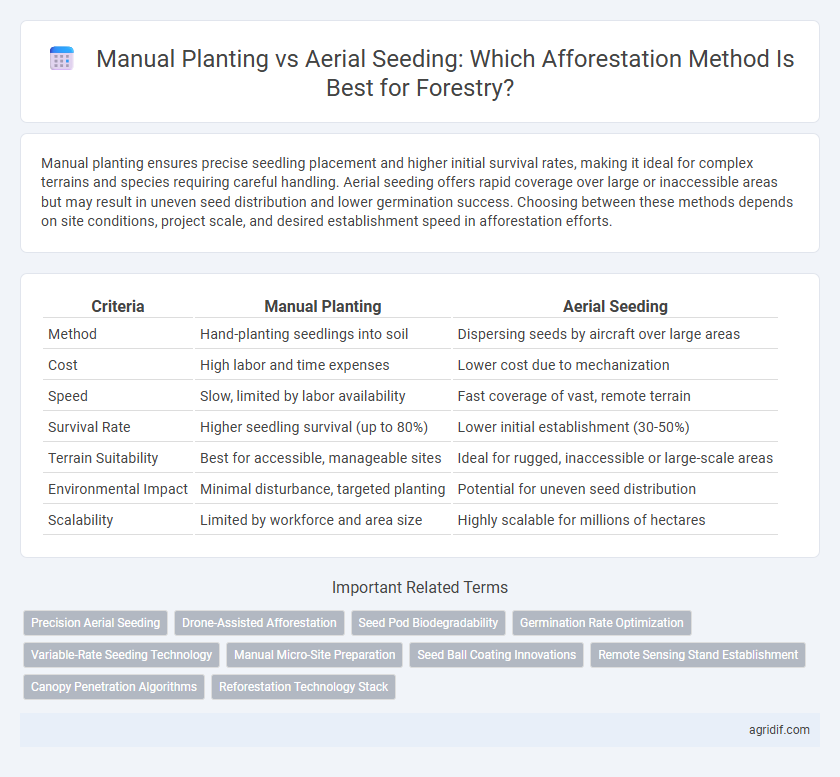
| Criteria | Manual Planting | Aerial Seeding |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Hand-planting seedlings into soil | Dispersing seeds by aircraft over large areas |
| Cost | High labor and time expenses | Lower cost due to mechanization |
| Speed | Slow, limited by labor availability | Fast coverage of vast, remote terrain |
| Survival Rate | Higher seedling survival (up to 80%) | Lower initial establishment (30-50%) |
| Terrain Suitability | Best for accessible, manageable sites | Ideal for rugged, inaccessible or large-scale areas |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal disturbance, targeted planting | Potential for uneven seed distribution |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce and area size | Highly scalable for millions of hectares |
Overview of Manual Planting and Aerial Seeding
Manual planting involves physically placing seedlings into prepared soil, allowing precise control over spacing and species selection, which promotes higher initial survival rates and better growth monitoring. Aerial seeding disperses seeds over large areas using aircraft, enabling rapid coverage of inaccessible or extensive terrain but may result in lower germination success due to environmental exposure and predation. Both methods are critical for afforestation efforts, with manual planting favored for smaller, high-value sites and aerial seeding preferred for cost-effective restoration of vast or remote landscapes.
Cost Comparison: Manual Planting vs Aerial Seeding
Manual planting in afforestation incurs higher labor costs due to intensive human involvement and slower planting rates, typically ranging from $800 to $1,500 per hectare. Aerial seeding offers a cost-effective alternative, with expenses generally between $200 and $600 per hectare, driven by faster coverage and reduced manpower requirements. Variability in terrain, seed type, and project scale can influence cost efficiency, but aerial seeding remains the preferred economic choice for large-scale reforestation efforts.
Labor Requirements in Afforestation Methods
Manual planting demands intensive labor, requiring skilled workers to plant each seedling precisely, which can be time-consuming and costly. Aerial seeding significantly reduces labor needs by dispersing seeds over large, inaccessible areas quickly, minimizing on-ground workforce requirements. Labor efficiency in aerial seeding enhances scalability for afforestation projects, especially in rugged or remote terrains.
Seedling Survival Rates: Ground vs Air Approaches
Manual planting in afforestation generally results in higher seedling survival rates, often exceeding 80%, due to precise soil preparation and controlled placement. In contrast, aerial seeding offers rapid coverage of large areas but typically experiences lower establishment rates around 30-50%, influenced by factors such as seed dispersal, ground contact, and environmental conditions. Optimizing seed quality and site conditions can improve outcomes for both methods, but ground-based manual planting remains more reliable for maximizing seedling establishment.
Suitability for Different Terrain and Land Types
Manual planting provides precise seedling placement, making it highly suitable for uneven terrain, rocky soils, and smaller, irregular-shaped plots where careful handling is required. Aerial seeding excels in vast, remote, or inaccessible areas with rugged topography, such as steep slopes and dense forests, enabling rapid cover over large land extents. Selection depends on terrain complexity, soil stability, and land size, with manual planting favored for controlled environments and aerial seeding optimized for expansive, challenging landscapes.
Environmental Impact: Soil Disturbance and Biodiversity
Manual planting minimizes soil disturbance by carefully placing seedlings, preserving the natural soil structure and promoting higher biodiversity compared to aerial seeding. Aerial seeding, while efficient over large areas, can cause uneven seed distribution and increased soil compaction, potentially disrupting habitat quality and reducing species diversity. Selecting the appropriate method based on site conditions significantly influences long-term ecosystem health and forest regeneration success.
Technological Advances in Aerial Seeding
Technological advances in aerial seeding have significantly increased efficiency and precision in afforestation efforts by utilizing GPS-guided drones and aircraft to distribute seeds over large, inaccessible areas. High-resolution imagery and real-time data analytics enable optimized seed placement, improving germination rates and reducing seed waste compared to manual planting. Innovations such as seed coating with nutrients and moisture-retaining gels further enhance survival rates and accelerate forest regeneration in diverse ecological zones.
Challenges and Limitations of Manual Planting
Manual planting in afforestation faces challenges such as high labor costs and slow planting rates, limiting its scalability in vast or remote forest areas. The method requires skilled laborers to ensure proper seedling placement and survival, which may be scarce in some regions. Soil disturbance and inconsistent spacing can also reduce overall forest uniformity and growth efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful Afforestation Projects
Case studies reveal that manual planting often achieves higher initial survival rates in afforestation projects due to precise seedling placement and site-specific care, as demonstrated in the New Zealand East Coast Project. Aerial seeding, employed successfully in Canada's boreal forests, enables rapid large-area coverage and lower operational costs, proving effective for remote or difficult terrains. Combining both methods has optimized reforestation outcomes in Australia's post-wildfire recovery efforts, balancing speed and seedling establishment success.
Future Trends in Afforestation Techniques
Emerging afforestation techniques emphasize drone-assisted aerial seeding combined with AI-driven site analysis to optimize seed distribution and growth rates. Manual planting remains valuable for species requiring precise placement and care, but automation promises scalability and cost efficiency in reforestation projects. Advances in bioengineering also enable development of seed coatings that improve germination and resilience against climate stressors, accelerating forest recovery efforts.
Related Important Terms
Precision Aerial Seeding
Precision aerial seeding utilizes GPS technology and advanced seed dispersal mechanisms to enhance tree density and species diversity, outperforming traditional manual planting in terms of speed and cost-efficiency for large-scale afforestation projects. This method reduces labor intensity and ensures uniform seed distribution, promoting higher germination rates and forest regeneration success in diverse terrains.
Drone-Assisted Afforestation
Drone-assisted afforestation enhances aerial seeding by enabling precise seed dispersal over large, inaccessible areas, increasing planting efficiency and reducing labor costs compared to manual planting. This technology allows for rapid reforestation efforts with improved seedling survival rates due to optimized seed placement and real-time environmental monitoring.
Seed Pod Biodegradability
Seed pods used in aerial seeding for afforestation are often designed with biodegradable materials that decompose naturally, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional manual planting methods. These biodegradable seed pods enhance soil health by releasing nutrients during decomposition, supporting sustainable reforestation efforts and minimizing plastic waste.
Germination Rate Optimization
Manual planting achieves higher germination rates by allowing precise seed placement and optimal soil contact, essential for seedling survival in afforestation projects. In contrast, aerial seeding offers broader coverage but often results in lower germination due to seed displacement and inconsistent soil conditions.
Variable-Rate Seeding Technology
Variable-rate seeding technology in aerial seeding enables precise distribution of seeds based on site-specific conditions, enhancing survival rates and forest density compared to uniform manual planting. This technology optimizes seed usage by adjusting seeding rates according to soil fertility, slope, and moisture levels, resulting in cost-effective and ecologically adaptive afforestation.
Manual Micro-Site Preparation
Manual micro-site preparation during afforestation enables precise soil disturbance and targeted vegetation removal, optimizing seedling establishment and growth conditions. Compared to aerial seeding, this hands-on approach enhances microsite quality, increases survival rates, and supports species diversity by customizing planting spots to specific site conditions.
Seed Ball Coating Innovations
Seed ball coating innovations enhance germination rates and protect seeds from pests and harsh environmental conditions in both manual planting and aerial seeding methods for afforestation. Advanced coatings incorporating nutrients, moisture retainers, and biocontrol agents significantly improve seedling establishment success, making aerial seeding more efficient and manual planting more effective.
Remote Sensing Stand Establishment
Manual planting ensures precise seedling placement and healthier initial stand establishment, which can be accurately monitored through high-resolution remote sensing data for detailed growth analysis. Aerial seeding covers larger areas quickly but creates heterogeneous stands that pose challenges for remote sensing-based assessment due to variable canopy closure and uneven germination rates.
Canopy Penetration Algorithms
Canopy penetration algorithms significantly improve the accuracy of aerial seeding by optimizing seed distribution through dense forest canopies, ensuring higher germination rates compared to manual planting. These algorithms analyze LiDAR and multispectral data to adjust seeding patterns in real time, enhancing afforestation efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Reforestation Technology Stack
Manual planting ensures precise seedling placement and species selection, enhancing survival rates in targeted reforestation zones, while aerial seeding accelerates large-area coverage with cost-effective seed dispersal using drones or aircraft. Integrating GIS mapping, drone technology, and soil analysis into the forestry technology stack optimizes site-specific afforestation strategies and monitors reforestation progress with real-time data analytics.
Manual Planting vs Aerial Seeding for Afforestation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com