Silviculture emphasizes practical forest management techniques aimed at cultivating and sustaining healthy tree populations, focusing on growth, regeneration, and harvesting methods. Dendrology specializes in the scientific identification and classification of trees based on botanical characteristics such as leaf shape, bark texture, and reproductive structures. Understanding the distinction between silviculture and dendrology is essential for effective forest conservation and resource management strategies.
Table of Comparison
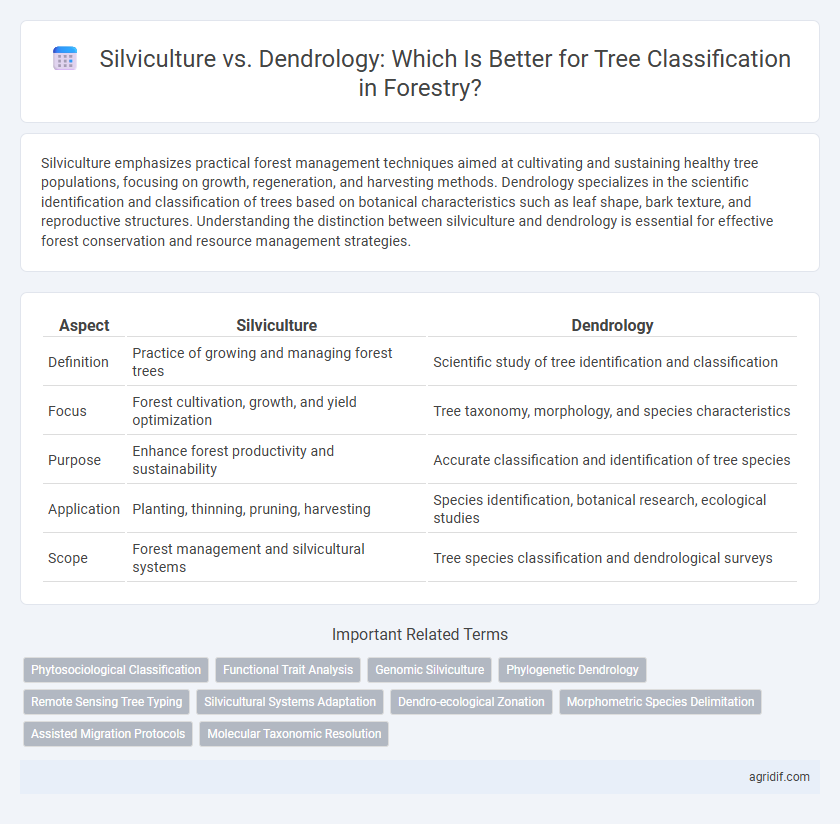
| Aspect | Silviculture | Dendrology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practice of growing and managing forest trees | Scientific study of tree identification and classification |
| Focus | Forest cultivation, growth, and yield optimization | Tree taxonomy, morphology, and species characteristics |
| Purpose | Enhance forest productivity and sustainability | Accurate classification and identification of tree species |
| Application | Planting, thinning, pruning, harvesting | Species identification, botanical research, ecological studies |
| Scope | Forest management and silvicultural systems | Tree species classification and dendrological surveys |
Overview of Silviculture and Dendrology
Silviculture involves the practical management and cultivation of forests to meet specific ecological and economic goals, emphasizing growth, health, and quality of tree stands. Dendrology focuses on the scientific study and identification of individual tree species, including their taxonomy, morphology, and ecological relationships. Understanding silviculture enables effective forest management strategies, while dendrology provides the essential knowledge of tree species characteristics crucial for classification and conservation efforts.
Defining Tree Classification in Forestry
Tree classification in forestry involves organizing trees based on their biological and ecological characteristics to aid in forest management and conservation. Silviculture emphasizes practical classification for managing tree growth, health, and yield, focusing on species selection and stand dynamics. Dendrology provides a scientific foundation by identifying and describing tree species through morphological traits and taxonomy, supporting accurate species identification and ecological studies.
Core Principles of Silviculture
Silviculture focuses on the practical management and cultivation of forest trees to optimize growth, health, and yield, emphasizing techniques such as regeneration, thinning, and harvesting. It integrates ecological principles to ensure sustainable forest development and productivity, addressing species selection, site preparation, and stand dynamics. Unlike dendrology, which primarily classifies and studies tree species based on taxonomy and morphology, silviculture applies these classifications to real-world forest management practices.
Key Concepts in Dendrology
Dendrology focuses on the scientific study and identification of trees, emphasizing morphological characteristics such as leaf shape, bark texture, and reproductive structures to classify species accurately. Key concepts in dendrology include understanding tree taxonomy, growth patterns, and physiological traits critical for species differentiation and ecological research. This discipline provides essential knowledge for forest management by enabling precise species identification necessary for informed silvicultural practices.
Methods of Tree Identification: Silviculture vs Dendrology
Silviculture emphasizes practical methods for tree identification based on growth patterns, site conditions, and species' ecological roles to optimize forest management and regeneration. Dendrology focuses on the scientific classification of trees using morphological traits such as leaf shape, bark texture, and reproductive structures to accurately identify species. Both disciplines utilize field observations but differ in purpose: silviculture applies identification for forest productivity, while dendrology provides taxonomic precision essential for biodiversity studies.
Practical Applications in Forest Management
Silviculture emphasizes practical applications such as tree spacing, thinning, and species selection to optimize forest growth, health, and timber yield, while dendrology focuses on the scientific study and identification of tree species based on morphological and anatomical characteristics. Forest managers rely on silvicultural techniques to implement effective regeneration methods and improve stand dynamics, whereas dendrological knowledge supports accurate tree species identification essential for biodiversity assessments and ecological planning. Integrating both silviculture and dendrology enhances decision-making in forest management, ensuring sustainable exploitation and conservation of forest resources.
Influence on Biodiversity Assessment
Silviculture and dendrology offer distinct approaches to tree classification that directly impact biodiversity assessment accuracy. Silviculture emphasizes tree growth patterns and forest management techniques, supporting dynamic ecosystem evaluations and sustainable biodiversity conservation. Dendrology focuses on species identification and taxonomy, providing a detailed understanding of species composition crucial for precise biodiversity inventories.
Role in Sustainable Forest Practices
Silviculture and dendrology play distinct yet complementary roles in sustainable forest practices by combining practical forest management with scientific tree identification. Silviculture focuses on the cultivation and growth of forests to ensure regeneration, health, and productivity, directly influencing sustainable harvesting and conservation strategies. Dendrology provides critical knowledge on tree species identification, characteristics, and ecological requirements, enabling informed decision-making for biodiversity preservation and adaptive forest management.
Challenges in Tree Classification Approaches
Silviculture and dendrology both contribute to tree classification but face distinct challenges in accuracy and scope. Silviculture emphasizes practical management and species adaptability, often requiring dynamic classification to inform forest cultivation, while dendrology focuses on botanical identification through morphological traits, which can be complicated by phenotypic plasticity and hybridization. Inherent variability within tree populations and environmental influences further complicate consistent classification, demanding integrated approaches for effective forestry management.
Integrating Silvicultural and Dendrological Insights
Silviculture focuses on the practical management and cultivation techniques for forest regeneration, while dendrology emphasizes the scientific identification and classification of tree species based on botanical characteristics. Integrating silvicultural practices with dendrological knowledge enhances sustainable forest management by aligning species-specific growth requirements with ecosystem dynamics. This combined approach supports precision in species selection, improves forest health, and optimizes timber production within diverse ecological contexts.
Related Important Terms
Phytosociological Classification
Silviculture focuses on managing tree growth and forest stand development, employing phytosociological classification to analyze plant communities and guide forest management practices. Dendrology emphasizes the identification and taxonomy of individual tree species but incorporates phytosociological classification primarily to understand species distribution within forest ecosystems.
Functional Trait Analysis
Silviculture emphasizes the practical applications of tree classification for forest management, integrating functional trait analysis to enhance growth optimization and species selection. Dendrology focuses on the identification and taxonomy of tree species, using functional traits primarily for scientific classification and understanding evolutionary relationships.
Genomic Silviculture
Genomic silviculture integrates genetic and genomic data to enhance tree classification and forest management, surpassing traditional dendrology, which primarily focuses on morphological characteristics for identifying species. This advanced approach enables precise selection of tree genotypes with desirable traits, improving resilience, growth rates, and adaptation to environmental changes.
Phylogenetic Dendrology
Silviculture emphasizes practical forest management techniques for tree growth and health, while dendrology focuses on the scientific classification and identification of trees. Phylogenetic dendrology advances traditional taxonomy by analyzing evolutionary relationships through genetic data, enabling more accurate tree classification within forestry research and conservation practices.
Remote Sensing Tree Typing
Remote sensing tree typing leverages dendrology's detailed species identification by analyzing leaf morphology, bark texture, and tree crown structure through spectral and LiDAR data. Silviculture benefits from this precise classification by optimizing forest management practices, enabling targeted interventions based on species-specific growth patterns and ecological requirements.
Silvicultural Systems Adaptation
Silvicultural systems adaptation focuses on managing forest stands through techniques such as clear-cutting, shelterwood, and selection cutting to optimize tree growth, diversity, and resilience. Unlike dendrology, which classifies trees based on botanical characteristics, silviculture emphasizes practical applications that adjust management practices according to site conditions and forest dynamics for sustainable timber production and ecosystem health.
Dendro-ecological Zonation
Dendrology provides detailed identification and classification of tree species essential for understanding dendro-ecological zonation, which maps vegetation patterns based on climatic and soil factors. Silviculture applies these classifications to manage forest stands but relies heavily on dendrological data to align silvicultural practices with specific ecological zones for sustainable forestry.
Morphometric Species Delimitation
Silviculture emphasizes practical applications of tree classification to optimize forest management and growth, using morphometric species delimitation for identifying growth patterns and adaptive traits. Dendrology focuses on the taxonomic and morphological characteristics of trees, employing quantitative morphometric analyses to accurately classify species and understand evolutionary relationships.
Assisted Migration Protocols
Silviculture emphasizes practical applications of tree management, integrating Assisted Migration Protocols to select species and provenances adaptable to future climatic conditions, while dendrology focuses on the systematic classification and identification of tree species based on morphological and genetic traits. Assisted Migration Protocols in silviculture guide reforestation efforts by prioritizing species with resilience traits identified through dendrological studies, optimizing forest composition for climate change adaptation.
Molecular Taxonomic Resolution
Molecular taxonomic resolution in silviculture enhances tree classification by integrating genetic markers to improve forest management and species selection for sustainable growth. Dendrology traditionally relies on morphological traits, but molecular techniques provide higher precision in identifying cryptic species and assessing genetic diversity critical for conservation strategies.
Silviculture vs Dendrology for Tree Classification Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com