Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, resulting in faster growth and higher yields for leafy greens compared to traditional soil culture. Soil culture benefits from natural microbial activity that enhances plant health but requires more space and is susceptible to soil-borne diseases and pests. Choosing between hydroponics and soil culture depends on resource availability, environmental conditions, and desired production scale.
Table of Comparison
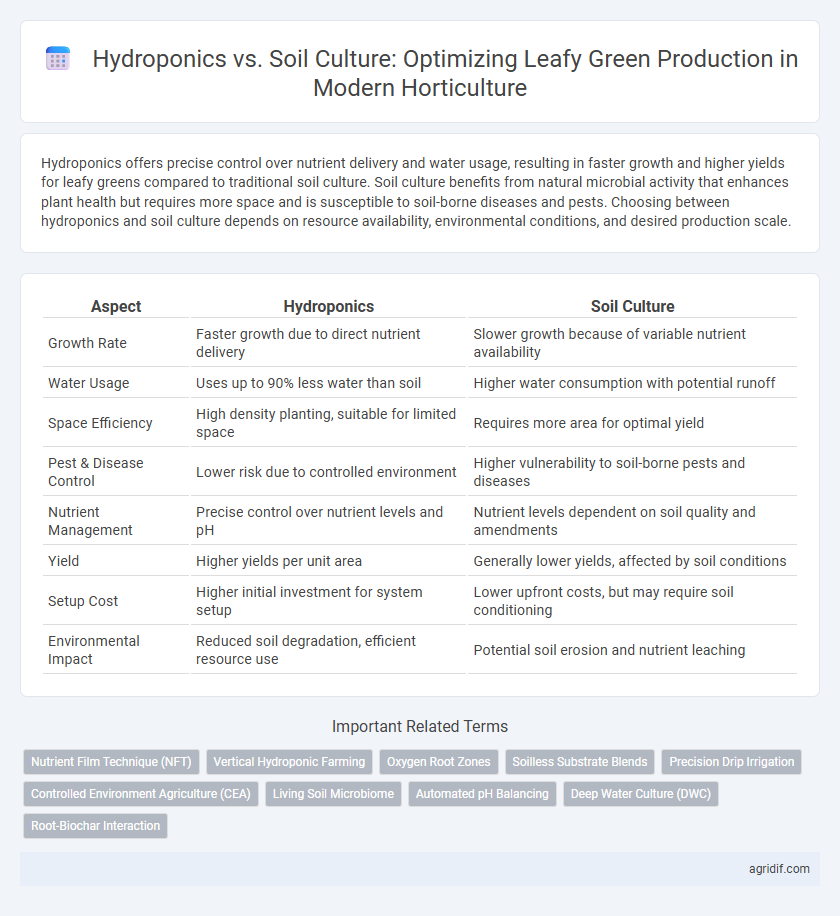
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster growth due to direct nutrient delivery | Slower growth because of variable nutrient availability |
| Water Usage | Uses up to 90% less water than soil | Higher water consumption with potential runoff |
| Space Efficiency | High density planting, suitable for limited space | Requires more area for optimal yield |
| Pest & Disease Control | Lower risk due to controlled environment | Higher vulnerability to soil-borne pests and diseases |
| Nutrient Management | Precise control over nutrient levels and pH | Nutrient levels dependent on soil quality and amendments |
| Yield | Higher yields per unit area | Generally lower yields, affected by soil conditions |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial investment for system setup | Lower upfront costs, but may require soil conditioning |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced soil degradation, efficient resource use | Potential soil erosion and nutrient leaching |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil Culture
Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method that uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow leafy greens, offering precise control over nutrient delivery and faster growth rates compared to traditional soil culture. Soil culture relies on natural soil media, which provides organic matter and microbial life but can be affected by variability in nutrient content, pests, and diseases. Comparative studies show hydroponic systems often yield higher biomass with reduced water use, making them efficient for leafy green production in controlled environments.
Key Principles of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems for leafy greens operate on key principles including nutrient solution management, oxygen availability, and root support without soil. These systems optimize leaf growth by delivering precise amounts of water and essential nutrients directly to the plant roots through solutions like nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC). Controlled environment factors such as pH, electrical conductivity, and temperature are maintained to maximize photosynthesis efficiency and plant health.
Fundamentals of Soil-Based Cultivation
Soil-based cultivation of leafy greens relies on natural soil ecosystems to provide essential nutrients, water retention, and microbial activity that enhance plant growth and health. This method depends on the soil's physical structure, organic matter content, and fertility to support root development and nutrient uptake. Proper soil management, including pH balance, aeration, and organic amendments, plays a critical role in optimizing yield and quality in traditional leafy green production.
Growth Rate Comparison in Leafy Greens
Hydroponics systems accelerate growth rates in leafy greens by providing precise nutrient delivery and optimal water availability, resulting in harvests up to 25-50% faster than traditional soil culture. Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and kale thrive in hydroponic setups due to controlled environmental factors, reducing growth cycle times from 45 days in soil to approximately 30 days hydroponically. Enhanced oxygenation of roots and disease control further contribute to increased biomass and consistent crop yields in hydroponic cultivation compared to soil-based methods.
Water Usage and Resource Efficiency
Hydroponics for leafy greens significantly reduces water usage by recirculating nutrient solutions, using up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil culture. Soil culture relies on natural soil moisture and often requires additional irrigation, leading to higher water consumption and potential nutrient runoff. The controlled environment of hydroponics enhances resource efficiency by minimizing waste and optimizing nutrient delivery, making it a sustainable choice for high-density leafy green production.
Nutrient Management and Control
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient management by delivering a controlled solution directly to leafy greens, ensuring optimal growth and reducing nutrient waste compared to soil culture, where nutrient availability can vary due to soil composition and microbial activity. In soil culture, nutrient uptake is less predictable due to factors like pH fluctuations and organic matter breakdown, making nutrient control more challenging for consistent leafy green production. Advanced hydroponic systems enable real-time monitoring and adjustment of nutrient concentrations, enhancing growth rates and nutrient use efficiency in leafy greens cultivation.
Pest and Disease Management Strategies
Hydroponics offers a controlled environment that significantly reduces pest infestations and soil-borne diseases common in leafy green cultivation, enabling precise nutrient delivery and limiting pathogen exposure. Soil culture requires rigorous pest and disease management strategies such as crop rotation, organic mulches, and chemical treatments to mitigate risks from soil pathogens and insect pests. Integrated pest management (IPM) in hydroponics often includes biological controls and sanitation protocols, whereas soil culture demands continuous monitoring and diverse interventions to address the broader ecosystem of pests and diseases.
Yield and Quality Differences
Hydroponics systems for leafy greens typically achieve higher yields per square foot compared to soil culture due to optimized nutrient delivery and controlled environmental conditions. Leafy greens grown hydroponically often exhibit superior quality traits such as uniform texture, vibrant color, and enhanced nutrient content, attributable to precise management of water and minerals. Soil culture may introduce variability in yield and quality because of inconsistent soil conditions and susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Economic Considerations and Startup Costs
Hydroponics systems for leafy greens require higher initial investment due to costs of pumps, nutrient solutions, and climate control technology, but offer faster growth cycles and higher yield per square foot, potentially increasing profitability. Soil culture demands lower startup costs and less technical expertise, making it more accessible for small-scale farmers, though it typically results in slower growth and lower density planting. Economic viability depends on scale, market demand, and access to resources, with hydroponics favored in urban and high-value markets, while soil culture remains cost-effective for traditional farming setups.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hydroponics significantly reduces water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional soil culture, promoting sustainable water management in leafy green production. The controlled environment of hydroponics minimizes pesticide use and nutrient runoff, reducing soil degradation and water pollution often associated with conventional soil farming. However, soil culture supports biodiversity and natural microbial activity, contributing to long-term soil health and carbon sequestration crucial for environmental sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) in hydroponics provides a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water directly to leafy green roots, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency compared to traditional soil culture. This method reduces water usage and minimizes pest-related issues, promoting faster growth and higher yields in controlled environments.
Vertical Hydroponic Farming
Vertical hydroponic farming significantly boosts leafy green yields by optimizing space and nutrient delivery compared to traditional soil culture, enabling up to 90% water savings and faster growth cycles. Controlled environment parameters in vertical systems reduce pest risks and increase consistency in leaf texture and nutrient density, making it a sustainable choice for urban horticulture.
Oxygen Root Zones
Hydroponics systems provide higher oxygen availability in root zones compared to soil culture, enhancing nutrient uptake and promoting faster growth of leafy greens. Optimal oxygenation in hydroponic solutions reduces root diseases and improves overall plant health, resulting in increased yield and quality.
Soilless Substrate Blends
Soilless substrate blends in hydroponics offer precise control over nutrient delivery and water retention, resulting in faster growth and higher yields for leafy greens compared to traditional soil culture. These blends, often composed of coco coir, perlite, and vermiculite, reduce soil-borne diseases and improve oxygen availability to roots, enhancing plant health and productivity.
Precision Drip Irrigation
Precision drip irrigation in hydroponics delivers nutrient-rich water directly to the roots of leafy greens, optimizing water and nutrient use efficiency compared to traditional soil culture. This targeted approach reduces runoff and promotes faster growth cycles, enhancing yield quality and consistency in controlled horticultural environments.
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Hydroponics in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) offers precise nutrient management and efficient water use for leafy greens, resulting in faster growth cycles and higher yields compared to traditional soil culture. Soil-based cultivation in CEA provides a natural microbiome that can enhance flavor and plant resilience but often requires more space and is less resource-efficient than hydroponic systems.
Living Soil Microbiome
Hydroponics enables controlled nutrient delivery for leafy greens, yet soil culture supports a diverse living soil microbiome that enhances plant health by promoting nutrient cycling and disease resistance. The presence of beneficial microorganisms in living soil improves root development and flavor profiles, aspects often diminished in soilless hydroponic systems.
Automated pH Balancing
Automated pH balancing in hydroponics ensures precise nutrient availability for leafy greens, promoting faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil culture, where pH fluctuations can limit nutrient uptake. Advanced sensors and control systems in hydroponic setups maintain optimal pH levels continuously, reducing manual intervention and improving overall crop quality.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponics delivers faster growth rates and higher yields for leafy greens like lettuce and spinach compared to traditional soil culture by providing constant oxygenation and nutrient-rich water directly to the roots. DWC systems reduce disease risk and water usage while enabling precise nutrient management, making it an efficient alternative to soil-based cultivation for leafy greens.
Root-Biochar Interaction
Hydroponics systems for leafy greens foster enhanced root-biochar interaction by providing controlled nutrient delivery and optimal oxygen levels, which improve biochar's capacity to retain moisture and microbial activity. In contrast, soil culture often presents variable conditions that can limit biochar's effectiveness in supporting root growth and nutrient uptake, impacting overall plant health and yield.
Hydroponics vs Soil culture for leafy greens Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com