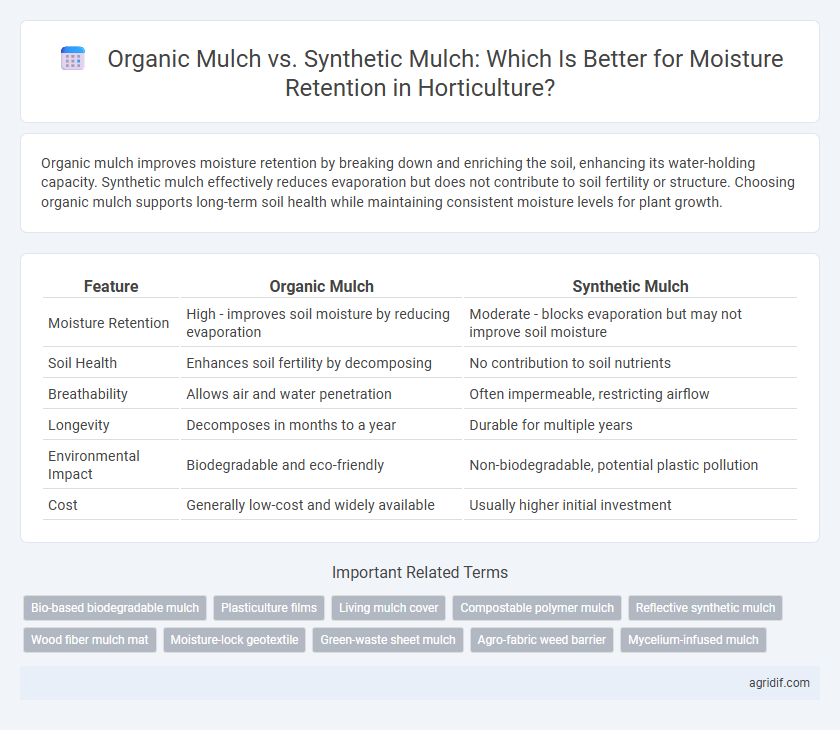
Organic mulch improves moisture retention by breaking down and enriching the soil, enhancing its water-holding capacity. Synthetic mulch effectively reduces evaporation but does not contribute to soil fertility or structure. Choosing organic mulch supports long-term soil health while maintaining consistent moisture levels for plant growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Organic Mulch | Synthetic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Retention | High - improves soil moisture by reducing evaporation | Moderate - blocks evaporation but may not improve soil moisture |
| Soil Health | Enhances soil fertility by decomposing | No contribution to soil nutrients |
| Breathability | Allows air and water penetration | Often impermeable, restricting airflow |
| Longevity | Decomposes in months to a year | Durable for multiple years |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, potential plastic pollution |
| Cost | Generally low-cost and widely available | Usually higher initial investment |
Introduction to Mulching in Horticulture
Organic mulch, such as wood chips, straw, and compost, excels at moisture retention by slowly absorbing and releasing water into the soil, enhancing soil structure and fertility. Synthetic mulch, typically made from plastic or rubber, provides a more effective barrier against evaporation, maintaining soil moisture levels more consistently but lacking the nutrient benefits of organic options. Understanding these differences helps horticulturists select the appropriate mulch type based on water conservation needs and soil health goals.
Defining Organic and Synthetic Mulches
Organic mulch consists of natural materials like wood chips, straw, or compost that decompose over time, enriching the soil and improving moisture retention by enhancing soil structure and water infiltration. Synthetic mulch, made from non-biodegradable materials such as plastic or rubber, creates a barrier that reduces evaporation but does not contribute nutrients or improve soil health. Both types serve to conserve soil moisture, but organic mulches support long-term soil fertility while synthetic mulches offer more consistent moisture control without decomposition benefits.
Moisture Retention Capabilities: Organic vs Synthetic
Organic mulch, composed of natural materials such as bark, leaves, and straw, excels in moisture retention by gradually releasing water into the soil and enhancing soil structure through decomposition. Synthetic mulch, often made from plastic or rubber, provides an effective moisture barrier that reduces evaporation but lacks the ability to improve soil health. Studies indicate organic mulch can increase soil moisture retention by up to 25%, while synthetic mulch offers more immediate but less sustainable moisture conservation.
Impact on Soil Structure and Water-Holding Capacity
Organic mulch enhances soil structure by decomposing into humus, which increases porosity and improves water infiltration and retention. Synthetic mulch, while effective at reducing evaporation, does not contribute to soil organic matter, potentially leading to compacted soil and decreased water-holding capacity over time. The use of organic mulch supports long-term soil health by promoting microbial activity and sustained moisture retention.
Decomposition Rates and Long-Term Moisture Benefits
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, decomposes over time, enriching soil with nutrients and improving moisture retention by enhancing soil structure and water-holding capacity. Synthetic mulch, made from materials like plastic or rubber, provides a longer-lasting barrier against evaporation but does not contribute to soil health and can inhibit natural moisture cycling. The slower decomposition rates of synthetic mulch result in sustained moisture conservation, while organic mulch offers long-term benefits through gradual nutrient release and improved soil aeration.
Temperature Regulation and Its Effect on Moisture
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, excels in temperature regulation by insulating soil, reducing temperature fluctuations, and promoting consistent moisture retention. Synthetic mulch, often made from plastic or rubber, can increase soil temperature, accelerating evaporation and decreasing moisture content. Effective temperature regulation by organic mulch minimizes plant stress and enhances water conservation in horticultural applications.
Effectiveness of Mulch Types in Different Climates
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, excels in moisture retention by slowly releasing water and improving soil structure, making it highly effective in arid and temperate climates. Synthetic mulches, like plastic sheeting, provide an impermeable barrier that prevents evaporation, often performing better in humid or rainy environments where excess moisture must be controlled. The choice between organic and synthetic mulch depends on local climate conditions, soil type, and specific water retention needs for optimal plant growth.
Environmental Impact of Mulch Choices
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, enhances soil moisture retention by breaking down and improving soil structure while supporting beneficial microorganisms, thereby promoting a healthier ecosystem. Synthetic mulch, typically made from plastic or rubber, also conserves moisture effectively but can contribute to soil degradation and environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable properties. Choosing organic mulch reduces waste accumulation and carbon footprint, aligning with sustainable horticultural practices that prioritize long-term soil health and biodiversity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Practical Application
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, provides superior moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity, which enhances long-term water absorption and reduces irrigation needs. Synthetic mulch, like plastic sheeting, offers immediate moisture conservation by creating a barrier against evaporation but lacks soil enrichment benefits and often requires replacement each season, increasing overall costs. Cost-effectiveness in horticulture depends on balancing initial investment with soil health improvements; organic mulch tends to be more sustainable and economically beneficial over time due to reduced water usage and improved soil fertility.
Best Practices for Mulch Selection in Horticulture
Organic mulch, such as straw, wood chips, and compost, excels in moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity, which enhances water absorption and reduces evaporation. Synthetic mulch, including plastic films and rubber mats, provides an effective moisture barrier but lacks the added benefits of soil enrichment and can increase soil temperature, potentially stressing plants. Best practices for mulch selection in horticulture recommend choosing organic mulch for long-term soil health and moisture retention while using synthetic options in controlled environments where moisture conservation without soil interaction is critical.
Related Important Terms
Bio-based biodegradable mulch
Bio-based biodegradable mulch enhances moisture retention by gradually breaking down and improving soil organic matter, promoting water infiltration and reducing evaporation more effectively than synthetic mulch. Its natural composition supports healthier soil ecosystems, making it a sustainable choice for maintaining optimal moisture levels in horticultural practices.
Plasticulture films
Organic mulch enhances soil moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity, while synthetic mulch, such as plasticulture films, provides a more consistent moisture barrier by reducing evaporation and limiting weed growth. Plasticulture films, commonly made from polyethylene, offer efficient water conservation in horticulture through their impermeability and durability, although they require proper disposal to mitigate environmental impact.
Living mulch cover
Living mulch cover, a type of organic mulch, enhances soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation and improving soil structure through root activity, offering superior benefits compared to synthetic mulches which primarily act as physical barriers. Organic living mulches also promote microbial activity and nutrient cycling, supporting plant health and sustainable water management in horticultural systems.
Compostable polymer mulch
Compostable polymer mulch offers superior moisture retention compared to traditional synthetic mulch by slowly decomposing and enriching soil organic matter, which enhances water retention capacity. Unlike conventional plastic mulches that create runoff and hinder soil respiration, compostable polymer mulch improves soil health and reduces the need for frequent irrigation in horticultural applications.
Reflective synthetic mulch
Reflective synthetic mulch excels in moisture retention by reducing soil evaporation through its light-reflective properties, which also help regulate soil temperature and deter pests. Compared to organic mulch, it offers longer durability and consistent moisture levels but lacks the soil-enriching benefits of decomposing organic materials.
Wood fiber mulch mat
Wood fiber mulch mats provide superior moisture retention compared to synthetic mulches by enhancing soil aeration and reducing evaporation through natural fiber absorption. Their biodegradable composition improves soil health over time, contrasting with synthetic mulches that can impede water penetration and contribute to soil temperature fluctuations.
Moisture-lock geotextile
Moisture-lock geotextile outperforms traditional organic mulch by providing superior water retention while preventing soil erosion and weed growth. Its synthetic fibers create a durable barrier that maintains consistent moisture levels, enhancing plant health and reducing irrigation frequency in horticultural applications.
Green-waste sheet mulch
Green-waste sheet mulch, an organic mulch derived from decomposed plant materials, enhances soil moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity, which reduces evaporation and supports sustainable water conservation. In contrast, synthetic mulches provide a physical barrier to evaporation but do not contribute nutrients or soil health, making green-waste mulch a superior choice for long-term moisture retention and ecological benefits in horticulture.
Agro-fabric weed barrier
Organic mulch such as wood chips and straw enhances moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting microbial activity, while synthetic mulches like agro-fabric weed barriers provide a durable, impermeable layer that effectively suppresses weeds and conserves soil moisture by reducing evaporation. Agro-fabric barriers excel in long-term wetness control and erosion prevention, especially in commercial horticulture, whereas organic mulches require more frequent replenishment but contribute to soil fertility.
Mycelium-infused mulch
Mycelium-infused organic mulch enhances moisture retention by improving soil structure and promoting beneficial fungal networks that increase water absorption and retention compared to synthetic mulch. This biologically active mulch supports soil health and reduces evaporation, offering sustainable moisture management in horticulture.
Organic mulch vs Synthetic mulch for moisture retention Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com