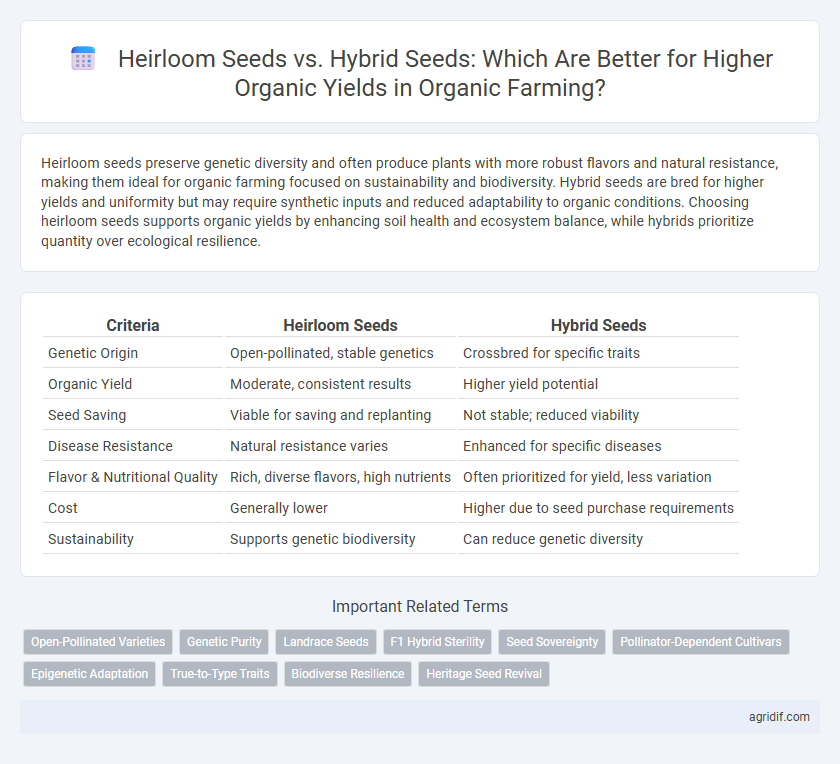
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and often produce plants with more robust flavors and natural resistance, making them ideal for organic farming focused on sustainability and biodiversity. Hybrid seeds are bred for higher yields and uniformity but may require synthetic inputs and reduced adaptability to organic conditions. Choosing heirloom seeds supports organic yields by enhancing soil health and ecosystem balance, while hybrids prioritize quantity over ecological resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Heirloom Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Origin | Open-pollinated, stable genetics | Crossbred for specific traits |
| Organic Yield | Moderate, consistent results | Higher yield potential |
| Seed Saving | Viable for saving and replanting | Not stable; reduced viability |
| Disease Resistance | Natural resistance varies | Enhanced for specific diseases |
| Flavor & Nutritional Quality | Rich, diverse flavors, high nutrients | Often prioritized for yield, less variation |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to seed purchase requirements |
| Sustainability | Supports genetic biodiversity | Can reduce genetic diversity |
Introduction to Heirloom and Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, valued for their genetic diversity and adaptability in organic farming systems. Hybrid seeds result from controlled cross-pollination between two distinct parent plants, designed for specific traits like higher yield and disease resistance but often requiring annual purchase. Organic yield benefits from heirloom seeds' resilience and soil compatibility, while hybrid seeds offer uniformity and vigor under intensive organic practices.
Defining Heirloom Seeds: Heritage and Traits
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, preserving unique genetic traits and regional adaptability essential for organic farming. These seeds offer stable characteristics such as flavor, color, and resistance to local pests and diseases, making them valuable for sustainable, chemical-free cultivation. Unlike hybrid seeds, heirlooms maintain genetic diversity, promoting soil health and ecological balance critical to organic yield optimization.
What Are Hybrid Seeds? Science and Development
Hybrid seeds result from cross-pollinating two distinct plant varieties to combine desirable traits such as higher yield, disease resistance, and uniformity. Developed through scientific breeding techniques, these seeds exhibit hybrid vigor (heterosis), enhancing growth and productivity under controlled conditions. While hybrid seeds offer consistent performance, their seeds typically do not produce true-to-type offspring, making them less suitable for seed saving in organic farming systems.
Seed Purity and Genetic Diversity
Heirloom seeds maintain seed purity by preserving open-pollinated varieties that enhance genetic diversity, which supports resilience in organic farming systems. Hybrid seeds, created through controlled crossbreeding, often exhibit uniform traits but can reduce genetic variation, potentially limiting adaptability in organic environments. Emphasizing heirloom seeds promotes organic yield sustainability through robust plant genetics and ecosystem balance.
Yield Performance: Heirloom vs Hybrid in Organic Fields
Heirloom seeds often showcase moderate yield performance in organic fields, prized for genetic diversity and resilience against local pests and diseases. Hybrid seeds, engineered for high yield and uniformity, typically outperform heirlooms in absolute organic yield but may require more precise management and inputs. Organic farmers must balance the higher productivity of hybrids with the sustainability and seed-saving advantages inherent in heirloom varieties.
Pest and Disease Resistance Comparison
Heirloom seeds often exhibit greater genetic diversity, enhancing their natural pest and disease resistance, which is crucial for organic farming where chemical inputs are limited. Hybrid seeds are typically bred for specific traits including increased resistance to certain pests and diseases, but this resistance may be narrower and less adaptable over time. Organic farmers often prefer heirloom seeds for their resilience and ability to maintain healthy crops in diverse environmental conditions without synthetic pesticides.
Flavor, Nutrition, and Culinary Qualities
Heirloom seeds often provide superior flavor and richer nutritional profiles compared to hybrid seeds, making them highly valued in organic farming for gourmet culinary applications. While hybrid seeds are bred for higher yields and disease resistance, heirlooms excel in maintaining genetic diversity and unique taste characteristics essential for organic produce quality. Organic farmers prioritize heirloom varieties to enhance flavor complexity and nutritional content, supporting sustainable agriculture and consumer demand for authentic, nutrient-dense food.
Seed Saving: Sustainability Implications
Heirloom seeds offer significant advantages for organic farming by enabling seed saving, which promotes biodiversity and reduces dependency on commercial seed suppliers. Unlike hybrid seeds, which often produce sterile offspring or lose key traits in subsequent generations, heirlooms maintain genetic stability, supporting long-term sustainability in organic yield production. Seed saving from heirloom varieties enhances resilience to pests, diseases, and climate variability, reinforcing sustainable agricultural practices in organic systems.
Economic Considerations for Organic Farmers
Heirloom seeds, known for their genetic diversity and adaptability, often require less input cost but may result in lower or less uniform yields compared to hybrid seeds, which are bred for higher productivity and disease resistance. Organic farmers must weigh the higher initial expense and limited seed saving potential of hybrids against the market premium and sustainability benefits of heirlooms. Economic considerations include seed cost, yield stability, market demand for organic heirloom varieties, and long-term soil health impacts influencing overall farm profitability.
Choosing the Right Seed for Organic Success
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and adapt well to organic farming conditions, often producing resilient crops with rich flavors ideal for organic yield. Hybrid seeds, while engineered for higher uniformity and disease resistance, may require external inputs that conflict with organic principles. Selecting seeds that align with organic standards ensures sustainable growth, soil health, and long-term productivity.
Related Important Terms
Open-Pollinated Varieties
Open-pollinated heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and adapt well to local organic farming conditions, often producing resilient, high-quality yields without synthetic inputs. In contrast, hybrid seeds may offer higher initial yields but can lack seed-saving capability and long-term adaptability crucial for sustainable organic systems.
Genetic Purity
Heirloom seeds maintain genetic purity through open pollination, preserving traits that enhance resilience and flavor in organic farming systems. Hybrid seeds, produced by crossbreeding specific plants, often lose genetic consistency in subsequent generations, making them less ideal for sustainable organic yield.
Landrace Seeds
Landrace seeds, known for their genetic diversity and adaptability to local organic farming conditions, often outperform hybrid seeds in sustaining long-term soil health and yield stability. Unlike hybrids, heirloom landrace seeds provide organic farmers with resilient crops that thrive without synthetic inputs, preserving biodiversity and enhancing ecosystem balance.
F1 Hybrid Sterility
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and thrive in organic farming by producing stable, fertile crops over generations, whereas F1 hybrid seeds often suffer from hybrid sterility, leading to lower seed viability in subsequent plantings. This sterility in F1 hybrids reduces organic yield sustainability since farmers cannot save seeds without losing hybrid vigor, unlike heirloom varieties that ensure consistent organic crop productivity.
Seed Sovereignty
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and empower farmers with seed sovereignty by allowing them to save and exchange seeds naturally adapted to local organic conditions. Hybrid seeds, while often higher yielding, limit seed saving and dependency on commercial suppliers, posing challenges to sustainable organic farming practices.
Pollinator-Dependent Cultivars
Heirloom seeds, prized for their genetic diversity and adaptation to local environments, support robust pollinator-dependent cultivars that enhance organic yield stability through natural cross-pollination. Hybrid seeds, while often offering higher immediate yields, may rely less on pollinator interactions and can reduce biodiversity essential for sustaining organic farming ecosystems.
Epigenetic Adaptation
Heirloom seeds exhibit greater epigenetic adaptation in organic farming systems, promoting resilience and sustainable yield under variable environmental conditions compared to hybrid seeds. The genetic stability of heirlooms enables organic crops to better respond to soil microbiome interactions and stress factors, enhancing long-term productivity.
True-to-Type Traits
Heirloom seeds preserve true-to-type traits, ensuring consistent genetic qualities that align with organic farming's emphasis on biodiversity and seed saving. Hybrid seeds, while often higher-yielding, can lose these stable traits in subsequent generations, making them less reliable for organic yield sustainability.
Biodiverse Resilience
Heirloom seeds promote biodiverse resilience by preserving genetic diversity, enhancing soil health, and supporting ecosystem stability in organic farming systems. Hybrid seeds often prioritize uniform yield and disease resistance but may reduce genetic variability, potentially limiting long-term adaptability and ecological balance.
Heritage Seed Revival
Heirloom seeds used in organic farming preserve genetic diversity and adapt better to local conditions, often resulting in resilient, flavorful crops, while hybrid seeds prioritize uniformity and higher yields but may lack long-term sustainability. Heritage Seed Revival emphasizes restoring traditional heirloom varieties to support organic yield through natural pest resistance and enhanced soil health.
Heirloom seeds vs hybrid seeds for organic yield Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com