Neem oil and pyrethrin are both effective options for organic pest management in pet care, with neem oil offering a broad-spectrum, long-lasting effect by disrupting insect growth and reproduction. Pyrethrin provides rapid knockdown of pests but tends to break down quickly in the environment, requiring more frequent application. Choosing between neem oil and pyrethrin depends on the specific pest challenge, desired duration of control, and sensitivity of the pets involved.
Table of Comparison
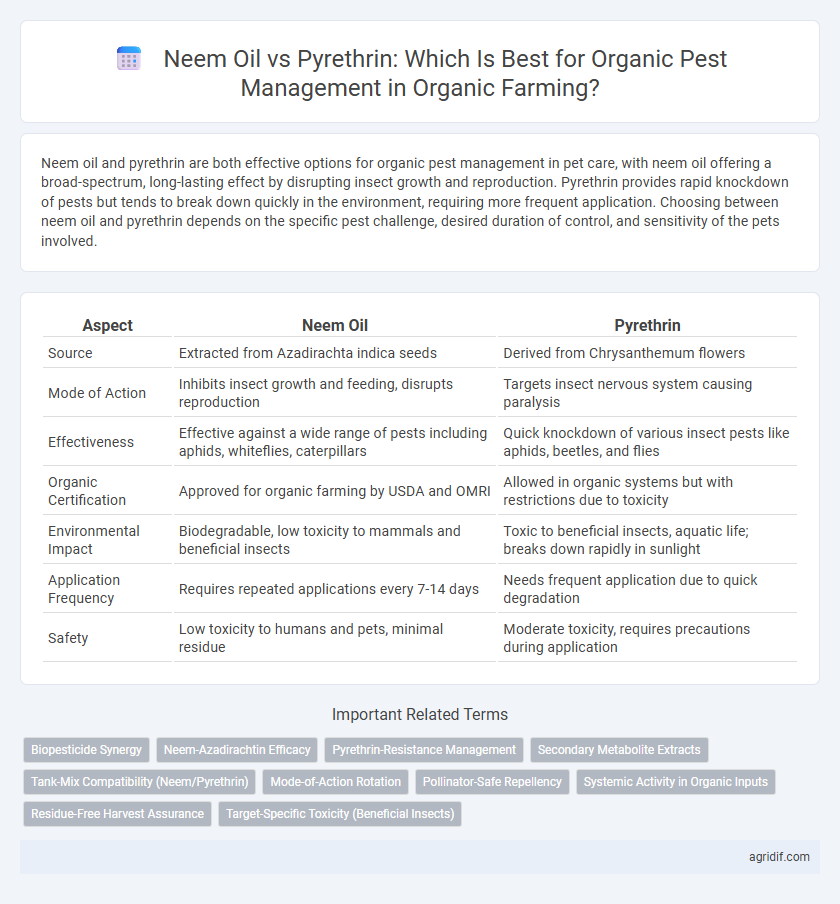
| Aspect | Neem Oil | Pyrethrin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from Azadirachta indica seeds | Derived from Chrysanthemum flowers |
| Mode of Action | Inhibits insect growth and feeding, disrupts reproduction | Targets insect nervous system causing paralysis |
| Effectiveness | Effective against a wide range of pests including aphids, whiteflies, caterpillars | Quick knockdown of various insect pests like aphids, beetles, and flies |
| Organic Certification | Approved for organic farming by USDA and OMRI | Allowed in organic systems but with restrictions due to toxicity |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity to mammals and beneficial insects | Toxic to beneficial insects, aquatic life; breaks down rapidly in sunlight |
| Application Frequency | Requires repeated applications every 7-14 days | Needs frequent application due to quick degradation |
| Safety | Low toxicity to humans and pets, minimal residue | Moderate toxicity, requires precautions during application |
Introduction to Organic Pest Management
Neem oil and pyrethrin are widely used in organic pest management due to their natural insecticidal properties. Neem oil, derived from the neem tree, disrupts insect growth and reproduction while also providing antifungal benefits, making it effective against a broad spectrum of pests. Pyrethrin, extracted from chrysanthemum flowers, acts quickly by targeting the nervous system of insects, offering rapid knockdown of pests with minimal impact on beneficial insects when used correctly.
Understanding Neem Oil: Sources and Properties
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, contains bioactive compounds such as azadirachtin that disrupt insect growth and feeding behavior. Its biodegradable and low-toxicity properties make it highly suitable for organic pest management, providing a broad spectrum of control against aphids, whiteflies, and other common pests. Unlike pyrethrin, which is extracted from chrysanthemum flowers and causes rapid insect paralysis, neem oil acts more gradually by inhibiting reproduction and deterring infestation, ensuring minimal impact on beneficial insects and soil health.
What Is Pyrethrin? Origins and Composition
Pyrethrin is a natural insecticide extracted from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium and Chrysanthemum coccineum, belonging to the Asteraceae family. It consists of six related esters that target the nervous system of insects, causing paralysis and death, making it highly effective for organic pest management. Derived from plant-based sources, pyrethrin offers quick knockdown effects while breaking down rapidly in sunlight, minimizing environmental persistence.
Mechanisms of Action: Neem Oil vs Pyrethrin
Neem oil disrupts insect hormone systems by inhibiting molting and reproduction through its active compound azadirachtin, leading to reduced pest populations over time. Pyrethrin acts on the nervous system of insects by targeting sodium channels, causing paralysis and rapid knockdown of pests. Both are effective organic pesticides, but neem oil provides longer-term pest control while pyrethrin offers immediate but short-lived action.
Efficacy Against Common Agricultural Pests
Neem oil and pyrethrin are both effective organic pesticides, but they differ in their spectrum and mode of action against common agricultural pests. Neem oil disrupts insect growth and feeding by targeting hormonal systems, making it highly effective against aphids, whiteflies, and mites while also providing antifungal properties. Pyrethrin offers rapid knockdown of soft-bodied insects like caterpillars and beetles, acting on the nervous system for quick pest suppression but with a shorter residual effect compared to neem oil.
Safety and Toxicity: Impacts on Humans and Non-target Species
Neem oil exhibits lower toxicity to humans and beneficial insects due to its natural azadirachtin compounds, making it a safer option for organic pest management. Pyrethrin, while effective, poses higher risks to pollinators and aquatic organisms because of its neurotoxic effects. Careful application of neem oil minimizes environmental impact and protects non-target species in organic farming systems.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Residue and Persistence
Neem oil degrades rapidly in sunlight and breaks down into non-toxic compounds, resulting in minimal environmental persistence and low residue levels on crops. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, also breaks down quickly but can be more toxic to beneficial insects and aquatic life, leading to concerns about its impact despite low residue persistence. Both substances are favored in organic farming for pest control, but neem oil's biodegradability and lower toxicity to non-target organisms enhance its environmental profile.
Application Methods and Timing for Optimal Results
Neem oil is typically applied as a foliar spray targeting early pest infestations, with effectiveness peaking within 24-48 hours post-application ideally repeated every 7-14 days depending on pest pressure. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, acts rapidly and requires frequent application every 5-7 days due to its quick degradation in sunlight, often best used during cooler parts of the day to minimize volatilization. Both agents demand precise timing aligned with pest life cycles and environmental conditions to maximize pest suppression while maintaining organic certification standards.
Regulatory Status and Organic Certification
Neem oil is widely accepted in organic farming due to its natural origin from the neem tree and minimal environmental impact, meeting stringent organic certification standards set by organizations like USDA Organic and OMRI. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, is also approved for use in organic agriculture but faces stricter regulatory scrutiny because of its potential toxicity to beneficial insects and aquatic life. Compliance with organic certification bodies requires thorough documentation and adherence to application guidelines, ensuring both substances maintain their regulatory status as permissible organic pest management tools.
Choosing Between Neem Oil and Pyrethrin: Key Considerations
Neem oil and pyrethrin are both effective organic pest management options, but neem oil acts as a systemic insect repellent with antifungal properties, making it ideal for long-term pest control and plant health improvement. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, offers fast-acting contact insecticide effects suitable for immediate pest knockdown but may require more frequent applications. Choosing between them depends on pest type, application frequency, crop sensitivity, and environmental impact considerations in organic farming.
Related Important Terms
Biopesticide Synergy
Neem oil and pyrethrin exhibit biopesticide synergy in organic pest management by combining neem's ability to disrupt insect growth and reproduction with pyrethrin's rapid neurotoxic effects on pests. This synergistic action enhances pest mortality rates while reducing the likelihood of resistance development, making the combination highly effective for sustainable organic farming.
Neem-Azadirachtin Efficacy
Neem oil, rich in azadirachtin, disrupts insect growth and reproduction, offering long-lasting control against a wide range of pests in organic farming. Pyrethrin provides rapid knockdown effects but lacks the systemic efficacy and prolonged pest resistance that neem azadirachtin delivers in sustainable pest management.
Pyrethrin-Resistance Management
Pyrethrin exhibits a rapid knockdown effect on pests but poses a high risk of resistance development due to its neurotoxic mode of action targeting sodium channels. Neem oil offers a multi-site mode of action with insect growth regulators that reduce resistance risks, making it essential to rotate with pyrethrin in organic farming to effectively manage pyrethrin-resistance.
Secondary Metabolite Extracts
Neem oil, rich in azadirachtin, disrupts insect growth and reproduction by acting as a potent secondary metabolite extract with antifeedant and repellent properties. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, serves as a natural neurotoxin targeting the nervous system of pests, offering rapid knockdown but with shorter residual effects compared to the prolonged activity of neem oil in organic pest management.
Tank-Mix Compatibility (Neem/Pyrethrin)
Neem oil and pyrethrin exhibit high tank-mix compatibility in organic pest management, allowing simultaneous application without reducing efficacy or causing phytotoxicity. This combination enhances pest control by leveraging neem oil's antifeedant properties and pyrethrin's rapid insecticidal action, optimizing organic crop protection strategies.
Mode-of-Action Rotation
Neem oil disrupts insect growth and reproduction by inhibiting molting hormone, while pyrethrin rapidly targets the nervous system causing paralysis and death; rotating these modes of action in organic pest management reduces resistance development in pests, enhancing long-term efficacy. Employing a strategic rotation between azadirachtin-based neem oil and neurotoxic pyrethrin aligns with sustainable agriculture practices and regulatory standards for organic certification.
Pollinator-Safe Repellency
Neem oil and pyrethrin offer effective organic pest management solutions, but neem oil is favored for its pollinator-safe repellency due to its selective action on pests without harming beneficial insects like bees and butterflies. Pyrethrin, while natural, poses higher toxicity risks to pollinators, making neem oil a preferred choice for sustainable, pollinator-friendly organic farming practices.
Systemic Activity in Organic Inputs
Neem oil exhibits systemic activity by penetrating plant tissues and disrupting insect feeding and reproduction, making it effective for long-lasting pest control in organic farming. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, acts primarily as a contact insecticide with limited systemic properties, providing rapid but short-term pest knockdown.
Residue-Free Harvest Assurance
Neem oil and pyrethrin are both effective organic pest management solutions, but neem oil offers a significant advantage in residue-free harvest assurance due to its rapid biodegradation and minimal persistence on crops. Pyrethrin, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, may leave trace residues that break down slower, making neem oil the preferred choice for farmers prioritizing clean, residue-free organic produce.
Target-Specific Toxicity (Beneficial Insects)
Neem oil demonstrates selective toxicity by primarily disrupting the feeding and reproduction of pest insects while causing minimal harm to beneficial insects like bees and ladybugs, supporting ecological balance in organic farming. Pyrethrin, though effective against a broad spectrum of pests, exhibits higher toxicity to beneficial insects, potentially threatening pollinator populations and natural predators critical for sustainable pest management.
Neem oil vs pyrethrin for organic pest management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com