Mulching in organic farming provides natural weed suppression by blocking sunlight and enriching the soil with organic matter, promoting healthier plant growth and improved soil structure. Plastic sheeting effectively prevents weed growth by creating a physical barrier but can lead to soil overheating and reduced microbial activity, which may harm long-term soil health. Choosing mulching supports sustainable pet-safe organic farming by enhancing soil fertility while suppressing weeds naturally.
Table of Comparison
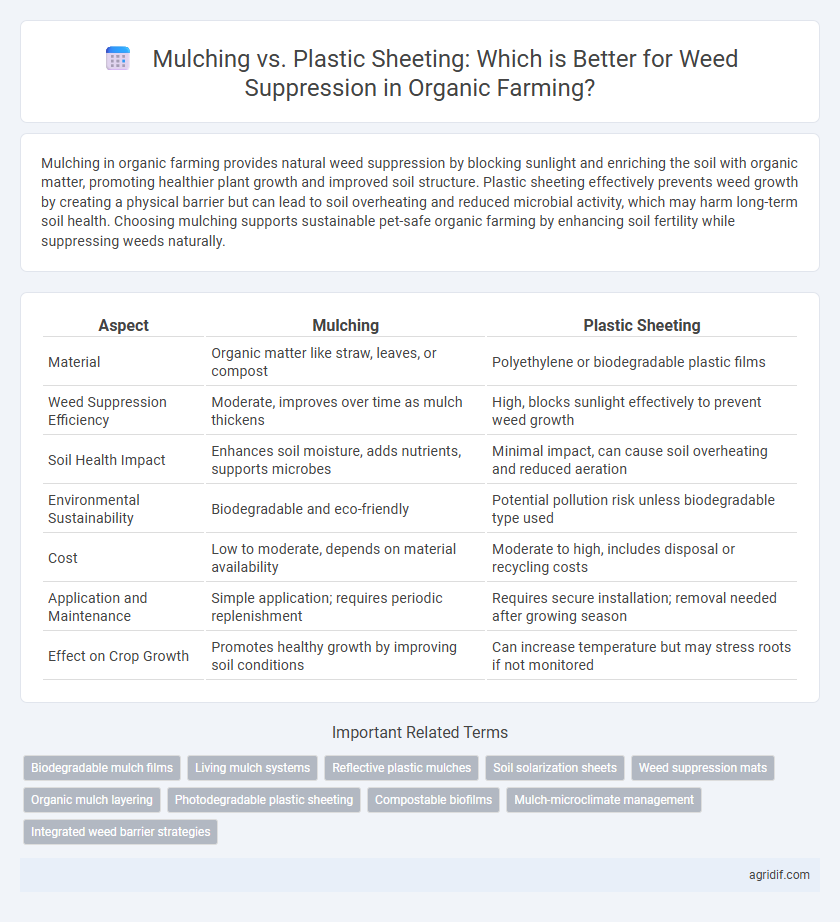
| Aspect | Mulching | Plastic Sheeting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Organic matter like straw, leaves, or compost | Polyethylene or biodegradable plastic films |
| Weed Suppression Efficiency | Moderate, improves over time as mulch thickens | High, blocks sunlight effectively to prevent weed growth |
| Soil Health Impact | Enhances soil moisture, adds nutrients, supports microbes | Minimal impact, can cause soil overheating and reduced aeration |
| Environmental Sustainability | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Potential pollution risk unless biodegradable type used |
| Cost | Low to moderate, depends on material availability | Moderate to high, includes disposal or recycling costs |
| Application and Maintenance | Simple application; requires periodic replenishment | Requires secure installation; removal needed after growing season |
| Effect on Crop Growth | Promotes healthy growth by improving soil conditions | Can increase temperature but may stress roots if not monitored |
Understanding Mulching and Plastic Sheeting in Organic Farming
Mulching in organic farming involves applying organic materials like straw, leaves, or compost to suppress weeds, enhance soil moisture, and improve soil health through natural decomposition. Plastic sheeting, often made from biodegradable or recycled materials in organic systems, physically blocks sunlight to prevent weed growth but does not contribute organic matter to the soil. Understanding the benefits and limitations of both methods helps optimize weed control strategies while maintaining soil fertility and sustainability in organic farming practices.
Natural Mulches: Types and Applications
Natural mulches, such as straw, wood chips, and compost, provide effective weed suppression by blocking sunlight and improving soil moisture retention, while enriching soil organic matter. These organic materials gradually decompose, enhancing soil fertility and promoting beneficial microbial activity crucial for sustainable organic farming. Selecting appropriate mulch types depends on crop requirements and local climate conditions to maximize weed control and soil health benefits.
Plastic Sheeting: Options and Usage in Weed Control
Plastic sheeting, commonly made from polyethylene, offers an effective barrier against weed growth by blocking sunlight and preventing weed seed germination in organic farming. Available in various thicknesses and colors, black plastic sheeting is the most popular choice for weed suppression due to its durability and heat retention properties that also promote soil warming. Proper installation and disposal of plastic sheeting are essential to minimize environmental impact and ensure compliance with organic farming standards.
Comparative Effectiveness for Weed Suppression
Mulching with organic materials such as straw, wood chips, or compost improves soil health while effectively suppressing weeds by blocking sunlight and retaining moisture, promoting sustainable farming practices. Plastic sheeting, commonly polyethylene, provides a strong physical barrier against weeds but may contribute to soil temperature fluctuations and hinder water infiltration, potentially impacting soil microbiota negatively. Comparative studies indicate organic mulches enhance long-term weed control and soil fertility, whereas plastic sheeting offers immediate, high-efficiency weed suppression at the cost of environmental concerns and reduced soil quality.
Impact on Soil Health and Microbial Activity
Mulching enhances soil health by improving moisture retention, regulating temperature, and promoting microbial activity through organic matter decomposition. In contrast, plastic sheeting suppresses weeds effectively but can impede gas exchange and reduce microbial diversity due to lack of organic input. Organic mulches support nutrient cycling and beneficial soil organisms, fostering a more resilient and fertile soil ecosystem compared to plastic sheeting.
Moisture Retention: Mulch vs Plastic Sheeting
Mulching enhances soil moisture retention by creating a breathable barrier that reduces evaporation while allowing air and water exchange, promoting healthier root systems. In contrast, plastic sheeting significantly limits moisture loss by forming an impermeable layer but may cause water runoff and restrict soil aeration, potentially impacting soil health. Organic mulches also contribute nutrients as they decompose, improving soil structure beyond mere moisture conservation.
Environmental Sustainability and Decomposition
Mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips enhances environmental sustainability by enriching soil health through natural decomposition, releasing nutrients and improving moisture retention. Plastic sheeting, while effective for weed suppression, poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature, contributing to soil pollution and waste management issues. Organic mulches support biodiversity and carbon sequestration, making them a preferred choice for sustainable farming practices.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Mulching with organic materials such as straw or wood chips typically incurs lower upfront costs compared to plastic sheeting but may require more frequent replacement and labor for application. Plastic sheeting offers more effective long-term weed suppression and moisture retention, potentially reducing irrigation and herbicide expenses, yet its initial investment and disposal costs can be higher and less environmentally sustainable. Economic considerations favor mulching in low-budget or small-scale organic farms, while plastic sheeting may suit larger operations prioritizing labor efficiency and prolonged weed control.
Practical Challenges and Labor Requirements
Mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips enhances soil health but demands frequent replenishment and intensive manual labor for effective weed suppression. Plastic sheeting offers a more durable barrier against weeds, reducing labor intensity but can cause soil overheating and hinder moisture infiltration. Farmers must balance the sustainable benefits of mulching against the convenience and potential environmental drawbacks of plastic sheeting in organic farming systems.
Choosing the Best Weed Suppression Method for Your Farm
Mulching using organic materials such as straw or wood chips improves soil moisture retention and enriches soil health while suppressing weeds effectively on organic farms. Plastic sheeting offers a more immediate and durable weed barrier but does not contribute to soil fertility and may cause overheating or soil degradation. Selecting the best weed suppression method depends on balancing farm goals, long-term soil health priorities, and the specific crop requirements.
Related Important Terms
Biodegradable mulch films
Biodegradable mulch films offer an eco-friendly alternative to plastic sheeting by suppressing weeds effectively while decomposing naturally, reducing soil pollution and environmental impact in organic farming systems. These films enhance soil moisture retention and temperature regulation, promoting healthier crop growth without the disposal challenges associated with conventional plastic mulches.
Living mulch systems
Living mulch systems enhance weed suppression by establishing cover crops that compete with weeds while improving soil health, unlike plastic sheeting which provides a physical barrier but can hinder soil aeration and microbial activity. These organic mulches contribute to increased biodiversity, moisture retention, and nutrient cycling, offering sustainable advantages in organic farming practices.
Reflective plastic mulches
Reflective plastic mulches enhance weed suppression by reflecting sunlight, which disrupts weed seed germination and growth more effectively than traditional organic mulches. They also help increase soil temperature and moisture retention, boosting crop yield in organic farming systems.
Soil solarization sheets
Soil solarization sheets, a form of plastic sheeting used in organic farming, leverage solar energy to effectively suppress weeds by increasing soil temperature and disrupting weed seed germination. Unlike traditional mulching, these sheets enhance soil sterilization and nutrient retention while minimizing chemical use, promoting healthier crop growth and sustainable weed control.
Weed suppression mats
Weed suppression mats provide effective organic mulching by blocking sunlight, reducing weed growth while retaining soil moisture and improving soil health without synthetic inputs. Unlike plastic sheeting, these biodegradable mats enhance soil aeration and microbial activity, supporting sustainable weed management in organic farming systems.
Organic mulch layering
Organic mulch layering effectively suppresses weeds by blocking sunlight and enhancing soil moisture retention, promoting beneficial microbial activity that improves soil health. Unlike plastic sheeting, organic mulches decompose naturally, adding nutrients to the soil while preventing weed growth without the environmental drawbacks of plastic waste.
Photodegradable plastic sheeting
Photodegradable plastic sheeting offers effective weed suppression in organic farming by breaking down under sunlight, reducing plastic waste compared to conventional plastic mulches. This method enhances soil moisture retention and temperature regulation while minimizing labor for weed control, aligning with sustainable agricultural practices.
Compostable biofilms
Compostable biofilm mulching offers a sustainable alternative to plastic sheeting by effectively suppressing weeds while enhancing soil health and reducing environmental impact in organic farming systems. These biofilms decompose naturally, enriching soil organic matter and promoting microbial activity, unlike conventional plastic that contributes to landfill waste and soil contamination.
Mulch-microclimate management
Mulching enhances soil moisture retention, moderates soil temperature, and improves microbial activity, creating a favorable microclimate for organic crop growth, unlike plastic sheeting which can lead to soil overheating and reduced aeration. Organic mulches like straw or wood chips decompose over time, enriching soil structure and nutrient content, thereby supporting sustainable weed suppression while promoting overall soil health.
Integrated weed barrier strategies
Mulching with organic materials such as straw or wood chips improves soil health by enhancing moisture retention and nutrient cycling, while plastic sheeting provides a more immediate and effective weed suppression by blocking sunlight, reducing water evaporation, and minimizing soil disturbance. Integrated weed barrier strategies combine both methods to optimize weed control, balancing the environmental benefits of organic mulches with the durability and rapid efficacy of plastic sheeting to support sustainable organic farming systems.
Mulching vs Plastic sheeting for weed suppression Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com