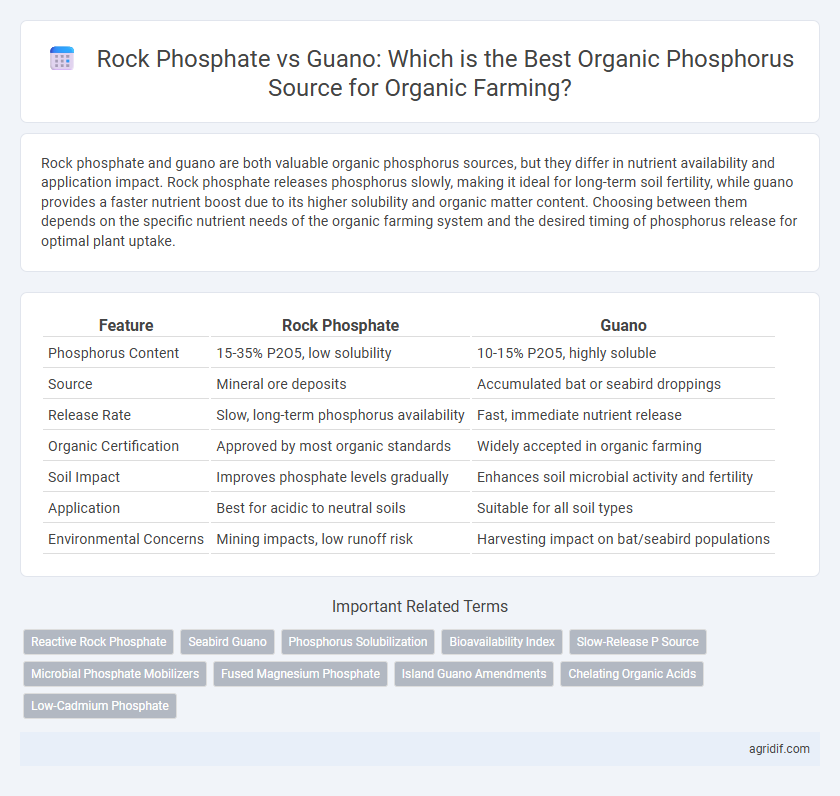
Rock phosphate and guano are both valuable organic phosphorus sources, but they differ in nutrient availability and application impact. Rock phosphate releases phosphorus slowly, making it ideal for long-term soil fertility, while guano provides a faster nutrient boost due to its higher solubility and organic matter content. Choosing between them depends on the specific nutrient needs of the organic farming system and the desired timing of phosphorus release for optimal plant uptake.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rock Phosphate | Guano |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphorus Content | 15-35% P2O5, low solubility | 10-15% P2O5, highly soluble |
| Source | Mineral ore deposits | Accumulated bat or seabird droppings |
| Release Rate | Slow, long-term phosphorus availability | Fast, immediate nutrient release |
| Organic Certification | Approved by most organic standards | Widely accepted in organic farming |
| Soil Impact | Improves phosphate levels gradually | Enhances soil microbial activity and fertility |
| Application | Best for acidic to neutral soils | Suitable for all soil types |
| Environmental Concerns | Mining impacts, low runoff risk | Harvesting impact on bat/seabird populations |
Introduction to Organic Phosphorus Sources
Rock phosphate and guano serve as primary organic phosphorus sources in sustainable agriculture, each offering distinct nutrient release profiles. Rock phosphate provides a slow-release phosphorus supply, ideal for long-term soil fertility improvement, whereas guano, derived from accumulated bat or bird excrement, offers a more readily available phosphorus form, enhancing immediate plant nutrient uptake. Both inputs contribute to organic farming by maintaining phosphorus levels while supporting soil microbial activity and minimizing environmental impact.
Rock Phosphate: Origins and Composition
Rock phosphate is a naturally occurring mineral primarily composed of calcium phosphate, extracted from sedimentary deposits formed in ancient marine environments. This phosphate rock contains varying amounts of phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), essential for plant growth, along with trace minerals that enhance soil fertility in organic farming systems. Its slow-release properties make rock phosphate a preferred organic phosphorus source, enriching soil nutrient content sustainably over time.
Guano: Nature’s Phosphorus-Rich Fertilizer
Guano, a natural fertilizer derived from accumulated seabird or bat excrement, offers a highly bioavailable source of phosphorus that supports robust plant growth in organic farming systems. Unlike rock phosphate, which requires acidic soil conditions for phosphorus release, guano provides readily soluble phosphorus along with essential micronutrients, enhancing soil fertility and microbial activity. Its sustainable harvesting and rich nutrient profile make guano a preferred organic phosphorus input for improving crop yield and soil health.
Nutrient Availability in Rock Phosphate vs Guano
Rock phosphate releases phosphorus slowly due to its low solubility, making nutrient availability gradual but long-lasting in organic farming soils. Guano contains highly bioavailable phosphorus, providing immediate nutrient release and rapid uptake by plants. Choosing between rock phosphate and guano depends on timing and soil phosphorus needs for optimal crop growth.
Soil Compatibility and Application Methods
Rock phosphate offers a slow-release phosphorus source compatible with alkaline and neutral soils, requiring finely ground application to enhance solubility and microbial action. Guano provides readily available phosphorus due to its high organic content, best suited for acidic soils and applied through top-dressing or as a component in compost for rapid nutrient uptake. Both inputs support organic phosphorus availability, but the choice depends on soil pH compatibility and the desired release rate aligned with crop nutrient demands.
Environmental Impact of Rock Phosphate and Guano
Rock phosphate is a slow-release phosphorus source with low solubility that minimizes leaching but may contain heavy metals, raising environmental concerns. Guano, rich in bioavailable phosphorus and nutrients, enhances soil fertility rapidly but harvesting can disrupt ecosystems and deplete natural bird populations. Both inputs require sustainable management to balance phosphorus availability with ecosystem preservation in organic farming systems.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Rock phosphate offers a more cost-effective option for organic phosphorus input, with prices typically lower than guano due to its abundant availability in many regions. Guano, derived from accumulated seabird or bat excrement, tends to be more expensive and less accessible because of limited sources and higher demand. Farmers prioritizing affordability and steady supply often prefer rock phosphate, while guano is chosen for its higher nutrient concentration despite its premium cost and limited availability.
Role in Building Soil Health and Fertility
Rock phosphate and guano serve as critical organic phosphorus sources that enhance soil health and fertility by promoting microbial activity and nutrient availability. Rock phosphate provides a slow-release phosphorus source, improving long-term soil structure and root development, while guano offers a rapid nutrient boost rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and trace minerals that stimulate microbial biomass and organic matter decomposition. The combined use of these materials fosters balanced nutrient cycling, increases soil organic content, and supports sustainable crop productivity in organic farming systems.
Certification Standards for Organic Use
Rock phosphate is widely accepted in organic farming certification standards such as USDA Organic and EU Organic due to its natural mineral origin and slow-release phosphorus benefits. Guano also qualifies under these standards, valued for its high phosphorus content and organic certification compatibility, but its variable nutrient profile requires thorough sourcing verification. Certification bodies emphasize traceability and environmental sustainability, making both inputs compliant when responsibly sourced and processed without synthetic additives.
Choosing the Right Phosphorus Source for Your Farm
Rock phosphate provides a slow-release, natural source of phosphorus ideal for long-term soil enrichment in organic farming systems. Guano, rich in nitrogen and phosphorus, offers a fast-acting nutrient boost but may vary in nutrient content depending on the source. Selecting between rock phosphate and guano depends on your farm's soil pH, crop phosphorus demand, and the desired nutrient release rate to optimize organic phosphorus availability.
Related Important Terms
Reactive Rock Phosphate
Reactive Rock Phosphate provides a slow-release source of organic phosphorus essential for sustainable crop nutrition, offering greater long-term availability compared to rapidly soluble guano. Its mineral composition enhances soil pH buffering and microbial activity, supporting efficient phosphorus uptake in organic farming systems.
Seabird Guano
Seabird guano provides a highly bioavailable source of organic phosphorus, rich in nitrogen and trace minerals that enhance soil fertility more effectively than rock phosphate, which is slower to release nutrients due to its mineral composition. The rapid nutrient cycling and microbial stimulation from seabird guano improve phosphorus uptake in organic farming systems, making it a preferred amendment for sustainable crop production.
Phosphorus Solubilization
Rock phosphate releases phosphorus slowly due to its low solubility, requiring microbial activity for effective phosphorus solubilization in organic farming systems. In contrast, guano contains readily available phosphorus forms and organic acids that enhance phosphorus solubilization and uptake by plants, promoting faster nutrient cycling.
Bioavailability Index
Rock phosphate offers a slower, more sustained release of phosphorus with a bioavailability index typically lower than guano, which contains highly soluble phosphorus compounds that provide quicker uptake by plants. The bioavailability index of guano often exceeds that of rock phosphate by 20-30%, enhancing organic phosphorus availability and accelerating nutrient cycling in organic farming systems.
Slow-Release P Source
Rock phosphate provides a slow-release phosphorus source essential for maintaining nutrient availability in organic farming systems, improving soil fertility over extended periods. Guano also delivers phosphorus but releases nutrients more rapidly, making rock phosphate preferable for sustained phosphorus input in organic crops.
Microbial Phosphate Mobilizers
Rock phosphate provides a slow-release source of phosphorus but relies heavily on microbial phosphate mobilizers like Bacillus and Pseudomonas species to solubilize the mineral for plant uptake, enhancing soil nutrient availability. Guano, rich in readily available organic phosphorus compounds, supports a diverse microbial community that accelerates phosphorus cycling, improving bioavailability and promoting sustainable organic farming systems.
Fused Magnesium Phosphate
Fused Magnesium Phosphate (FMP) offers a more stable and slowly available phosphorus source compared to rock phosphate and guano, enhancing nutrient uptake in organic farming systems. Its balanced magnesium and phosphorus content supports sustainable soil fertility, reducing the risk of phosphorus leaching common with more soluble inputs.
Island Guano Amendments
Island guano amendments provide a highly bioavailable source of organic phosphorus, enhancing soil fertility more effectively than rock phosphate due to their rapid mineralization and rich nutrient profile. While rock phosphate offers a slow-release phosphorus option, island guano supplies essential micronutrients and promotes beneficial microbial activity critical for sustainable organic farming systems.
Chelating Organic Acids
Rock phosphate and guano differ in their efficacy as organic phosphorus sources, with guano providing a more readily available phosphorus due to its richer content of chelating organic acids that enhance phosphorus solubility. Chelating organic acids like citric and oxalic acids in guano play a critical role in mobilizing phosphorus by binding to metal ions, thus improving phosphorus uptake in organic farming systems.
Low-Cadmium Phosphate
Rock phosphate with low-cadmium content offers a safer organic phosphorus input compared to guano, minimizing heavy metal contamination risks in organic farming. Its slow-release properties improve phosphorus availability while maintaining soil health and reducing environmental impact.
Rock phosphate vs guano for organic phosphorus input Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com