Horizontal integration in poultry farming involves expanding by acquiring or merging with other farms at the same production stage, which can increase market share and reduce competition. Vertical integration combines multiple stages of production, from hatcheries to processing and distribution, allowing greater control over quality and cost efficiency. Choosing between horizontal and vertical integration depends on the farm's goals for growth, resource availability, and desired operational control.
Table of Comparison
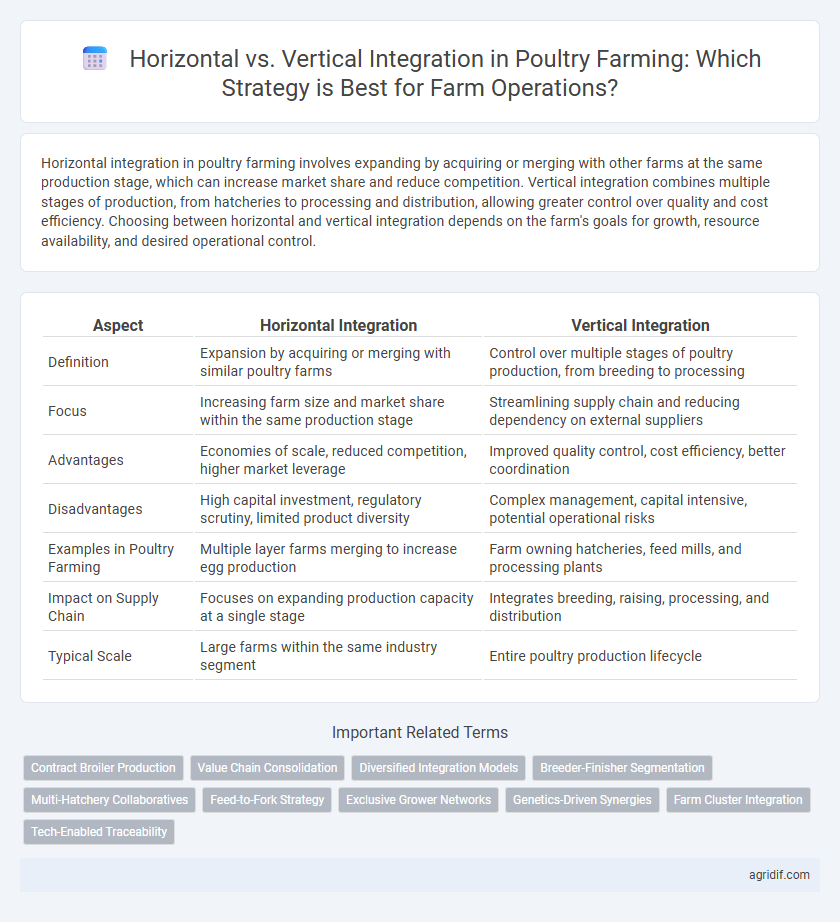
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expansion by acquiring or merging with similar poultry farms | Control over multiple stages of poultry production, from breeding to processing |
| Focus | Increasing farm size and market share within the same production stage | Streamlining supply chain and reducing dependency on external suppliers |
| Advantages | Economies of scale, reduced competition, higher market leverage | Improved quality control, cost efficiency, better coordination |
| Disadvantages | High capital investment, regulatory scrutiny, limited product diversity | Complex management, capital intensive, potential operational risks |
| Examples in Poultry Farming | Multiple layer farms merging to increase egg production | Farm owning hatcheries, feed mills, and processing plants |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Focuses on expanding production capacity at a single stage | Integrates breeding, raising, processing, and distribution |
| Typical Scale | Large farms within the same industry segment | Entire poultry production lifecycle |
Understanding Horizontal Integration in Poultry Farming
Horizontal integration in poultry farming involves expanding operations by acquiring or merging with other poultry farms to increase production capacity and market share. This strategy enables farms to achieve economies of scale, reduce competition, and enhance bargaining power with suppliers and distributors. By concentrating similar production processes, horizontal integration helps optimize resource use and streamline supply chain management across multiple poultry operations.
What is Vertical Integration in Farm Operations?
Vertical integration in farm operations refers to a management approach where a single company controls multiple stages of the poultry production process, from breeding and hatching to processing and distribution. This integration streamlines supply chain management, enhances quality control, and reduces costs by minimizing reliance on external suppliers. By owning various components of the production cycle, poultry farms can achieve greater operational efficiency and improve product consistency.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration in poultry farming involves expanding operations by acquiring or merging with other farms producing similar poultry products, increasing market share and reducing competition. Vertical integration entails controlling multiple stages of production, from hatching chicks to processing meat and distributing products, optimizing the supply chain and reducing costs. Key differences include the scope of control--horizontal integration focuses on growth within the same production stage, while vertical integration manages multiple stages to enhance efficiency and product quality.
Advantages of Horizontal Integration for Poultry Farms
Horizontal integration in poultry farming enhances operational efficiency by expanding the farm's capacity to produce a uniform product, leading to cost reductions through economies of scale. This integration allows poultry farms to increase market share, improve bargaining power with suppliers and distributors, and reduce competition within the same production stage. By consolidating similar operations, farms benefit from streamlined management, shared resources, and improved access to technology and innovation.
Benefits of Vertical Integration in Poultry Production
Vertical integration in poultry production enhances operational efficiency by consolidating supply chain stages, from breeding to processing, under a single management. This integration reduces costs, improves product quality control, and enables faster response to market demands. Access to real-time data through vertically integrated systems facilitates better decision-making and streamlines resource allocation in poultry farms.
Challenges Faced in Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration in poultry farming faces challenges such as increased competition among merged entities, difficulties in coordinating operations across multiple farms, and regulatory hurdles related to monopolistic practices. Managing disease outbreaks becomes more complex due to the larger geographic spread and diverse environmental conditions. Economies of scale may be offset by logistical inefficiencies and varying local market demands.
Limitations of Vertical Integration in Poultry Farming
Vertical integration in poultry farming often faces limitations such as high capital investment requirements and reduced operational flexibility. This model can also lead to increased vulnerability to market fluctuations due to dependence on a single supply chain. Furthermore, vertical integration may limit innovation and adaptation by concentrating control within one company, reducing diverse input and potential collaboration in the farming process.
Economic Impact: Comparing Both Integration Strategies
Horizontal integration in poultry farming consolidates operations across farms, leading to cost reductions through bulk purchasing and shared resources, enhancing market influence and pricing power. Vertical integration controls multiple stages from feed production to processing, improving supply chain efficiency, reducing transaction costs, and securing product quality, which often results in higher profit margins. Economically, vertical integration tends to offer greater long-term stability and control over production variables, while horizontal integration can provide quicker scale expansion and competitive positioning in the regional market.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Integration Approaches
Successful poultry farming operations demonstrate distinct advantages of both horizontal and vertical integration strategies. Tyson Foods exemplifies vertical integration by controlling breeding, hatching, feed production, processing, and distribution, leading to enhanced efficiency and quality control across its supply chain. In contrast, Pilgrim's Pride utilizes horizontal integration by acquiring regional farms to expand market share and leverage economies of scale, resulting in increased production capacity and competitive pricing.
Choosing the Right Integration Model for Your Poultry Farm
Selecting the appropriate integration model for a poultry farm depends on factors such as scale, resource availability, and market control objectives. Horizontal integration involves expanding within the same production stage to increase market share, while vertical integration combines multiple stages like breeding, feed production, and processing to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Evaluating operational capacity and long-term goals ensures optimal alignment with either horizontal or vertical integration strategies to maximize profitability and sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Contract Broiler Production
Contract broiler production in poultry farming benefits from vertical integration by streamlining supply chains, enhancing quality control, and reducing production costs through centralized management from hatchery to processing. Horizontal integration, involving expansion across similar production units, increases market share and resource efficiency but may face challenges in maintaining consistent contract compliance and operational oversight.
Value Chain Consolidation
Horizontal integration in poultry farming consolidates similar operations such as multiple farms or processing plants, enhancing market share and bargaining power within the value chain. Vertical integration combines sequential stages of production from feed supply to processing and distribution, enabling tighter control over quality, cost efficiency, and supply chain reliability.
Diversified Integration Models
Horizontal integration in poultry farming involves expanding operations by acquiring or merging with farms producing similar products, enhancing market share and reducing competition. Vertical integration consolidates multiple stages of production--from hatcheries to processing--within one organization, improving control over supply chains, reducing costs, and ensuring product consistency through diversified integration models.
Breeder-Finisher Segmentation
Horizontal integration in poultry farming involves expanding breeder-finisher segmentation by acquiring or merging with similar operations to increase scale and market share, enhancing genetic diversity and production capacity. Vertical integration streamlines breeder-finisher processes within a single company, optimizing supply chain control, reducing costs, and improving biosecurity and product consistency across the entire poultry production cycle.
Multi-Hatchery Collaboratives
Multi-hatchery collaboratives in poultry farming enhance vertical integration by streamlining hatchery operations, improving genetic consistency, and optimizing chick quality control across farms. Horizontal integration fosters resource sharing and reduces costs through cooperative management of multiple hatcheries, increasing market competitiveness and operational scalability.
Feed-to-Fork Strategy
Horizontal integration in poultry farming expands operations by acquiring or merging with other farms at the same level, enhancing market share and resource pooling, while vertical integration controls multiple stages from feed production to processing and retail, optimizing the feed-to-fork supply chain for efficiency, quality control, and cost reduction. Implementing a vertical integration feed-to-fork strategy enables tighter coordination of feed formulation, bird health management, processing standards, and distribution logistics, ensuring consistent product quality and traceability from farm to consumer.
Exclusive Grower Networks
Exclusive grower networks enhance vertical integration in poultry farming by allowing companies to control multiple stages of production from breeding to processing, improving quality and consistency. In contrast, horizontal integration combines farms at a single production level, which can increase scale but lacks the same degree of oversight across the entire supply chain.
Genetics-Driven Synergies
Horizontal integration in poultry farming enhances genetics-driven synergies by expanding breeding stock across multiple farms, allowing for more diverse gene pools and improved disease resistance. Vertical integration consolidates breeding, hatchery, and grow-out processes, optimizing genetic selection and uniformity to maximize productivity and biosecurity efficiencies within a controlled supply chain.
Farm Cluster Integration
Farm cluster integration in poultry farming enhances operational efficiency by combining horizontal integration, which unites multiple farms at the same production stage, with vertical integration, linking different stages from breeding to processing. This integrated approach optimizes resource use, reduces costs, and strengthens supply chain control, driving productivity and profitability in competitive markets.
Tech-Enabled Traceability
Tech-enabled traceability in poultry farming enhances both horizontal and vertical integration by providing real-time data on supply chain activities, improving biosecurity and operational efficiency. Implementing blockchain and IoT sensors allows farms to monitor product quality from hatch to market, ensuring transparency and compliance across integrated operations.
Horizontal vs Vertical Integration for Farm Operations Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com