Breeder Seed is the original genetic stock developed by plant breeders, ensuring the highest purity and genetic identity for seed multiplication. Foundation Seed, derived from Breeder Seed, maintains genetic purity and uniformity while serving as the primary source for producing Certified Seed. Utilizing Foundation Seed in seed multiplication guarantees consistent crop quality and performance, essential for successful agricultural production.
Table of Comparison
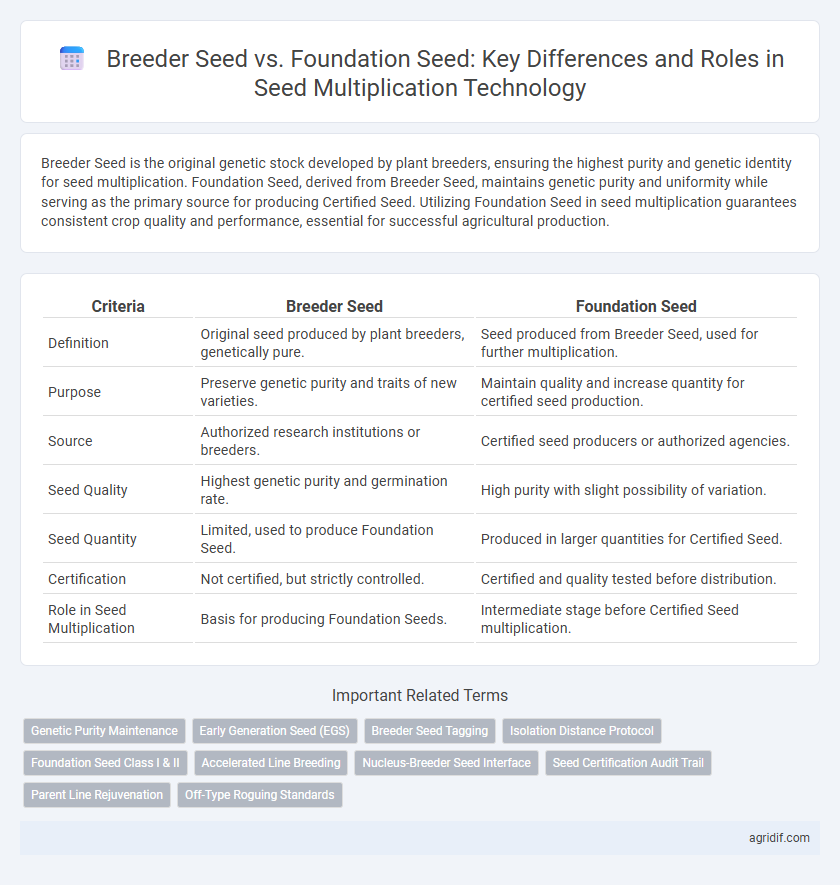
| Criteria | Breeder Seed | Foundation Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Original seed produced by plant breeders, genetically pure. | Seed produced from Breeder Seed, used for further multiplication. |
| Purpose | Preserve genetic purity and traits of new varieties. | Maintain quality and increase quantity for certified seed production. |
| Source | Authorized research institutions or breeders. | Certified seed producers or authorized agencies. |
| Seed Quality | Highest genetic purity and germination rate. | High purity with slight possibility of variation. |
| Seed Quantity | Limited, used to produce Foundation Seed. | Produced in larger quantities for Certified Seed. |
| Certification | Not certified, but strictly controlled. | Certified and quality tested before distribution. |
| Role in Seed Multiplication | Basis for producing Foundation Seeds. | Intermediate stage before Certified Seed multiplication. |
Introduction to Seed Classes in Agriculture
Breeder seed represents the initial pure seed source, developed and maintained by the plant breeder, ensuring genetic purity and true-to-type characteristics essential for seed multiplication. Foundation seed is directly produced from breeder seed under strict supervision to maintain genetic identity, serving as the base for producing certified seed used by farmers. Both seed classes play a critical role in the seed supply chain by preserving genetic integrity and supporting high-quality crop production in agriculture.
Defining Breeder Seed: Origin and Characteristics
Breeder seed is the initial seed source produced by the plant breeder or originating institution, ensuring the genetic purity and authenticity of a crop variety. It serves as the foundation for all subsequent seed multiplication stages and maintains strict quality control to preserve genetic traits. Originating directly from breeder's stock, breeder seed exhibits uniformity, high germination rates, and freedom from diseases, setting a benchmark for foundation seed production.
Understanding Foundation Seed: Key Features
Foundation seed serves as the critical link between breeder seed and commercial seed production, maintaining genetic purity and high quality essential for successful seed multiplication. It is produced directly from breeder seed under strict supervision to ensure authenticity and uniformity in traits. The controlled production and certification processes of foundation seed help guarantee seed viability and optimal field performance for large-scale agricultural use.
Breeder Seed Production Process
Breeder seed production involves the initial stage of seed multiplication where genetically pure parent lines are developed and maintained under strict conditions to ensure genetic integrity and high seed quality. This process uses controlled environments, meticulous record-keeping, and rigorous testing to produce breeder seeds, which serve as the genetic source for foundation seed production. Maintaining strict isolation and implementing disease management protocols are critical to preserving the genetic purity and vigor of breeder seeds in seed technology.
Foundation Seed Multiplication Techniques
Foundation seed multiplication techniques emphasize maintaining genetic purity and high germination rates by using controlled isolation and strict field inspections. The process involves precise seed treatment, roguing of off-types, and optimal planting densities to ensure uniform growth and vigor. Foundation seeds serve as the critical link between breeder seeds and certified seeds, providing high-quality planting material essential for successful commercial seed production.
Genetic Purity: Breeder vs Foundation Seed
Breeder seeds possess the highest level of genetic purity as they are directly produced and maintained by the plant breeder to preserve the original cultivar traits. Foundation seeds, derived from breeder seeds, maintain high genetic purity but may undergo slight changes due to environmental factors during their multiplication. Strict quality control measures ensure that both breeder and foundation seeds retain the genetic identity essential for successful seed multiplication and crop performance.
Role of Breeder and Foundation Seed in Seed Chain
Breeder seed acts as the genetic source in the seed chain, developed and maintained by plant breeders to ensure genetic purity and true-to-type characteristics. Foundation seed, derived from breeder seed, serves as the primary seed for large-scale multiplication, preserving genetic integrity while increasing quantity. The role of breeder seed is to provide the original elite genotype, whereas foundation seed ensures consistent quality as it transitions toward commercial seed production.
Certification Standards for Breeder and Foundation Seeds
Breeder seed is the initial seed source directly derived from the genetic stock and must comply with strict certification standards ensuring genetic purity and identity, serving as the reference for all subsequent seed classes. Foundation seed is produced from breeder seed under controlled conditions and is subjected to rigorous certification protocols that verify physical purity, germination rates, and varietal characteristics to maintain seed quality during multiplication. Adhering to these certification standards guarantees the integrity and performance of seeds throughout the seed multiplication process, crucial for agricultural productivity and cultivar uniformity.
Key Differences: Breeder Seed vs Foundation Seed
Breeder seed is the initial, genetically pure seed produced by the plant breeder and serves as the primary source for all subsequent seed generations. Foundation seed is derived from breeder seed and undergoes rigorous quality testing and certification to ensure genetic purity and high germination rates, making it suitable for further multiplication. Key differences include the origin (breeder seed from the breeding program, foundation seed from breeder seed) and certification level, with foundation seed being certified for commercial seed production.
Importance of Seed Classes in Sustainable Agriculture
Breeder seed forms the genetic base for all subsequent seed classes, ensuring the purity and quality of crop varieties essential for sustainable agriculture. Foundation seed, derived from breeder seed, serves as the critical source for producing certified seeds that farmers use to optimize yield and maintain genetic integrity. The strict regulation and management of these seed classes guarantee long-term crop resilience, productivity, and ecosystem balance in sustainable farming systems.
Related Important Terms
Genetic Purity Maintenance
Breeder seed serves as the original source with the highest genetic purity, ensuring the integrity of the crop's traits during seed multiplication. Foundation seed, derived from breeder seed, maintains strict quality controls and genetic purity standards to preserve varietal identity throughout large-scale propagation.
Early Generation Seed (EGS)
Breeder Seed represents the original genetic material produced by plant breeders and serves as the highest quality seed source for producing Early Generation Seed (EGS), ensuring genetic purity and uniformity. Foundation Seed, derived from Breeder Seed, is multiplied under strict supervision to maintain seed quality and provides the critical link for large-scale seed multiplication before distribution to commercial growers.
Breeder Seed Tagging
Breeder seed tagging is crucial in seed multiplication as it certifies genetic purity and ensures traceability from the original breeding process, distinguishing it from foundation seed which serves as the next generation for large-scale production. Accurate breeder seed tagging maintains the integrity of seed quality and supports the regulation of seed distribution within certified seed systems.
Isolation Distance Protocol
Breeder seed requires strict isolation distance protocols typically ranging from 400 to 800 meters to prevent genetic contamination, ensuring high genetic purity for subsequent seed multiplication stages. Foundation seed isolation distances often vary between 200 to 400 meters, balancing genetic purity maintenance with increased production scale for certified seed development.
Foundation Seed Class I & II
Foundation Seed Class I and II serve as critical intermediates in seed multiplication, providing genetically pure and high-quality seed derived from breeder seed to ensure uniform crop production. While breeder seed represents the original genetic stock developed by plant breeders, Foundation Seed Class I and II undergo rigorous quality control and certification processes, facilitating large-scale multiplication while maintaining genetic purity and varietal identity essential for commercial seed production.
Accelerated Line Breeding
Breeder Seed, produced directly from the breeder's original stock, ensures genetic purity and serves as the source for Foundation Seed, which undergoes initial multiplication while maintaining high genetic fidelity. In accelerated line breeding, utilizing Breeder Seed allows faster generation advancement and precise selection, enhancing genetic gain and uniformity during subsequent Foundation Seed multiplication stages.
Nucleus-Breeder Seed Interface
The Nucleus-Breeder seed interface ensures genetic purity and integrity by maintaining strict isolation and certification protocols at the Breeder Seed stage, which is critical before transitioning to Foundation Seed multiplication. Effective management of this interface allows breeders to deliver high-quality, genetically stable seeds that serve as the cornerstone for subsequent large-scale seed multiplication.
Seed Certification Audit Trail
Breeder Seed serves as the original, genetically pure seed source, while Foundation Seed is the direct progeny used for large-scale seed multiplication, both requiring stringent seed certification audit trails to ensure genetic fidelity and quality. The audit trail involves meticulous documentation of seed origin, handling, and storage practices, enabling traceability and compliance with certification standards essential for maintaining seed purity and farmer trust.
Parent Line Rejuvenation
Breeder seed serves as the primary genetic source for parent line rejuvenation, ensuring the genetic purity and vigor required for subsequent foundation seed production. Foundation seed, derived from breeder seed, maintains genetic stability while scaling seed multiplication for commercial use.
Off-Type Roguing Standards
Breeder seed maintains genetic purity and uniformity with strict off-type roguing standards, typically allowing less than 0.5% off-type plants, ensuring the foundation seed's quality. Foundation seed multiplication enforces rigorous off-type removal protocols, usually permitting up to 1% off-types, to preserve varietal identity while scaling seed volumes.
Breeder Seed vs Foundation Seed for Seed Multiplication Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com