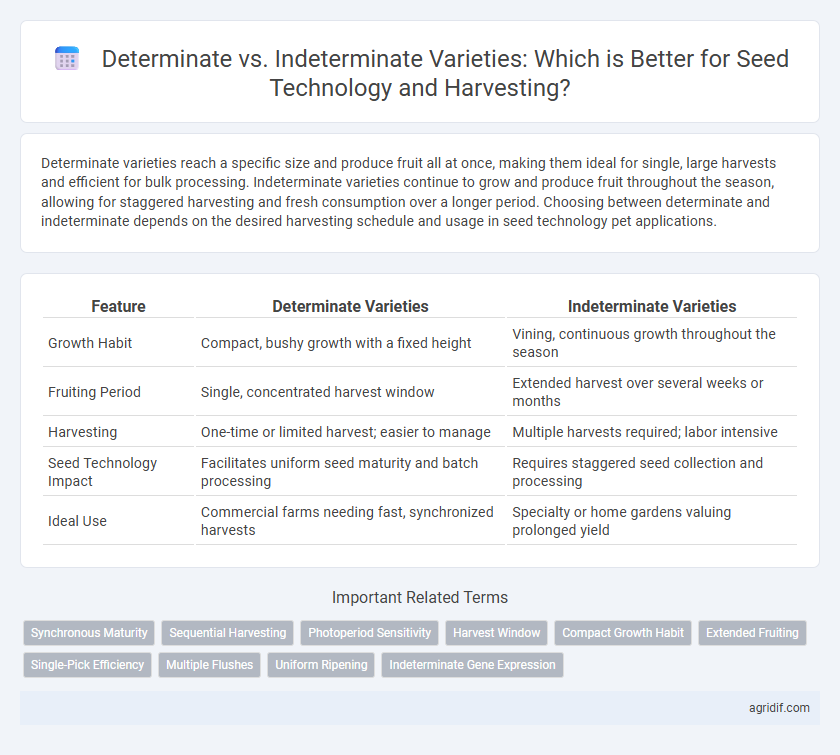
Determinate varieties reach a specific size and produce fruit all at once, making them ideal for single, large harvests and efficient for bulk processing. Indeterminate varieties continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the season, allowing for staggered harvesting and fresh consumption over a longer period. Choosing between determinate and indeterminate depends on the desired harvesting schedule and usage in seed technology pet applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Determinate Varieties | Indeterminate Varieties |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Habit | Compact, bushy growth with a fixed height | Vining, continuous growth throughout the season |
| Fruiting Period | Single, concentrated harvest window | Extended harvest over several weeks or months |
| Harvesting | One-time or limited harvest; easier to manage | Multiple harvests required; labor intensive |
| Seed Technology Impact | Facilitates uniform seed maturity and batch processing | Requires staggered seed collection and processing |
| Ideal Use | Commercial farms needing fast, synchronized harvests | Specialty or home gardens valuing prolonged yield |
Understanding Determinate and Indeterminate Varieties
Determinate varieties of crops, such as tomatoes, grow to a fixed size and produce fruit all at once, making them ideal for single, large harvests. Indeterminate varieties continue growing and fruiting throughout the season, offering multiple harvests over time with staggered ripening. Understanding the growth patterns helps farmers optimize planting schedules and harvesting strategies for maximum yield and efficiency.
Key Differences in Growth Habits
Determinate varieties exhibit a bushy growth habit with a defined maturation period, where most fruit develops simultaneously, making them ideal for single, large-scale harvests. Indeterminate varieties grow vining plants that continue producing fruit over an extended period, allowing multiple harvests but requiring ongoing maintenance. Understanding these growth habits helps optimize planting schedules and management practices in seed technology.
Flowering and Fruiting Patterns
Determinate varieties exhibit a concentrated flowering and fruiting period, leading to a uniform and predictable harvest, which is ideal for mechanical harvesting and large-scale production. Indeterminate varieties continuously produce flowers and fruits over an extended period, allowing for multiple harvests but requiring more labor and management. Understanding the distinct flowering and fruiting patterns of determinate and indeterminate varieties enhances seed selection for optimized yield and efficient harvest scheduling in seed technology.
Maturity and Harvest Timing Comparison
Determinate varieties reach maturity uniformly and complete fruit development within a shorter timeframe, enabling a single, efficient harvest ideal for mechanized or bulk collection. Indeterminate varieties continue flowering and fruiting over an extended period, offering staggered harvests that provide fresh produce over time but require multiple pickings. Understanding the maturity and harvest timing differences helps optimize crop scheduling, labor allocation, and post-harvest management strategies in seed technology.
Yield Potential and Consistency
Determinate varieties offer consistent yield potential by maturing simultaneously, simplifying harvesting and reducing labor costs. Indeterminate varieties provide extended harvesting periods with potentially higher cumulative yields due to continuous flowering and fruiting. Choosing between these types depends on balancing consistency versus maximum yield over time in seed technology applications.
Suitability for Mechanical Harvesting
Determinate varieties are highly suitable for mechanical harvesting due to uniform fruit maturation and synchronized ripening, reducing harvest time and minimizing crop loss. Indeterminate varieties exhibit continuous growth and staggered fruit production, complicating mechanical harvesting and often requiring multiple passes. Selecting determinate cultivars enhances efficiency and reduces labor costs in large-scale seed production operations.
Disease Resistance and Management
Determinate seed varieties often provide easier disease management due to their synchronized harvesting period, reducing the window for pathogen exposure. Indeterminate varieties, with extended flowering and fruiting, require ongoing monitoring and treatment to control diseases effectively. Selecting disease-resistant determinate cultivars can minimize fungicide use and improve overall crop health during the harvest stage.
Adaptation to Climate and Growing Conditions
Determinate seed varieties, characterized by a defined growth period and simultaneous fruiting, are well-suited for regions with shorter growing seasons and predictable climates, enabling efficient, single-harvest management. In contrast, indeterminate varieties continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the season, offering adaptability to diverse and fluctuating climates, which benefits areas with extended growing periods and variable weather patterns. Choosing the appropriate variety based on local climate and soil conditions enhances yield stability and optimizes harvest timing for seed producers.
Seed Production Considerations
Determinate varieties offer a concentrated flowering and fruiting period, enabling a uniform harvesting schedule that simplifies seed collection and enhances seed quality control. Indeterminate varieties produce flowers and fruits continuously over an extended period, requiring multiple harvests and careful monitoring to ensure seed maturity and avoid mixing seed cohorts. Choosing between determinate and indeterminate types depends on the seed production goals, labor availability, and climate conditions to optimize seed yield and viability.
Selection Criteria for Farmers and Seed Producers
Farmers and seed producers prioritize selection criteria such as growth habit, yield consistency, and harvest timing when choosing between determinate and indeterminate seed varieties. Determinate varieties offer uniform maturity and facilitate mechanized harvesting, making them suitable for large-scale production systems, while indeterminate varieties provide extended harvest periods and adaptability to variable climates, benefiting regions with fluctuating growing conditions. Seed quality, disease resistance, and market demand also influence the selection process to optimize productivity and economic returns.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Maturity
Determinate seed varieties exhibit synchronous maturity, allowing uniform harvesting and reducing labor costs by minimizing multiple picking rounds. Indeterminate varieties mature over an extended period, necessitating staggered harvesting that can increase operational complexity and resource use.
Sequential Harvesting
Determinate varieties produce uniform fruit sets that mature simultaneously, enabling a single, efficient harvest, while indeterminate varieties yield continuous fruiting, allowing sequential harvesting over an extended period to maximize yield and market flexibility. Sequential harvesting in indeterminate plants reduces labor spikes and storage challenges by spreading harvest times but requires careful management to optimize seed viability and quality.
Photoperiod Sensitivity
Determinate varieties exhibit limited flowering periods triggered by specific photoperiod sensitivity, enabling synchronized and uniform harvesting ideal for mechanized seed collection. Indeterminate varieties, less sensitive to photoperiod changes, continuously produce flowers and seeds, offering extended harvesting windows but requiring more labor-intensive seed management.
Harvest Window
Determinate varieties have a concentrated harvest window, allowing for uniform and efficient crop collection within a short time frame. Indeterminate varieties produce fruit continuously over an extended period, offering a prolonged harvest window but requiring multiple harvests and increased labor.
Compact Growth Habit
Determinate seed varieties exhibit a compact growth habit, producing fruit in a concentrated period ideal for single, efficient harvests, while indeterminate varieties grow continuously and require multiple harvests over time. Compact growth habit in determinate types optimizes space and labor, enhancing yield predictability and facilitating mechanized harvesting in seed production.
Extended Fruiting
Determinate varieties exhibit a concentrated fruiting period, allowing for a single, uniform harvest, while indeterminate varieties provide extended fruiting over weeks, enabling multiple harvests. Extended fruiting in indeterminate types enhances yield potential and flexibility in seed production schedules.
Single-Pick Efficiency
Determinate varieties enable single-pick efficiency by maturing fruit uniformly within a short timeframe, reducing labor and harvest costs. Indeterminate varieties prolong fruit production over weeks, requiring multiple harvests that increase labor intensity and complicate scheduling.
Multiple Flushes
Determinate seed varieties produce a single, concentrated harvest flush, allowing for uniform crop maturity and simplified harvesting schedules. Indeterminate varieties generate multiple flushes over an extended period, offering prolonged harvesting opportunities but requiring more labor-intensive management practices.
Uniform Ripening
Determinate varieties exhibit uniform ripening, allowing for a single, efficient harvest and reducing labor costs, while indeterminate varieties produce fruit continuously, necessitating multiple harvests to collect mature seeds. Uniform ripening in determinate plants enhances seed quality consistency and optimizes post-harvest processing for seed technology applications.
Indeterminate Gene Expression
Indeterminate varieties exhibit continuous flowering and fruit development controlled by specific gene expression patterns, allowing extended harvesting periods and increased yield potential. The regulation of indeterminate gene expression involves key transcription factors such as TFL1 and FT, which modulate growth cycles and optimize seed production timelines.
Determinate vs Indeterminate varieties for harvesting Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com