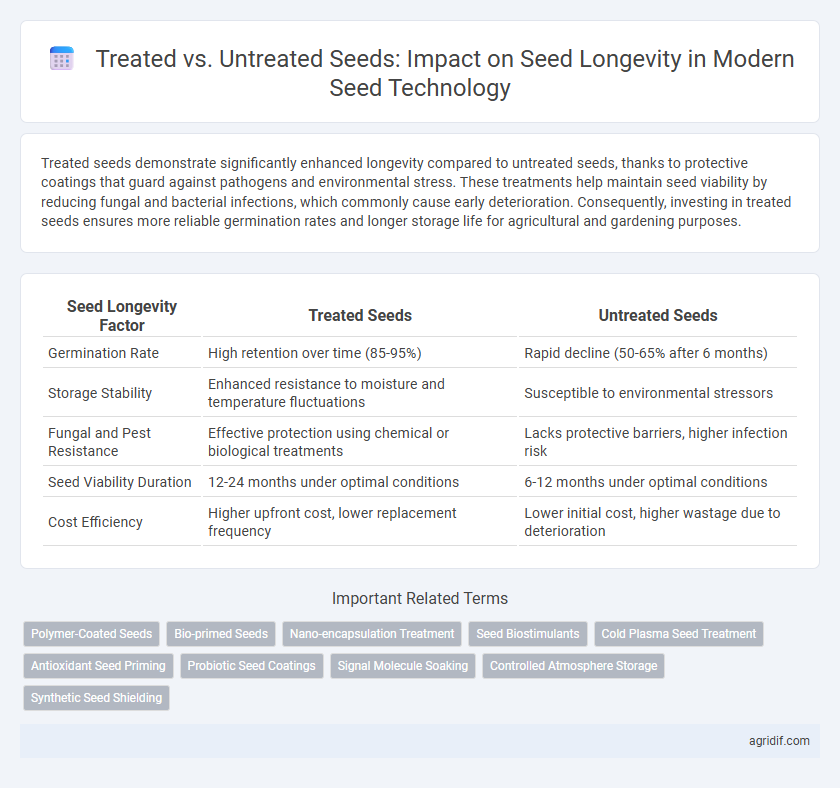
Treated seeds demonstrate significantly enhanced longevity compared to untreated seeds, thanks to protective coatings that guard against pathogens and environmental stress. These treatments help maintain seed viability by reducing fungal and bacterial infections, which commonly cause early deterioration. Consequently, investing in treated seeds ensures more reliable germination rates and longer storage life for agricultural and gardening purposes.
Table of Comparison
| Seed Longevity Factor | Treated Seeds | Untreated Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Germination Rate | High retention over time (85-95%) | Rapid decline (50-65% after 6 months) |
| Storage Stability | Enhanced resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations | Susceptible to environmental stressors |
| Fungal and Pest Resistance | Effective protection using chemical or biological treatments | Lacks protective barriers, higher infection risk |
| Seed Viability Duration | 12-24 months under optimal conditions | 6-12 months under optimal conditions |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront cost, lower replacement frequency | Lower initial cost, higher wastage due to deterioration |
Understanding Seed Longevity in Agriculture
Seed longevity significantly influences crop yield stability, with treated seeds exhibiting enhanced resistance to environmental stresses compared to untreated seeds. Chemical and biological seed treatments protect against pathogens and promote faster germination, extending the viable life span during storage. Understanding the differential impact of seed treatments on viability loss rates helps farmers optimize storage conditions and choose appropriate seed lots for planting cycles.
Defining Treated and Untreated Seeds
Treated seeds are those that have been coated or soaked with chemical or biological agents to enhance germination, protect against pests, and increase seed longevity. Untreated seeds remain in their natural state without any application of protective substances, making them more susceptible to environmental stresses and pathogens. Understanding the distinction between treated and untreated seeds is crucial for optimizing storage conditions and improving seed viability over time.
Factors Affecting Seed Longevity
Seed longevity is significantly influenced by factors such as moisture content, temperature, and seed treatment methods. Treated seeds, often coated with fungicides or insecticides, typically exhibit enhanced resistance to pathogens and environmental stress, which prolongs viability compared to untreated seeds. Storage conditions, including humidity control and stable, low temperatures, also play a critical role in maintaining seed vigor over extended periods.
Types of Seed Treatments and Their Purposes
Seed treatments, including fungicidal, insecticidal, and biostimulant coatings, significantly enhance seed longevity by protecting against pathogens, pests, and environmental stress. Treated seeds benefit from improved germination rates and seedling vigor compared to untreated seeds, which are vulnerable to soil-borne diseases and deterioration. Specific treatments like sulfur-based protectants and polymer coatings maintain seed viability during storage, ensuring consistent field performance.
Comparative Analysis: Longevity of Treated vs Untreated Seeds
Treated seeds exhibit significantly enhanced longevity compared to untreated seeds due to protective coatings that prevent fungal infections, moisture loss, and pest damage. Studies show treated seeds maintain higher germination rates over extended storage periods, often exceeding untreated seeds by 30-50% in viability retention. Seed treatments with fungicides, insecticides, and polymer coatings create a microenvironment that stabilizes seed physiology, thereby extending shelf life and improving crop establishment success.
Impact of Seed Treatment on Germination Rates
Seed treatment significantly enhances germination rates by protecting seeds from pathogens, pests, and environmental stresses that typically reduce seed viability. Treated seeds exhibit higher germination percentages and more uniform emergence compared to untreated seeds, which often suffer from fungal infections and insect damage. This improved germination contributes directly to better crop establishment and yield potential in agricultural production.
Storage Practices for Prolonging Seed Viability
Treated seeds, coated with fungicides or insecticides, exhibit enhanced longevity compared to untreated seeds by resisting microbial decay and insect damage during storage. Optimal storage conditions--low temperature, controlled humidity around 8-10%, and airtight containers--further prolong seed viability by minimizing metabolic activity and moisture absorption. Regular monitoring of seed moisture content and storage environment ensures maximum preservation of germination potential over extended periods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Treated Seeds
Treated seeds significantly enhance seed longevity by providing protection against fungal infections, pests, and environmental stressors, leading to higher germination rates and improved crop yields. The primary disadvantage of treated seeds is the potential environmental impact due to chemical residues, which may affect soil health and beneficial organisms. Despite these concerns, the use of treated seeds remains a preferred choice for ensuring seed viability during storage and improving overall agricultural productivity.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Treated seeds use chemical coatings that enhance seed longevity by protecting against pathogens and environmental stresses, but may introduce concerns related to chemical runoff and human exposure. Untreated seeds avoid potential toxic residues, promoting safer handling and reduced environmental impact, yet they often exhibit shorter viability due to lack of protective agents. Balancing seed treatment benefits with environmental sustainability and health safety is critical for optimizing agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
Best Practices for Seed Selection and Storage
Treated seeds exhibit enhanced longevity compared to untreated seeds due to protective coatings that reduce susceptibility to pathogens and environmental stress. Optimal seed selection involves choosing high-viability seeds with uniform size and moisture content below 12%, critical for maintaining germination potential. Proper storage in controlled environments with low humidity and temperatures between 0-5degC significantly extends seed viability for treated seeds versus untreated counterparts.
Related Important Terms
Polymer-Coated Seeds
Polymer-coated seeds significantly enhance seed longevity by creating a protective barrier that reduces moisture loss and shields against pathogens, unlike untreated seeds which are more susceptible to environmental stress and deterioration. This coating technology improves germination rates and shelf life, making it a critical advancement in seed preservation strategies.
Bio-primed Seeds
Bio-primed seeds exhibit enhanced longevity compared to untreated seeds due to beneficial microbial inoculation that improves seed vigor and stress resistance. This treatment extends storage life by reducing deterioration rates and promoting faster, more uniform germination in varying environmental conditions.
Nano-encapsulation Treatment
Nano-encapsulation treatment significantly enhances seed longevity by protecting seeds from environmental stressors, pathogens, and oxidation compared to untreated seeds. This technology improves controlled release of nutrients and pesticides, ensuring prolonged viability and higher germination rates during storage.
Seed Biostimulants
Seed biostimulants enhance longevity by improving germination rates, stress resistance, and seedling vigor compared to untreated seeds. Treated seeds show increased enzyme activity and antioxidant production, which reduces oxidative damage and extends seed viability during storage.
Cold Plasma Seed Treatment
Cold plasma seed treatment significantly enhances seed longevity by improving germination rates and protecting seeds from microbial contamination, unlike untreated seeds that are more prone to deterioration and reduced viability over time. The reactive species generated during cold plasma exposure stimulate seed metabolism and increase resistance to environmental stress, resulting in prolonged shelf life and more consistent crop emergence.
Antioxidant Seed Priming
Antioxidant seed priming significantly enhances seed longevity by reducing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation compared to untreated seeds, resulting in improved germination rates and seedling vigor over extended storage periods. Treated seeds exhibit higher activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, which protect cellular structures from deterioration during storage.
Probiotic Seed Coatings
Probiotic seed coatings significantly enhance seed longevity by promoting beneficial microbial activity that protects seeds from pathogens and environmental stress, outperforming untreated seeds in maintaining viability during storage. These treatments improve germination rates and vigor by creating a balanced microbial ecosystem around the seed, which untreated seeds lack, leading to faster deterioration and reduced shelf life.
Signal Molecule Soaking
Signal molecule soaking enhances seed longevity by activating metabolic pathways that bolster stress resistance and delay aging processes, making treated seeds significantly more viable over time than untreated ones. This technique optimizes seed vigor and germination rates by promoting cellular repair mechanisms and antioxidant activity during storage.
Controlled Atmosphere Storage
Controlled atmosphere storage significantly enhances seed longevity by regulating oxygen, carbon dioxide, and humidity levels, slowing down metabolic processes and reducing oxidative damage in treated seeds compared to untreated ones. Treated seeds stored under controlled atmospheres maintain higher viability and germination rates over extended periods, ensuring optimal performance for agricultural use.
Synthetic Seed Shielding
Synthetic seed shielding enhances seed longevity by creating a protective barrier that prevents moisture loss and microbial contamination, significantly outperforming untreated seeds in preserving viability during storage. Treated seeds with this advanced coating show improved germination rates and extended shelf life, making synthetic seed shielding a critical technology for effective seed preservation.
Treated vs Untreated for Seed Longevity Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com