Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for water conservation in sustainable agriculture. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a larger area but often results in higher evaporation rates and water wastage compared to drip systems. Choosing drip irrigation supports precise water management, reducing overall water usage and promoting eco-friendly farming practices.
Table of Comparison
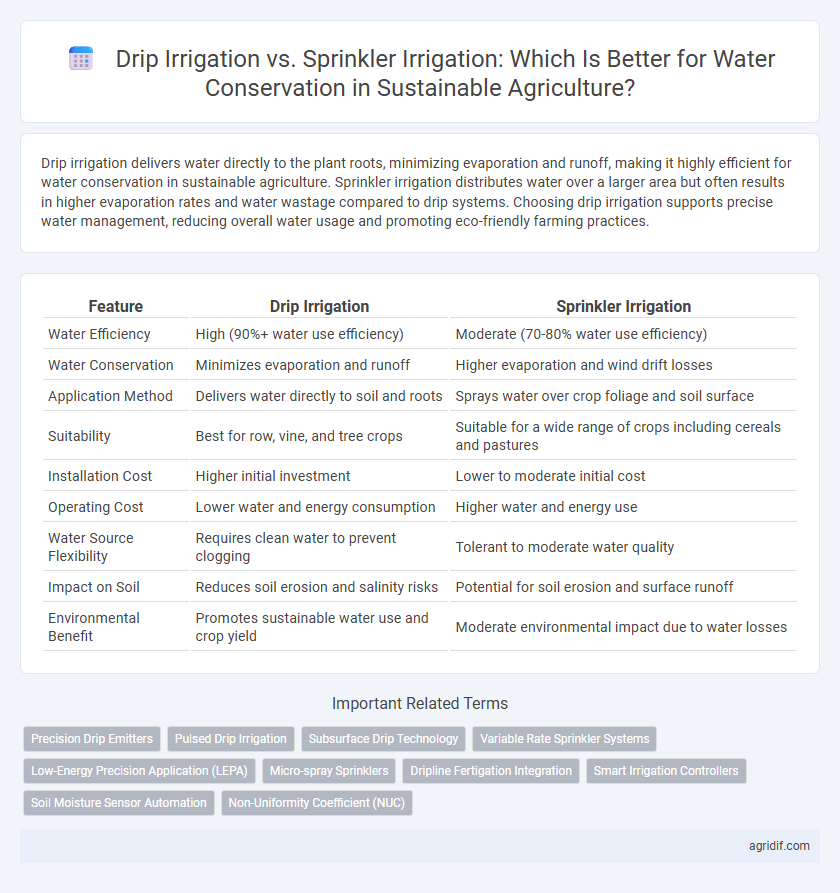
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (90%+ water use efficiency) | Moderate (70-80% water use efficiency) |
| Water Conservation | Minimizes evaporation and runoff | Higher evaporation and wind drift losses |
| Application Method | Delivers water directly to soil and roots | Sprays water over crop foliage and soil surface |
| Suitability | Best for row, vine, and tree crops | Suitable for a wide range of crops including cereals and pastures |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower to moderate initial cost |
| Operating Cost | Lower water and energy consumption | Higher water and energy use |
| Water Source Flexibility | Requires clean water to prevent clogging | Tolerant to moderate water quality |
| Impact on Soil | Reduces soil erosion and salinity risks | Potential for soil erosion and surface runoff |
| Environmental Benefit | Promotes sustainable water use and crop yield | Moderate environmental impact due to water losses |
Introduction: The Need for Efficient Irrigation in Sustainable Agriculture
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of valves and tubes, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to sprinkler systems that spray water over larger areas. This targeted approach enhances water use efficiency, making it ideal for regions facing water scarcity and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Efficient irrigation techniques like drip irrigation are essential for conserving water resources while maintaining crop productivity.
Overview of Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation utilizes a network of tubes and emitters to deliver water directly to the root zone, maximizing water efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water through overhead sprinklers, covering larger areas but often resulting in higher water loss due to evaporation and wind drift. Both systems can improve water conservation in sustainable agriculture, but drip irrigation typically offers greater precision and reduced water usage.
Water Conservation: Drip vs Sprinkler Efficiency
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of tubes, reducing evaporation and runoff, resulting in water savings of up to 50% compared to traditional methods. Sprinkler irrigation sprays water over crops, often leading to higher evaporation rates and less targeted water use, with efficiency ranging from 70-80% under optimal conditions. For water conservation, drip irrigation demonstrates superior efficiency, especially in arid regions where precise water application minimizes waste and maximizes crop yield.
Impact on Soil Health and Plant Growth
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing soil erosion and reducing nutrient leaching, which promotes healthier soil structure and optimal plant growth. Sprinkler irrigation, while effective for covering large areas, can increase soil compaction and surface runoff, potentially degrading soil health and causing uneven water distribution. Selecting drip irrigation enhances water use efficiency, supports sustainable soil management, and improves crop yields by maintaining consistent moisture levels around root zones.
Energy and Resource Requirements Comparison
Drip irrigation uses significantly less water and energy by delivering water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, while sprinkler irrigation generally requires higher water pressure and energy consumption for widespread coverage. The low-pressure operation of drip systems results in lower fuel or electricity usage, making it more resource-efficient, especially in arid regions. Sprinkler irrigation systems demand more maintenance and infrastructure investments, increasing their overall resource footprint compared to the targeted efficiency of drip irrigation technology.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Drip irrigation systems require precise installation with emitters placed near the plant root zones, minimizing water wastage and reducing soil erosion. Maintenance involves regular flushing of emitters to prevent clogging and periodic inspection of tubing for leaks, ensuring efficient water delivery. Sprinkler irrigation demands careful placement of sprinkler heads to achieve uniform coverage, with maintenance focusing on nozzle cleaning and system pressure checks to avoid water loss.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Drip irrigation requires a higher initial investment due to the cost of tubing, emitters, and installation, but it offers significant long-term savings by minimizing water waste and reducing energy expenses. Sprinkler irrigation generally has lower upfront costs but tends to consume more water, resulting in higher operational costs over time. Studies show that drip systems can reduce water use by up to 50% compared to sprinklers, leading to substantial savings in water bills and improved crop yields.
Suitability for Different Crops and Farm Sizes
Drip irrigation offers precise water delivery, making it highly suitable for row crops, orchards, and vineyards on small to medium-sized farms where water conservation is critical. Sprinkler irrigation is more versatile for larger fields and crops such as cereals and pasture grasses but tends to have higher water evaporation losses. Choosing between drip and sprinkler systems depends on crop type, farm size, and the efficiency requirements for sustainable water management.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Implications
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff, which enhances water use efficiency by up to 90% compared to traditional methods. Sprinkler irrigation, while providing broader coverage, often results in higher water loss through evaporation and wind drift, decreasing overall efficiency to around 70%. The targeted water delivery of drip systems minimizes soil erosion and nutrient leaching, promoting sustainable agriculture by conserving water resources and reducing environmental degradation.
Choosing the Right Irrigation System for Sustainable Agriculture
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing water loss through evaporation and runoff by up to 30-50%, making it highly efficient for sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid regions. Sprinkler irrigation mimics natural rainfall and is suitable for diverse crop types and terrain but typically results in higher water usage due to evaporation and wind drift. Selecting the right irrigation system depends on factors such as soil type, crop requirements, water availability, and energy costs to optimize water conservation and enhance agricultural sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Precision Drip Emitters
Precision drip emitters deliver water directly to the root zone with minimal evaporation and runoff, significantly enhancing water conservation compared to sprinkler irrigation. This precise application reduces water waste by up to 60%, promoting sustainable agriculture through improved water-use efficiency and crop yield optimization.
Pulsed Drip Irrigation
Pulsed drip irrigation enhances water conservation by delivering precise water amounts directly to plant roots in intermittent pulses, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional sprinkler systems. This method improves soil moisture uniformity and crop yield while minimizing water waste, making it a more sustainable choice for resource-efficient agriculture.
Subsurface Drip Technology
Subsurface drip technology delivers water directly to plant roots below the soil surface, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional sprinkler irrigation methods. This precision in water application enhances water conservation and improves crop yield efficiency in sustainable agriculture.
Variable Rate Sprinkler Systems
Variable Rate Sprinkler Systems enhance traditional sprinkler irrigation by adjusting water application based on soil moisture, crop type, and topography, significantly improving water use efficiency compared to uniform drip irrigation. This technology reduces water waste and supports sustainable agriculture by optimizing irrigation schedules and minimizing runoff in diverse field conditions.
Low-Energy Precision Application (LEPA)
Drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation both serve sustainable agriculture, but Low-Energy Precision Application (LEPA) enhances sprinkler efficiency by reducing energy use and water loss through targeted, low-pressure water delivery directly to the soil surface. LEPA systems cut water consumption by up to 30% compared to conventional sprinklers while minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it a competitive alternative to drip irrigation in water conservation efforts.
Micro-spray Sprinklers
Micro-spray sprinklers offer precise water distribution with reduced evaporation and runoff compared to traditional sprinkler systems, enhancing water conservation in sustainable agriculture. These systems deliver fine droplets close to the soil surface, improving irrigation efficiency and minimizing water waste relative to drip irrigation in certain crop and soil conditions.
Dripline Fertigation Integration
Drip irrigation combined with fertigation delivers water and nutrients directly to plant roots, reducing water wastage by up to 40% compared to sprinkler irrigation, which often experiences higher evaporation and runoff losses. Integrating dripline fertigation enhances precise nutrient management, improving crop yield and water use efficiency, making it a superior choice for sustainable agriculture practices focused on water conservation.
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers enhance water conservation by optimizing drip irrigation systems, delivering precise amounts of water directly to plant roots and reducing evaporation and runoff. Compared to sprinkler irrigation, which sprays water over larger areas with higher losses, smart drip irrigation significantly improves efficiency and sustainability in agricultural water management.
Soil Moisture Sensor Automation
Drip irrigation combined with soil moisture sensor automation delivers precise water application directly to plant roots, significantly enhancing water conservation by reducing evaporation and runoff compared to sprinkler irrigation. This method optimizes water use efficiency in sustainable agriculture by activating irrigation only when sensors detect soil moisture levels below optimal thresholds.
Non-Uniformity Coefficient (NUC)
Drip irrigation exhibits a lower Non-Uniformity Coefficient (NUC) compared to sprinkler irrigation, highlighting its superior efficiency in water distribution and conservation. This reduced NUC minimizes water loss and enhances crop yield by delivering precise moisture levels directly to plant roots.
Drip irrigation vs Sprinkler irrigation for water conservation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com