Hydroponics involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, providing direct access to essential minerals, which promotes faster growth compared to traditional soil methods. Aeroponics, on the other hand, suspends plant roots in air and regularly mists them with nutrient solution, enhancing oxygen availability and nutrient absorption efficiency. Both systems optimize water use and space, but aeroponics generally offers higher growth rates and reduced water consumption, making it ideal for controlled-environment agriculture.
Table of Comparison
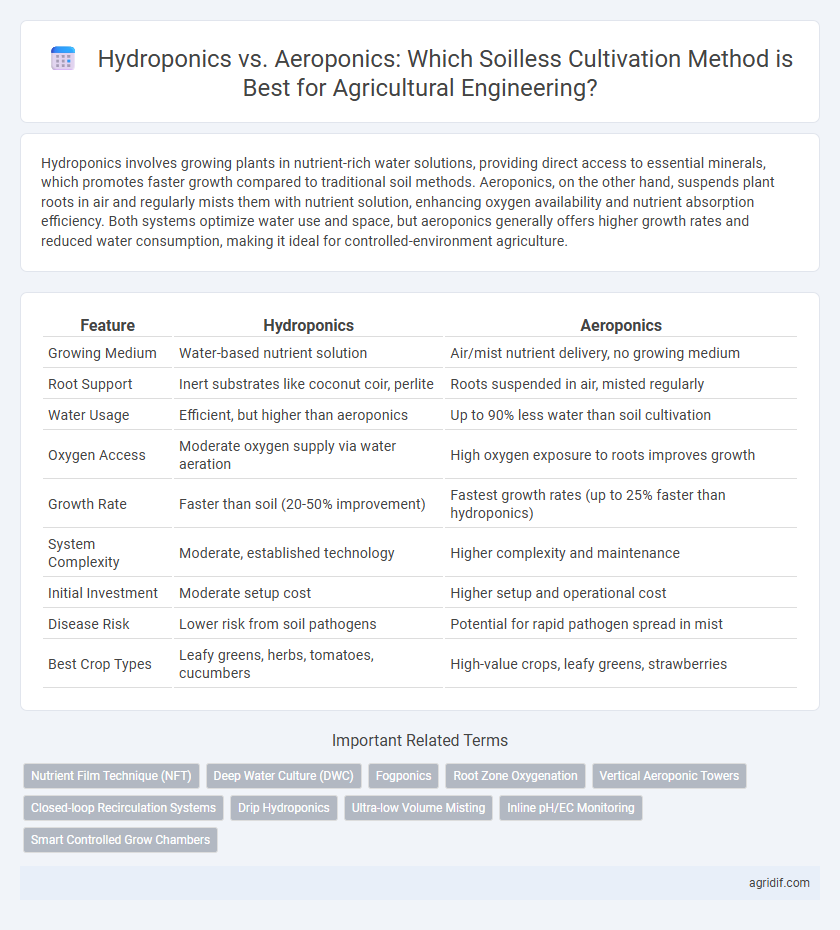
| Feature | Hydroponics | Aeroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Growing Medium | Water-based nutrient solution | Air/mist nutrient delivery, no growing medium |
| Root Support | Inert substrates like coconut coir, perlite | Roots suspended in air, misted regularly |
| Water Usage | Efficient, but higher than aeroponics | Up to 90% less water than soil cultivation |
| Oxygen Access | Moderate oxygen supply via water aeration | High oxygen exposure to roots improves growth |
| Growth Rate | Faster than soil (20-50% improvement) | Fastest growth rates (up to 25% faster than hydroponics) |
| System Complexity | Moderate, established technology | Higher complexity and maintenance |
| Initial Investment | Moderate setup cost | Higher setup and operational cost |
| Disease Risk | Lower risk from soil pathogens | Potential for rapid pathogen spread in mist |
| Best Crop Types | Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, cucumbers | High-value crops, leafy greens, strawberries |
Introduction to Soilless Cultivation Methods
Hydroponics and aeroponics represent advanced soilless cultivation methods crucial for maximizing crop yields in controlled environments. Hydroponics utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots, promoting efficient nutrient uptake and faster growth rates. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in the air and intermittently mists them with nutrient solutions, enhancing oxygen availability and reducing water usage compared to hydroponics.
Principles of Hydroponics
Hydroponics relies on nutrient-rich water solutions circulated through inert growing mediums such as perlite or coconut coir to deliver essential nutrients directly to plant roots, maximizing nutrient uptake efficiency. This method controls environmental variables like pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient concentration to optimize growth rates and yield. Unlike aeroponics, hydroponics submerges roots in a liquid medium, reducing dependency on misting systems and ensuring consistent nutrient availability.
Principles of Aeroponics
Aeroponics cultivates plants by suspending roots in air and misting them with nutrient-rich solutions, enabling high oxygen availability and efficient nutrient uptake. This principle enhances root aeration compared to hydroponics, where roots are submerged in nutrient solutions, often limiting oxygen access. Consequently, aeroponics supports faster growth rates and resource-efficient soilless cultivation in controlled agricultural environments.
System Setup and Infrastructure Requirements
Hydroponics systems require water-based nutrient solutions, reservoirs, pumps, and inert growing media such as coconut coir or perlite, along with support structures for the plants. Aeroponics demands a more advanced setup with high-pressure misting nozzles, specialized aeroponic chambers, and precise environmental control systems to maintain optimal moisture and oxygen levels for the roots. While hydroponics infrastructure is relatively simpler and cost-effective, aeroponics infrastructure involves higher initial investment and technical complexity to ensure efficient nutrient delivery and prevent root desiccation.
Water and Nutrient Management
Hydroponics utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions delivered directly to plant roots through substrates, ensuring precise control over nutrient concentration and water usage. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air, misting them with a nutrient solution that enhances oxygen availability and reduces water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional methods. Both systems optimize nutrient uptake efficiency, but aeroponics offers superior water conservation and faster nutrient absorption rates critical for sustainable soilless cultivation.
Crop Yield and Growth Performance
Hydroponics systems deliver nutrients through a water-based solution, resulting in consistent crop yields and faster growth rates compared to traditional soil cultivation. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and misting nutrient-rich solutions, enhancing oxygen availability and often producing up to 20% higher crop yields and accelerated growth performance. Both methods optimize resource efficiency, but aeroponics tends to exhibit superior nutrient uptake and biomass accumulation due to improved root oxygenation.
Energy and Resource Efficiency
Hydroponics systems typically consume less energy by relying on nutrient-rich water solutions circulated through plants, optimizing water usage and reducing fertilizer runoff compared to traditional soil cultivation. Aeroponics, while offering superior oxygenation and potentially faster plant growth, demands higher energy input to power misting devices and maintain precise environmental controls. Selecting between hydroponics and aeroponics requires balancing energy consumption with resource efficiency goals, considering factors such as water recycling rates and nutrient delivery effectiveness.
Disease Management and Plant Health
Hydroponics systems use nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots, reducing soil-borne diseases but increasing risks of waterborne pathogens if not properly managed. Aeroponics employs misting roots in an oxygen-rich environment, enhancing oxygen availability and enabling quicker disease detection and treatment, which helps in maintaining robust plant health. Both methods require stringent sterilization protocols and precise environmental controls to mitigate pathogen outbreaks and optimize crop yields in soilless cultivation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Hydroponics systems typically require lower initial capital investment with costs averaging between $15 to $35 per square foot, whereas aeroponics setups often exceed $50 per square foot due to advanced misting technology and precise environmental controls. Operational expense in hydroponics is generally reduced by simpler nutrient delivery and lower water usage, while aeroponics demands higher energy input and rigorous maintenance, increasing ongoing costs by up to 20%. Economic viability favors hydroponics for large-scale, cost-sensitive production, whereas aeroponics offers higher yield potential and faster growth cycles justifying premium pricing in niche markets.
Future Trends in Soilless Agriculture
Hydroponics and aeroponics are revolutionizing soilless cultivation by optimizing resource efficiency and crop yields through controlled environment agriculture. Future trends emphasize integrating advanced sensor technologies and automation to enhance nutrient delivery precision and reduce water consumption. Innovations in AI-driven monitoring systems and sustainable energy integration are poised to propel these methods toward higher scalability and environmental sustainability in agriculture.
Related Important Terms
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) in hydroponics utilizes a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water over plant roots, offering efficient oxygenation and nutrient uptake compared to aeroponics, where roots are misted with nutrient solutions. NFT systems provide stable nutrient delivery and reduced water usage, making them a cost-effective solution for soilless cultivation in controlled environment agriculture.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponics immerses plant roots in oxygenated nutrient-rich water, providing constant access to nutrients and oxygen that promote rapid plant growth, while aeroponics suspends roots in air, delivering nutrients via fine mist which enhances oxygen exposure but requires precise environmental control. Compared to aeroponics, DWC offers simpler system maintenance and lower operational costs, making it a practical choice for large-scale, soilless cultivation with consistent crop yields.
Fogponics
Fogponics, a subset of aeroponics, utilizes ultra-fine nutrient-rich mist to enhance root oxygenation and nutrient absorption, outperforming traditional hydroponics by reducing water usage by up to 90% and increasing plant growth rates by 30%. This method optimizes resource efficiency and fosters higher yields in controlled environment agriculture, making it a superior choice for sustainable soilless cultivation.
Root Zone Oxygenation
Root zone oxygenation in hydroponics relies on nutrient-rich water circulation with dissolved oxygen levels between 6-8 mg/L, promoting healthy root respiration and nutrient uptake. Aeroponics enhances oxygen availability by suspending roots in a mist environment, delivering up to 20 times more oxygen than hydroponics, which accelerates growth rates and improves nutrient absorption efficiency.
Vertical Aeroponic Towers
Vertical aeroponic towers maximize crop yield by delivering nutrient-rich mist directly to plant roots suspended in air, enabling higher oxygen availability compared to hydroponic systems where roots are submerged in nutrient solutions. This enhanced aeration promotes faster growth rates, reduces water usage by up to 90%, and minimizes disease risk in controlled environment agriculture.
Closed-loop Recirculation Systems
Closed-loop recirculation systems in hydroponics efficiently conserve water and nutrients by continuously cycling the solution through plant roots, reducing waste and improving growth consistency. Aeroponics enhances this efficiency by delivering nutrient mist directly to roots in a closed-loop, maximizing oxygen availability and nutrient uptake while minimizing water usage.
Drip Hydroponics
Drip hydroponics delivers nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots through a controlled irrigation system, maximizing water efficiency and nutrient uptake in soilless cultivation. Compared to aeroponics, drip hydroponics offers simpler system design and reliable nutrient delivery, reducing oxygenation issues while supporting high crop yields in greenhouse agriculture.
Ultra-low Volume Misting
Ultra-low volume misting in aeroponics delivers nutrient-rich aerosols directly to plant roots, enhancing oxygen uptake and promoting faster growth compared to hydroponics, which submerges roots in nutrient solutions. This precise misting technique optimizes water use efficiency and nutrient absorption, making aeroponics a superior method for soilless cultivation in controlled agricultural environments.
Inline pH/EC Monitoring
Inline pH/EC monitoring enhances nutrient management in both hydroponics and aeroponics by providing real-time data crucial for maintaining optimal growing conditions. Hydroponics systems benefit from stable nutrient solutions, while aeroponics requires precise control of misting nutrient concentrations, making continuous pH/EC tracking essential for maximizing plant growth and yield.
Smart Controlled Grow Chambers
Smart controlled grow chambers optimize both hydroponics and aeroponics by precisely regulating humidity, temperature, and nutrient delivery for enhanced plant growth without soil. Aeroponics offers superior oxygenation and nutrient absorption through misting roots, while hydroponics maintains nutrient-rich water solutions, both benefiting significantly from automated environmental controls.
Hydroponics vs Aeroponics for soilless cultivation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com