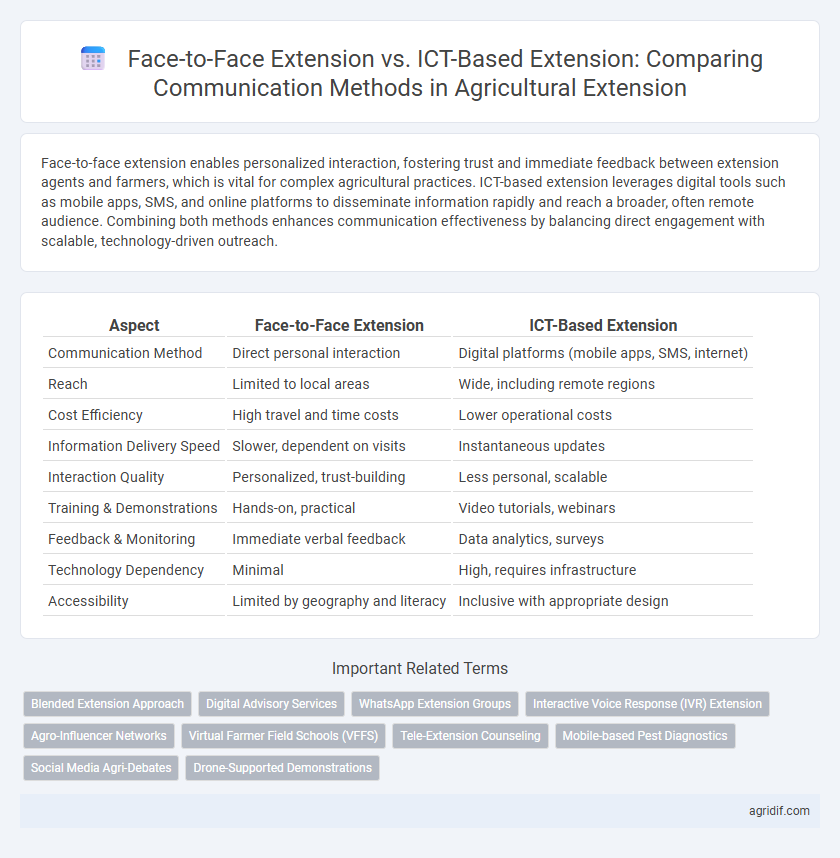
Face-to-face extension enables personalized interaction, fostering trust and immediate feedback between extension agents and farmers, which is vital for complex agricultural practices. ICT-based extension leverages digital tools such as mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms to disseminate information rapidly and reach a broader, often remote audience. Combining both methods enhances communication effectiveness by balancing direct engagement with scalable, technology-driven outreach.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Extension | ICT-Based Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Method | Direct personal interaction | Digital platforms (mobile apps, SMS, internet) |
| Reach | Limited to local areas | Wide, including remote regions |
| Cost Efficiency | High travel and time costs | Lower operational costs |
| Information Delivery Speed | Slower, dependent on visits | Instantaneous updates |
| Interaction Quality | Personalized, trust-building | Less personal, scalable |
| Training & Demonstrations | Hands-on, practical | Video tutorials, webinars |
| Feedback & Monitoring | Immediate verbal feedback | Data analytics, surveys |
| Technology Dependency | Minimal | High, requires infrastructure |
| Accessibility | Limited by geography and literacy | Inclusive with appropriate design |
Introduction to Agricultural Extension Communication Methods
Face-to-face extension offers personalized interaction and immediate feedback, fostering trust and tailored advice for farmers, which enhances the adoption of agricultural innovations. ICT-based extension leverages mobile phones, radio, and internet platforms to disseminate information rapidly and broadly, overcoming geographical barriers and reaching a larger audience. Integrating both methods maximizes communication effectiveness by combining the strengths of direct engagement with the scalability and accessibility of digital tools.
Defining Face-to-Face Extension in Agriculture
Face-to-face extension in agriculture involves direct personal interactions between extension agents and farmers, enabling tailored advice, hands-on demonstrations, and immediate feedback that enhance knowledge transfer. This method fosters strong trust and relationship-building, critical for addressing complex farming challenges and adopting innovative practices. Compared to ICT-based extension, face-to-face communication is particularly effective in regions with limited technology access and low digital literacy among farmers.
Exploring ICT-Based Extension Approaches
ICT-based extension approaches leverage mobile apps, SMS services, and online platforms to provide farmers with real-time access to agricultural knowledge, expert advice, and market information. These digital tools enhance communication efficiency by enabling timely updates and interactive learning, overcoming geographical barriers inherent in face-to-face extension methods. The scalability and cost-effectiveness of ICT-based extensions support widespread adoption and continuous farmer engagement, crucial for modern agricultural development.
Comparative Analysis: Face-to-Face vs ICT-Based Extension
Face-to-face agricultural extension facilitates direct interaction, enabling personalized guidance and immediate feedback, which enhances trust and adoption of complex farming techniques. ICT-based extension leverages mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms to deliver timely information at scale, improving reach and cost-efficiency, especially in remote areas. Comparative analyses reveal that integrating both methods optimizes knowledge transfer, combining the relational benefits of in-person contact with the accessibility and speed of digital communication.
Accessibility and Reach of Communication Methods
Face-to-face agricultural extension offers personalized, context-specific communication but often faces limitations in reaching remote or dispersed farming communities. ICT-based extension methods, such as mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms, significantly enhance accessibility by overcoming geographical barriers and enabling rapid dissemination of information to a broader audience. Combining both approaches can optimize the reach and effectiveness of agricultural knowledge transfer, particularly in regions with varying levels of digital infrastructure.
Effectiveness in Knowledge Transfer
Face-to-face agricultural extension facilitates personalized interaction, enabling immediate feedback and hands-on demonstrations, which significantly enhances knowledge retention among farmers. ICT-based extension leverages digital tools like mobile apps, videos, and SMS to deliver timely information to a broader audience, increasing accessibility especially in remote areas. Combining both methods maximizes effectiveness by addressing diverse learning preferences and overcoming geographic barriers in agricultural knowledge transfer.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Requirements
Face-to-face agricultural extension involves direct interaction between extension agents and farmers, demanding higher resource allocation such as travel expenses, time, and personnel. ICT-based extension leverages digital tools like mobile apps, SMS, and video calls, significantly reducing operational costs and enabling broader reach with fewer physical resources. Studies indicate that ICT-based methods enhance cost-effectiveness by minimizing logistical constraints and accelerating information dissemination across diverse farming communities.
Farmer Engagement and Participation Levels
Face-to-face extension methods foster higher farmer engagement and active participation through personalized interactions and immediate feedback, enhancing trust and knowledge retention. ICT-based extension leverages digital tools like mobile apps, SMS, and video tutorials to reach wider audiences efficiently but may encounter limitations in accessibility and personal connection. Combining both approaches can optimize communication strategies, ensuring inclusive and effective farmer involvement across diverse contexts.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Face-to-face agricultural extension offers personalized interaction and immediate feedback but faces challenges such as limited reach, time constraints, and high operational costs in remote areas. ICT-based extension expands outreach through mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms, yet struggles with digital literacy gaps, inconsistent internet access, and reduced personal engagement. Both methods require tailored strategies to overcome infrastructural, socio-economic, and technological barriers for effective farmer communication.
Future Directions for Agricultural Extension Communication
Face-to-face extension ensures personalized interaction and immediate feedback, fostering trust between farmers and extension agents, critical for adopting complex agricultural technologies. ICT-based extension, leveraging mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms, offers scalable, cost-effective dissemination of tailored information, reaching remote and diverse farming communities efficiently. Future directions emphasize integrating hybrid models that combine personalized support with digital tools, enhancing accessibility, real-time updates, and farmer engagement to drive sustainable agricultural development.
Related Important Terms
Blended Extension Approach
Blended extension approach combines face-to-face extension's personalized farmer engagement with ICT-based extension's wide-reaching, timely information delivery, enhancing adoption rates and knowledge retention. Integrating mobile apps, SMS alerts, and interactive voice response systems with on-ground expert visits creates a synergistic communication method tailored to diverse agricultural contexts.
Digital Advisory Services
Face-to-face extension fosters personalized farmer engagement and immediate feedback, enhancing trust and tailored advice, while ICT-based extension through Digital Advisory Services offers scalable, real-time access to agricultural information, enabling timely decision-making and overcoming geographic barriers. Integrating mobile apps, SMS alerts, and online platforms in Digital Advisory Services significantly boosts outreach efficiency and supports precision agriculture practices.
WhatsApp Extension Groups
Face-to-face agricultural extension fosters direct interaction and hands-on demonstrations, enhancing trust and immediate feedback, while ICT-based extension via WhatsApp Extension Groups enables rapid information dissemination, peer-to-peer learning, and real-time problem-solving among farmers. WhatsApp groups facilitate the sharing of multimedia content and localized advice, expanding outreach and supporting continuous engagement beyond physical constraints.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Extension
Face-to-face agricultural extension fosters personalized interaction and immediate feedback, enhancing trust and tailored advice, while ICT-based methods like Interactive Voice Response (IVR) extension enable scalable, cost-effective communication that delivers timely, accessible information to farmers with limited literacy or connectivity. IVR extension leverages automated voice messages and menu-driven responses to provide real-time guidance, weather updates, and market prices, improving decision-making and adoption of best practices in remote rural areas.
Agro-Influencer Networks
Face-to-face extension offers personalized interaction and immediate feedback crucial for building trust within Agro-Influencer Networks, enhancing knowledge dissemination and adoption of agricultural innovations. ICT-based extension leverages mobile technology and social media platforms to amplify the reach of Agro-Influencers, enabling rapid information sharing and real-time problem-solving across diverse farming communities.
Virtual Farmer Field Schools (VFFS)
Face-to-face extension offers personalized interaction and immediate feedback, enhancing farmer engagement through direct demonstrations and hands-on learning in Virtual Farmer Field Schools (VFFS). ICT-based extension leverages mobile apps, SMS, and online platforms to scale knowledge dissemination efficiently, overcoming geographical barriers and providing timely access to agricultural best practices in VFFS programs.
Tele-Extension Counseling
Tele-Extension Counseling leverages ICT platforms such as mobile apps, video calls, and SMS to provide timely, cost-effective agricultural advice, enhancing outreach compared to traditional face-to-face extension which remains essential for building trust and addressing complex, context-specific issues. Integrating digital tools with personal interactions optimizes knowledge transfer, improves farmer engagement, and supports real-time problem-solving in modern extension services.
Mobile-based Pest Diagnostics
Mobile-based pest diagnostics in ICT-based agricultural extension offer real-time, location-specific identification and management advice, significantly enhancing the speed and accuracy of pest control compared to traditional face-to-face methods. These digital tools improve farmer access to expert knowledge and timely interventions, reducing crop losses and boosting productivity by overcoming barriers like distance and limited extension agent availability.
Social Media Agri-Debates
Face-to-face extension methods foster direct interpersonal interactions, promoting trust and immediate feedback in agricultural knowledge transfer, while ICT-based extension, particularly through social media Agri-Debates, enables widespread participation, real-time information exchange, and diverse stakeholder engagement across remote farming communities. Social media Agri-Debates serve as dynamic platforms that amplify farmer voices, facilitate peer-to-peer learning, and integrate expert advice, enhancing the reach and impact of agricultural extension services beyond traditional face-to-face constraints.
Drone-Supported Demonstrations
Drone-supported demonstrations in agricultural extension enhance precision farming by providing real-time data and visual insights directly to farmers during face-to-face interactions, improving comprehension and immediate feedback. ICT-based extension leverages drones to deliver remote monitoring and virtual demonstrations, expanding outreach but potentially limiting hands-on experience and personalized guidance critical in traditional face-to-face methods.
Face-to-face extension vs ICT-based extension for communication methods Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com