Generalist agricultural extension agents possess a broad range of knowledge across multiple farming disciplines, enabling them to address diverse farmer needs and adapt to various agricultural challenges. Specialist agents, however, offer deep expertise in specific areas such as pest management or soil fertility, providing targeted solutions for complex or technical issues. Choosing between generalists and specialists depends on the agricultural context and goals, balancing comprehensive support with specialized knowledge to maximize extension effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
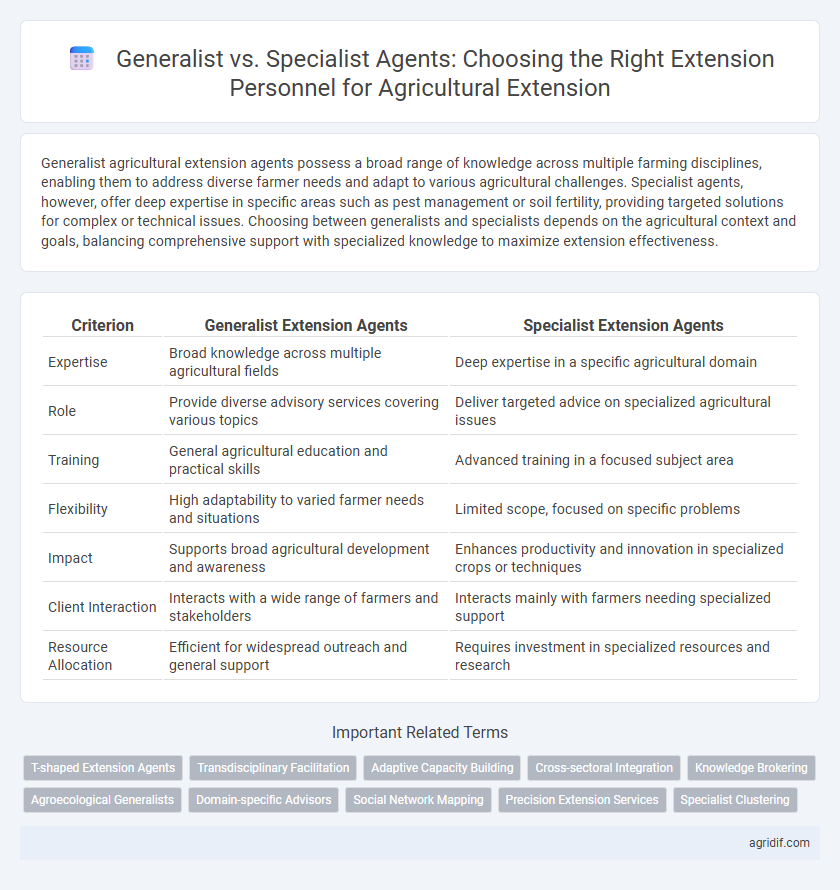
| Criterion | Generalist Extension Agents | Specialist Extension Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise | Broad knowledge across multiple agricultural fields | Deep expertise in a specific agricultural domain |
| Role | Provide diverse advisory services covering various topics | Deliver targeted advice on specialized agricultural issues |
| Training | General agricultural education and practical skills | Advanced training in a focused subject area |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to varied farmer needs and situations | Limited scope, focused on specific problems |
| Impact | Supports broad agricultural development and awareness | Enhances productivity and innovation in specialized crops or techniques |
| Client Interaction | Interacts with a wide range of farmers and stakeholders | Interacts mainly with farmers needing specialized support |
| Resource Allocation | Efficient for widespread outreach and general support | Requires investment in specialized resources and research |
Defining Generalist and Specialist Extension Agents
Generalist extension agents offer broad agricultural knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling them to address diverse farmer needs and adapt to various crop and livestock systems. Specialist extension agents possess deep expertise in specific areas such as pest management, soil science, or livestock health, focusing on advanced technical support and innovation dissemination within their specialty. Both roles are essential for comprehensive agricultural extension services, balancing wide-ranging advisory support with specialized interventions to improve farm productivity and sustainability.
Core Responsibilities of Generalist Agents
Generalist agents in agricultural extension undertake diverse roles including facilitating technology transfer, providing broad-based farm management advice, and coordinating community development initiatives. They often serve as the primary contact for farmers, diagnosing problems across crop production, livestock management, and resource conservation. Their core responsibilities emphasize versatility and integrated support to address multifaceted agricultural challenges efficiently.
Key Roles of Specialist Agents in Agriculture
Specialist agents in agricultural extension provide in-depth expertise in specific crops, livestock, or farming techniques, enabling tailored recommendations that enhance productivity and sustainability. Their role includes conducting advanced research, delivering targeted training, and resolving complex agronomic problems that generalist agents might not address effectively. This specialization improves adoption of innovative practices, leading to higher yields and improved farm management among diverse agricultural communities.
Training and Skill Requirements: Generalist vs Specialist
Generalist extension agents require broad training in multiple agricultural disciplines, enabling them to address diverse farmer needs, while specialist agents demand in-depth expertise in specific areas such as crop science, livestock, or pest management. Training programs for generalists emphasize versatility and adaptability, incorporating foundational knowledge across agronomy, soil science, and rural development, whereas specialists undergo rigorous, focused education and practical experience to develop advanced technical skills. Effective extension services often balance the deployment of both generalists, who provide comprehensive support, and specialists, who deliver detailed solutions to complex agricultural challenges.
Impact on Farmer Outreach and Support
Generalist extension agents provide comprehensive support across multiple farming disciplines, enabling broad farmer outreach and addressing diverse agricultural challenges in rural communities. Specialist agents focus on in-depth expertise in specific areas such as pest management or irrigation, delivering targeted solutions that enhance productivity and innovation for niche farmer groups. Balancing generalists and specialists in extension services optimizes resource allocation, maximizes farmer engagement, and improves overall agricultural development outcomes.
Adaptability in Addressing Diverse Agricultural Issues
Generalist agricultural extension agents possess broad knowledge across multiple farming practices, enabling them to adapt swiftly to a variety of agricultural challenges, from crop management to livestock care. Specialist agents bring deep expertise in specific areas like pest control or soil health, offering targeted solutions for complex issues. Adaptability in extension services is enhanced by integrating both generalist flexibility and specialist depth to effectively address diverse and evolving agricultural problems.
Efficiency and Depth of Knowledge in Extension Services
Generalist agents in agricultural extension provide broad, versatile knowledge across multiple farming topics, enhancing efficiency in reaching diverse producer needs. Specialist agents offer in-depth expertise in specific areas such as pest management or soil health, improving the accuracy and effectiveness of solutions. Balancing generalists for wide outreach and specialists for targeted interventions optimizes extension service impact on farm productivity and sustainability.
Challenges Faced by Generalists and Specialists
Generalist agricultural extension agents face challenges such as limited expertise in specific crops or technologies, which can hinder their ability to provide in-depth technical support to farmers. Specialist agents often encounter difficulties related to high demand for their focused expertise and the need to continuously update knowledge in rapidly evolving agricultural sectors. Both generalists and specialists must balance workload management and effective communication to address diverse farmer needs and local agricultural conditions.
Selecting the Right Agent Type for Extension Goals
Selecting the right extension agent type is crucial to achieving specific agricultural development goals, with generalist agents providing broad-based knowledge across multiple disciplines and specialist agents offering in-depth expertise in particular areas such as pest management or soil fertility. For complex, multifaceted agricultural challenges, specialist agents enable targeted interventions and precise technical support, while generalists are more effective in promoting integrated farming practices and facilitating multi-topic communication among farmers. Optimizing extension personnel allocation based on the local farming context and extension objectives enhances knowledge transfer, adoption rates, and sustainable agricultural outcomes.
Future Trends: Integrating Generalist and Specialist Approaches
Future trends in agricultural extension emphasize integrating generalist and specialist agents to enhance knowledge transfer and problem-solving capacity. Hybrid extension models leverage generalists' broad-based skills with specialists' technical expertise for addressing complex, evolving agricultural challenges. Data-driven decision support systems and digital platforms increasingly facilitate collaboration between these agents, improving responsiveness and tailored advisory services to farmers.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Extension Agents
T-shaped extension agents combine broad interdisciplinary knowledge with deep expertise in specific agricultural domains, enabling them to address complex farmer needs through integrated solutions and targeted advice. This hybrid skill set enhances adaptability and fosters innovation, improving extension service effectiveness across diverse rural contexts.
Transdisciplinary Facilitation
Generalist extension agents excel in transdisciplinary facilitation by integrating diverse agricultural knowledge systems and engaging multiple stakeholders to address complex farming challenges holistically. Specialist agents contribute deep expertise in specific domains such as soil science or pest management, enabling targeted interventions that complement the broad, systemic approach of generalists in extension services.
Adaptive Capacity Building
Generalist agricultural extension agents possess broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling flexible responses to diverse farming challenges and fostering adaptive capacity in variable environments. Specialist agents deliver in-depth expertise in specific areas, enhancing targeted problem-solving and innovation adoption but may require collaboration to address multifaceted agricultural systems effectively.
Cross-sectoral Integration
Generalist agricultural extension agents facilitate cross-sectoral integration by addressing diverse farming challenges, combining expertise in crop production, livestock management, and natural resource conservation. Specialist agents contribute deep technical knowledge but may limit holistic problem-solving, highlighting the need for balanced teams to enhance sustainable agricultural development and improve farmer resilience.
Knowledge Brokering
Generalist extension agents possess broad agricultural knowledge, enabling them to connect diverse stakeholders and facilitate knowledge exchange across multiple sectors. Specialist agents contribute deep expertise in specific crops or techniques, enhancing knowledge brokering by providing targeted, high-impact information to improve farm productivity and innovation adoption.
Agroecological Generalists
Agroecological generalist agents possess broad knowledge across diverse farming systems, enabling them to address a wide range of agroecological challenges and promote sustainable practices effectively. Their versatility fosters adaptive learning and holistic problem-solving, which are crucial for enhancing resilience and productivity in variable agroecological zones.
Domain-specific Advisors
Domain-specific advisors in agricultural extension provide targeted expertise that enhances crop management, pest control, and soil health, leading to increased farm productivity and sustainability. Their specialized knowledge supports tailored solutions for complex agricultural challenges, enabling more effective farmer training and resource allocation compared to generalist agents.
Social Network Mapping
Social network mapping reveals that generalist extension agents maintain broad, diverse connections across multiple farming communities, facilitating widespread knowledge dissemination and resource sharing. Specialist agents, however, develop dense, trust-based networks within focused sectors, enabling targeted technical support and deep expertise transfer in specific agricultural domains.
Precision Extension Services
Specialist extension agents with expertise in precision agriculture technologies enhance the effectiveness of precision extension services by delivering targeted recommendations based on data-driven insights, sensor analytics, and site-specific management practices. Generalist agents provide broad agricultural knowledge beneficial for smallholder farmers but may lack the technical depth required for advanced precision farming interventions.
Specialist Clustering
Specialist clustering in agricultural extension enhances knowledge depth by grouping agents with expertise in specific crops, livestock, or technologies, leading to targeted problem-solving and innovation dissemination. This approach improves efficiency and farmer trust, as specialists provide tailored advice that addresses complex challenges within their focus areas.
Generalist vs Specialist Agents for Extension Personnel Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com