Public extension services prioritize accessibility and support for smallholder farmers through government-funded programs, emphasizing knowledge dissemination and capacity building. Private extension providers offer tailored, market-driven solutions with advanced technologies and specialized expertise, often resulting in more efficient and innovative service delivery. Balancing public and private extension approaches enhances agricultural productivity by combining broad outreach with customized, high-quality advisory services.
Table of Comparison
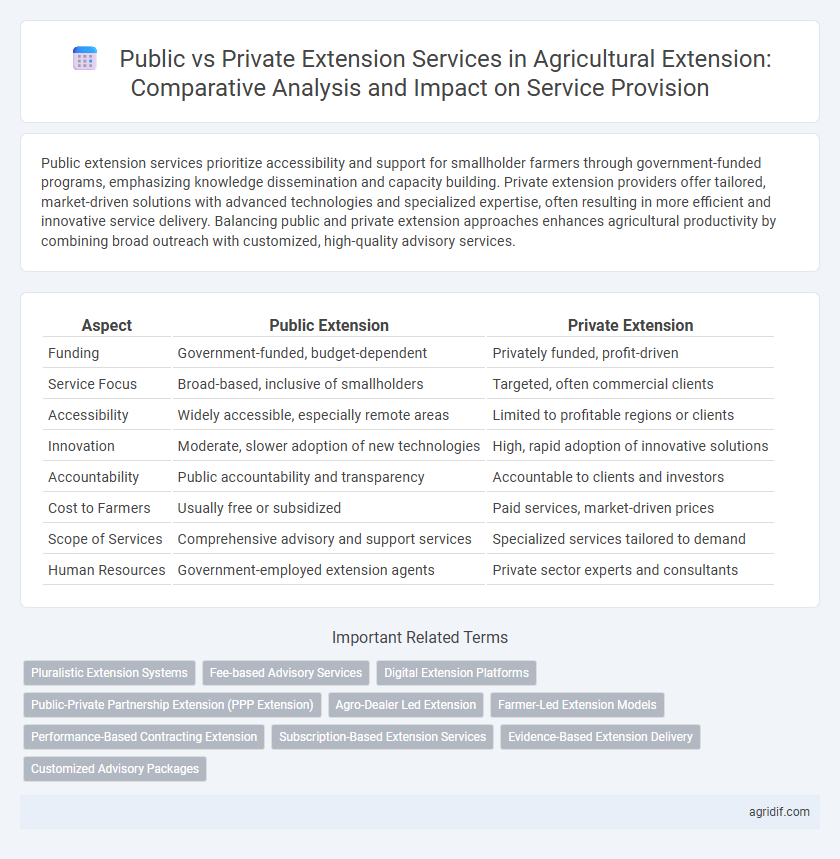
| Aspect | Public Extension | Private Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government-funded, budget-dependent | Privately funded, profit-driven |
| Service Focus | Broad-based, inclusive of smallholders | Targeted, often commercial clients |
| Accessibility | Widely accessible, especially remote areas | Limited to profitable regions or clients |
| Innovation | Moderate, slower adoption of new technologies | High, rapid adoption of innovative solutions |
| Accountability | Public accountability and transparency | Accountable to clients and investors |
| Cost to Farmers | Usually free or subsidized | Paid services, market-driven prices |
| Scope of Services | Comprehensive advisory and support services | Specialized services tailored to demand |
| Human Resources | Government-employed extension agents | Private sector experts and consultants |
Overview of Public and Private Agricultural Extension
Public agricultural extension services are government-funded and focus on providing broad access to research-based knowledge, targeting smallholder farmers to promote sustainable practices and food security. Private agricultural extension operates through market-driven models, delivering specialized, client-oriented services often tailored to commercial farmers seeking enhanced productivity and profitability. Both sectors play complementary roles in agricultural development, with public extension emphasizing inclusivity and public goods, while private extension prioritizes efficiency and innovation.
Historical Development of Extension Services
Public extension services historically emerged in the early 20th century as government-led efforts to disseminate agricultural knowledge and improve rural livelihoods, emphasizing broad access and community development. Private extension gained prominence in the late 20th century, driven by market demands and agribusiness interests, focusing on specialized, profit-oriented solutions for commercial farmers. The evolution reflects shifting policy frameworks and funding sources, with public extension focusing on inclusive outreach and private extension prioritizing efficiency and innovation in service delivery.
Structural Differences: Public vs Private Extension Models
Public extension models are generally characterized by government funding, centralized administration, and widespread service coverage prioritizing smallholder farmers and public welfare. Private extension services operate on a market-driven basis, emphasizing profitability, client-specific needs, and often focusing on commercial farms with tailored advisory support. Structural differences include governance, funding sources, scalability, accountability mechanisms, and target demographics, impacting efficiency and access to agricultural innovations.
Funding Mechanisms and Sustainability
Public agricultural extension often relies on government funding and donor support, ensuring widespread access but facing challenges in consistent budget allocations. Private extension services utilize client fees, agribusiness partnerships, and market-based models, promoting innovation and responsiveness but potentially limiting reach to wealthier farmers. Sustainable extension systems combine public-private partnerships to leverage diverse funding mechanisms, enhancing scalability and long-term viability in agricultural service provision.
Accessibility and Reach of Extension Services
Public extension services often provide wider accessibility and greater reach in rural and underserved areas due to government funding and mandates. Private extension services tend to focus on commercially viable regions and crops, which may limit accessibility for smallholder farmers. Combining both approaches can enhance overall service coverage by balancing public inclusivity and private sector efficiency.
Quality and Specialization of Extension Support
Public extension services often emphasize broad access and comprehensive support, ensuring equitable reach to diverse farmer populations with standardized quality controls. Private extension tends to deliver specialized, market-driven expertise tailored to specific crops or technologies, resulting in higher quality advisory for niche agricultural enterprises. The combination of public accessibility and private specialization enhances overall extension effectiveness and supports sustainable agricultural development.
Accountability and Farmer Feedback Mechanisms
Public extension services prioritize accountability through government oversight and structured farmer feedback mechanisms such as community meetings and formal surveys, ensuring transparency and broad accessibility. Private extension providers emphasize customer satisfaction and performance-based accountability, often using direct farmer feedback, digital platforms, and tailored advisory services to enhance service quality. Integrating public and private extension can optimize accountability frameworks by combining formal feedback channels with market-driven responsiveness, improving overall farmer engagement and service effectiveness.
Innovation and Technology Adoption
Public extension services often provide widespread access to agricultural knowledge but may face limitations in resources and innovation capacity. Private extension tends to drive faster technology adoption and innovation through market-oriented approaches and tailored service delivery. Combining public reach with private sector efficiency can enhance overall innovation diffusion in agriculture.
Challenges and Limitations in Service Provision
Public extension services often face challenges such as limited funding, bureaucratic delays, and insufficient staff capacity, which hinder timely and widespread delivery of agricultural knowledge to farmers. Private extension providers may deliver more specialized and market-driven advice but can be limited by high costs and uneven accessibility, especially for smallholder farmers. Both systems struggle with integrating modern technologies and maintaining consistent quality, impacting the overall effectiveness of agricultural service provision.
Future Prospects: Integrative Approaches in Agricultural Extension
Public extension services have traditionally focused on broad-based knowledge dissemination and farmer support, while private extension emphasizes market-driven, specialized advice and input supply. Future prospects in agricultural extension lie in integrative approaches that combine public-sector outreach with private-sector efficiency, leveraging digital technologies, public-private partnerships, and participatory methodologies. This hybrid model enhances resource use, improves farmer access to innovations, and fosters sustainable agricultural development.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Systems
Public extension services often emphasize broad accessibility and government-funded programs targeting smallholder farmers, while private extension providers focus on specialized, market-driven approaches catering to commercial agriculture. Pluralistic extension systems integrate both public and private sectors to enhance resource efficiency, ensure diverse service delivery, and promote innovation in agricultural knowledge dissemination.
Fee-based Advisory Services
Public extension services primarily offer free or subsidized agricultural advice funded by government budgets, while private extension providers deliver fee-based advisory services targeting specific farmer needs with market-driven solutions. Fee-based models in private extension enhance the adoption of innovative technologies and tailored support, promoting sustainability and efficiency in agricultural productivity.
Digital Extension Platforms
Public extension services often provide widespread access to digital extension platforms, ensuring affordability and inclusivity for smallholder farmers, while private extension providers tend to offer specialized, technology-driven solutions with personalized support. The integration of digital tools in both sectors enhances delivery efficiency, but public platforms emphasize broad knowledge dissemination whereas private platforms focus on market-oriented innovations and scalability.
Public-Private Partnership Extension (PPP Extension)
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Extension combines the strengths of public extension's broad reach and regulatory support with private extension's innovation and market-driven approaches to enhance agricultural service delivery. This collaborative model improves resource efficiency, farmer access to technology, and sustainable agricultural development by leveraging shared expertise and investment.
Agro-Dealer Led Extension
Agro-dealer led extension services enhance public extension by providing localized, market-driven agricultural inputs and tailored advice directly to farmers, improving accessibility and adoption of innovations. Private extension through agro-dealers facilitates timely dissemination of certified seeds, fertilizers, and pest control solutions, bridging gaps left by limited public sector resources and fostering agribusiness growth.
Farmer-Led Extension Models
Public extension services often provide widespread agricultural support with government funding but may struggle with limited resources and slow responsiveness, whereas private extension emphasizes market-driven, specialized advice enhancing innovation and efficiency. Farmer-led extension models bridge these approaches by empowering farmers to share knowledge and co-develop solutions, increasing adoption rates and resilience through localized expertise and participatory learning.
Performance-Based Contracting Extension
Public extension services often face challenges in efficiency and resource allocation, whereas private extension providers leveraging performance-based contracting demonstrate enhanced accountability and targeted service delivery. Performance-based contracts incentivize private agents through measurable outcomes, resulting in improved farmer adoption rates, cost-effectiveness, and innovation in agricultural practices.
Subscription-Based Extension Services
Subscription-based extension services in agriculture offer tailored, on-demand advisory support, often leveraging digital platforms to connect farmers with experts for real-time solutions, contrasting with public extension services that are typically free but less personalized and slower in response. Private extension services focus on value-added, market-driven approaches, increasing efficiency and adoption rates by providing customized information and follow-up, whereas public services emphasize broad outreach and capacity building at minimal or no cost.
Evidence-Based Extension Delivery
Public extension services often rely on government-funded programs that prioritize widespread access and equity in agricultural knowledge dissemination, leveraging evidence-based research to support smallholder farmers. Private extension providers focus on specialized, market-driven solutions that use data analytics and tailored recommendations to enhance productivity and profitability for commercial clients.
Customized Advisory Packages
Public extension services offer wide-reaching, subsidized customized advisory packages tailored to smallholder farmers, emphasizing inclusivity and local relevance. Private extension providers deliver specialized, market-driven advisory solutions focused on high-value crops and commercial farming enterprises, often utilizing advanced technology to enhance service personalization and effectiveness.
Public extension vs private extension for service provision Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com