Public extension services offer wide-reaching support to farmers through government-funded programs, ensuring access to essential agricultural knowledge and resources regardless of economic status. Private extension services provide specialized, market-driven advice and innovations tailored to specific client needs, often resulting in more rapid technology adoption and customized solutions. Balancing public and private extension approaches enhances service delivery by combining broad accessibility with targeted expertise, improving overall agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Table of Comparison
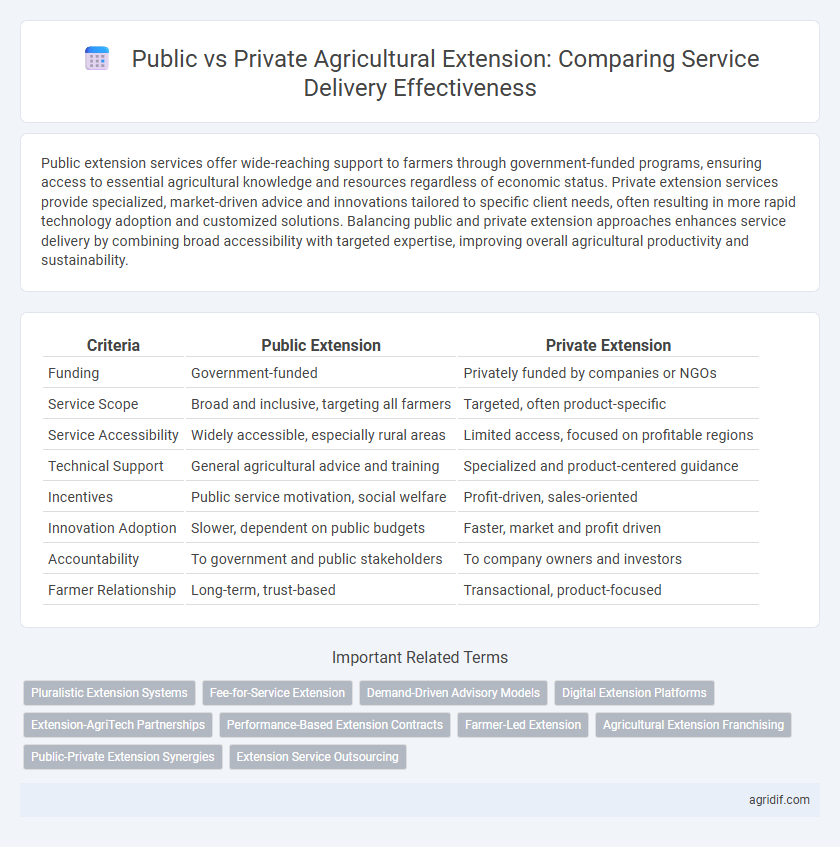
| Criteria | Public Extension | Private Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government-funded | Privately funded by companies or NGOs |
| Service Scope | Broad and inclusive, targeting all farmers | Targeted, often product-specific |
| Service Accessibility | Widely accessible, especially rural areas | Limited access, focused on profitable regions |
| Technical Support | General agricultural advice and training | Specialized and product-centered guidance |
| Incentives | Public service motivation, social welfare | Profit-driven, sales-oriented |
| Innovation Adoption | Slower, dependent on public budgets | Faster, market and profit driven |
| Accountability | To government and public stakeholders | To company owners and investors |
| Farmer Relationship | Long-term, trust-based | Transactional, product-focused |
Overview of Public and Private Agricultural Extension
Public agricultural extension services are government-funded programs aimed at delivering unbiased, accessible knowledge and technologies to smallholder farmers, often prioritizing food security and rural development. Private agricultural extension operates through market-driven entities, offering specialized services and innovative solutions tailored to commercial farmers' needs, typically emphasizing profit-oriented outcomes and efficiency. Both systems play complementary roles, with public extensions focusing on inclusivity and broad outreach, while private extensions accelerate adoption through competitive, client-focused approaches.
Historical Evolution of Extension Service Models
Public extension services have traditionally dominated agricultural knowledge dissemination, originating in the early 20th century with government-led programs aimed at improving smallholder productivity. The rise of private extension emerged in the late 20th century, driven by liberalization policies and increased involvement of agribusiness firms offering market-oriented advice and technology. This evolution reflects a shift from centralized, public-sector control to more diverse, demand-driven models integrating both public and private actors for enhanced service delivery and farmer outreach.
Key Differences: Public vs Private Extension Approaches
Public extension services are government-funded and prioritize broad stakeholder inclusivity, knowledge dissemination, and support for smallholder farmers through subsidies and capacity-building initiatives. Private extension focuses on market-driven approaches, providing specialized services tailored to commercial farmers and agribusinesses, often emphasizing profitability, technology adoption, and customer satisfaction. Key differences lie in funding sources, target audiences, service flexibility, and incentive structures, where public extension promotes accessibility and equity while private extension drives innovation and efficient resource allocation.
Funding and Resource Allocation in Extension Services
Public extension services primarily rely on government funding and subsidies to ensure wide-reaching support for smallholder farmers, often resulting in broader but sometimes less specialized agricultural advice. Private extension services attract investment through client fees and agribusiness partnerships, enabling targeted, efficient delivery of innovative technologies but potentially limiting access for resource-poor farmers. Resource allocation in public extension tends to emphasize equity and coverage, while private extension prioritizes profitability and market-driven solutions, creating complementary but distinct frameworks for agricultural service delivery.
Reach and Accessibility for Smallholder Farmers
Public extension services typically have broader reach and enhanced accessibility for smallholder farmers due to government funding and mandated coverage, especially in remote and marginalized areas. Private extension often offers specialized, demand-driven services but may focus on profitable regions and crop types, limiting accessibility for marginalized smallholders. Integrating public and private extension can optimize service delivery by combining widespread reach with tailored expertise for diverse smallholder needs.
Quality and Specialization of Extension Services
Public extension services often provide widespread access with a focus on inclusive agricultural education, yet they may face challenges in delivering highly specialized expertise due to limited resources. Private extension services tend to offer higher quality, tailored advice leveraging advanced technologies and market-oriented approaches, enhancing farmers' productivity and profitability. Integrating both public outreach and private specialization can optimize service delivery, ensuring comprehensive coverage alongside expert support in agricultural innovation.
Accountability and Monitoring Mechanisms
Public extension services operate under government oversight, ensuring high accountability through standardized monitoring systems and public reporting frameworks, which promote transparency and equitable access for smallholder farmers. Private extension providers, driven by market incentives, often implement performance-based monitoring and client feedback mechanisms to enhance service efficiency but may lack comprehensive accountability to public stakeholders. Combining public regulatory standards with private sector innovation can optimize accountability and monitoring effectiveness in agricultural extension service delivery.
Innovation and Technology Adoption Rates
Public extension services facilitate widespread access to agricultural innovations through government-supported programs, ensuring smallholder farmers benefit from new technologies. Private extension providers often demonstrate higher technology adoption rates due to tailored, market-driven solutions and incentivized service delivery. Collaboration between public and private sectors can enhance innovation diffusion and optimize resource allocation for improved agricultural productivity.
Partnership and Synergies Between Public and Private Sectors
Public extension services provide widespread access to agricultural knowledge through government-funded programs, while private extension offers specialized and market-driven solutions tailored to farmer needs. Effective partnerships leverage the strengths of both sectors by combining public resources and regulatory support with private innovation and responsiveness, enhancing service delivery efficiency and reach. Synergies between public and private extension foster sustainable agricultural development, improve technology adoption, and strengthen rural livelihoods by bridging gaps in expertise, funding, and infrastructure.
Future Trends in Agricultural Extension Service Delivery
Public extension services focus on broad-based knowledge dissemination and capacity building, while private extension emphasizes market-driven, specialized advisory services tailored to specific client needs. Future trends indicate a hybrid model leveraging digital technologies, big data analytics, and inclusive approaches to enhance efficiency, scalability, and farmer engagement. Integration of public-private partnerships and precision agriculture tools will transform agricultural extension service delivery landscapes.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Systems
Pluralistic extension systems integrate both public and private extension services to enhance agricultural knowledge dissemination and technology adoption among farmers. Combining government resources with private sector innovation enables more diverse, efficient, and demand-driven service delivery tailored to varied farmer needs.
Fee-for-Service Extension
Fee-for-service extension models in agricultural extension promote sustainable, demand-driven service delivery by allowing farmers to directly invest in expert knowledge and tailored support, enhancing accountability and customization compared to public extension. This approach leverages private sector efficiency and innovation while ensuring continuous engagement and responsiveness to farmer needs, contrasting with the often resource-constrained, broad-spectrum focus of public extension systems.
Demand-Driven Advisory Models
Public extension services target broad, resource-poor farmer groups with subsidized, standardized advice, while private extension emphasizes customized, demand-driven advisory models tailored to individual farmer needs and market opportunities. Demand-driven models in private extension leverage technology and market incentives to increase service efficiency, relevance, and farmer engagement, contrasting with the supply-driven approaches often found in public extension systems.
Digital Extension Platforms
Public extension services leverage digital extension platforms to provide accessible, wide-reaching agricultural advice, often prioritizing smallholder farmers and promoting sustainable practices through government or donor-funded programs. Private extension services utilize advanced digital tools and data analytics on proprietary platforms to deliver customized, market-driven solutions aimed at increasing productivity and profitability for commercial agribusiness clients.
Extension-AgriTech Partnerships
Public extension services traditionally offer broad, government-funded agricultural support, while private extension providers specialize in tailored, technology-driven solutions that enhance farmer productivity. Extension-AgriTech partnerships leverage these strengths by integrating public reach with private innovation, accelerating the adoption of digital tools like precision farming apps and remote sensing technologies.
Performance-Based Extension Contracts
Performance-based extension contracts in public extension systems often face challenges related to bureaucratic inefficiencies and limited incentives for innovation, whereas private extension services tend to demonstrate higher responsiveness and accountability through pay-for-performance models. Empirical studies indicate private extension contractors achieve greater adoption rates of improved agricultural technologies by aligning compensation with measurable farmer outcomes and service quality metrics.
Farmer-Led Extension
Public extension services, funded and managed by government agencies, prioritize widespread farmer access and equitable knowledge dissemination, while private extension services emphasize specialized, market-driven solutions tailored to specific farmer needs. Farmer-led extension fosters participatory approaches where farmers actively generate, share, and adapt information, enhancing the effectiveness of both public and private delivery systems through localized innovation and empowerment.
Agricultural Extension Franchising
Agricultural extension franchising bridges public extension's broad reach and private extension's market-driven efficiency by decentralizing service delivery through certified franchisees, increasing accessibility for smallholder farmers while maintaining quality standards. This hybrid model leverages public sector expertise and private sector incentives to enhance adoption of innovative agricultural technologies and improve farm productivity.
Public-Private Extension Synergies
Public extension services provide widespread access to agricultural knowledge and support, especially for smallholder farmers, while private extension often offers specialized, market-driven solutions. Combining public and private extension efforts leverages government reach and private sector innovation, enhancing service efficiency, technology adoption, and sustainable agricultural development.
Extension Service Outsourcing
Public extension services often lack the capacity and resources to reach all farmers effectively, leading to the increasing trend of outsourcing extension service delivery to private entities that offer specialized expertise and market-driven approaches. Private extension service outsourcing enhances efficiency, scalability, and innovation in agricultural advisory, promoting tailored solutions that meet diverse farmer needs and improve overall productivity.
Public Extension vs Private Extension for Service Delivery Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com