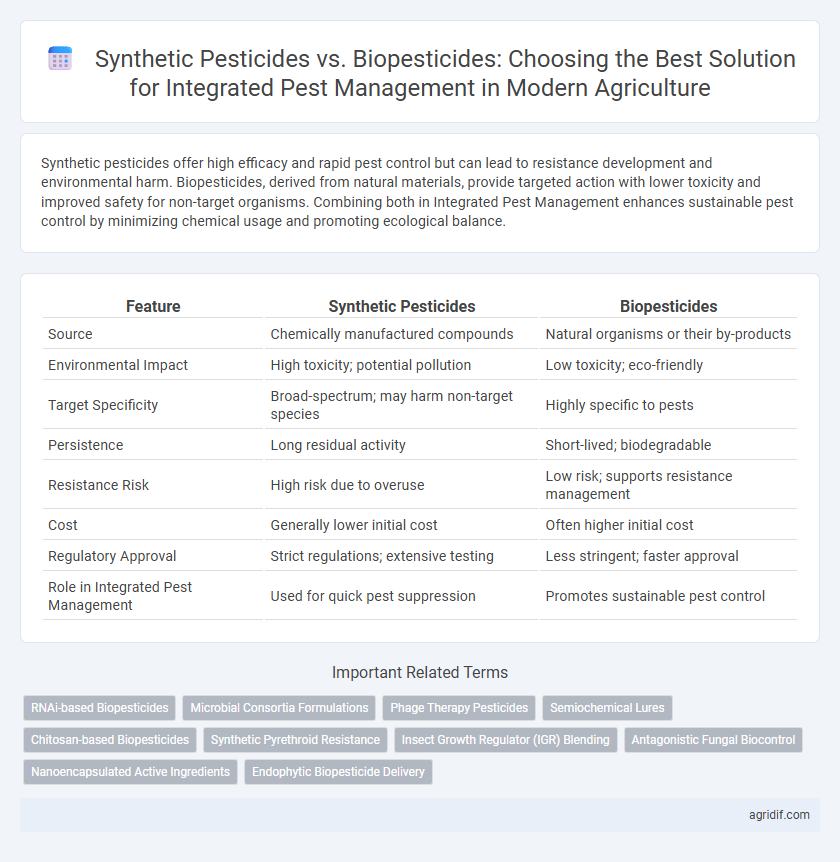
Synthetic pesticides offer high efficacy and rapid pest control but can lead to resistance development and environmental harm. Biopesticides, derived from natural materials, provide targeted action with lower toxicity and improved safety for non-target organisms. Combining both in Integrated Pest Management enhances sustainable pest control by minimizing chemical usage and promoting ecological balance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Pesticides | Biopesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chemically manufactured compounds | Natural organisms or their by-products |
| Environmental Impact | High toxicity; potential pollution | Low toxicity; eco-friendly |
| Target Specificity | Broad-spectrum; may harm non-target species | Highly specific to pests |
| Persistence | Long residual activity | Short-lived; biodegradable |
| Resistance Risk | High risk due to overuse | Low risk; supports resistance management |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Often higher initial cost |
| Regulatory Approval | Strict regulations; extensive testing | Less stringent; faster approval |
| Role in Integrated Pest Management | Used for quick pest suppression | Promotes sustainable pest control |
Defining Synthetic Pesticides and Biopesticides
Synthetic pesticides are chemically engineered substances designed to control, repel, or destroy pests and are commonly derived from non-natural sources for rapid and broad-spectrum pest management. Biopesticides consist of natural materials such as microorganisms, plant extracts, or biochemical substances that target specific pests with minimal environmental impact and promote ecological balance. Both play crucial roles in Integrated Pest Management by offering complementary approaches: synthetic pesticides provide immediate efficacy while biopesticides support long-term sustainability and reduced chemical residues.
Mechanisms of Action: Synthetic vs Biopesticides
Synthetic pesticides primarily function through chemical toxicity that disrupts the nervous system of pests, leading to rapid mortality, while biopesticides operate by utilizing biological agents such as bacteria, fungi, or natural plant extracts to target specific pests with minimal impact on non-target organisms. Synthetic compounds often interfere with neurotransmitters or enzymes, whereas biopesticides may induce pest resistance mechanisms or inhibit growth via microbial metabolism. Integrated Pest Management benefits from combining these mechanisms to enhance pest control efficiency and reduce environmental toxicity.
Efficacy and Spectrum of Control
Synthetic pesticides offer broad-spectrum control with rapid action against a wide variety of pests, making them highly effective in large-scale agricultural applications. Biopesticides, derived from natural organisms or substances, provide targeted pest management with lower environmental impact and reduced risk of resistance development. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) benefits from combining synthetic pesticides' efficacy with biopesticides' sustainability to achieve balanced pest control and minimize ecosystem disruption.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Synthetic pesticides often lead to environmental contamination through soil degradation, water pollution, and non-target species harm due to their persistent chemical residues. Biopesticides, derived from natural substances and microorganisms, degrade rapidly, reducing ecological toxicity and promoting biodiversity by targeting specific pests. Integrating biopesticides within pest management strategies minimizes negative environmental impacts and supports sustainable agriculture.
Human Health and Safety Considerations
Synthetic pesticides, widely used in agriculture, pose significant risks to human health due to their toxic chemical residues, potential for acute poisoning, and chronic effects such as respiratory issues and neurological disorders. Biopesticides, derived from natural materials like plants, bacteria, and minerals, are generally safer for human health, offering lower toxicity and reduced environmental persistence, which minimizes exposure risks for farmworkers and consumers. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies prioritize biopesticides to enhance safety while maintaining pest control efficacy, thereby reducing the reliance on hazardous synthetic chemicals and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Resistance Management in IPM Programs
Synthetic pesticides offer rapid pest control but often lead to resistance due to their single-mode actions, challenging long-term pest management in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs. Biopesticides, derived from natural organisms, provide diverse modes of action that reduce resistance development and enhance sustainability. Incorporating biopesticides in IPM aids resistance management by promoting ecological balance and minimizing chemical disruptions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Viability
Synthetic pesticides generally offer immediate and broad-spectrum pest control with lower upfront costs, making them economically viable for large-scale agricultural operations. Biopesticides, while often more expensive initially, provide long-term cost savings through improved environmental sustainability, reduced pest resistance, and potential market premiums for organic products. Integrated Pest Management benefits from combining synthetic pesticides' efficiency with biopesticides' eco-friendly attributes, optimizing both cost-effectiveness and economic viability over time.
Regulatory Frameworks and Approvals
Regulatory frameworks for synthetic pesticides typically involve rigorous testing for environmental impact, toxicity, and residue limits to ensure human and ecological safety before approval. Biopesticides undergo a distinct approval process emphasizing biodegradability, target-specificity, and minimal non-target effects, often facing faster regulatory pathways due to their natural origin. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) increasingly relies on harmonized regulations to facilitate the combined use of synthetic and biopesticides, optimizing pest control while minimizing risks and environmental footprints.
Adoption Challenges in Modern Agriculture
Synthetic pesticides dominate large-scale agriculture due to their broad-spectrum efficacy and rapid action, but concerns about environmental impact, pest resistance, and human health risks limit their sustainable use. Biopesticides, derived from natural organisms, offer targeted pest control with reduced ecological footprint, yet face hurdles such as inconsistent field performance, regulatory complexities, and higher production costs. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) adoption struggles to balance synthetic and biopesticide applications, demanding improved farmer education, robust supply chains, and supportive policy frameworks to enhance acceptance in modern agriculture.
Future Trends in Sustainable Pest Management
Future trends in sustainable pest management emphasize the increased adoption of biopesticides due to their environmental safety, biodegradability, and reduced resistance risk compared to synthetic pesticides. Advances in biotechnology and microbial formulations are driving innovation in biopesticide efficacy, integrating them within precision agriculture systems for targeted pest control. Regulatory support and growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products further accelerate the shift towards biopesticides in integrated pest management strategies.
Related Important Terms
RNAi-based Biopesticides
RNAi-based biopesticides offer targeted pest control by silencing specific genes in pests, reducing off-target effects typically seen with synthetic pesticides. Their integration into Integrated Pest Management enhances crop protection sustainability by minimizing chemical residues and promoting ecological balance.
Microbial Consortia Formulations
Microbial consortia formulations in biopesticides offer a sustainable alternative to synthetic pesticides by enhancing pest resistance through synergistic microbial interactions while reducing chemical residues in crops. These formulations promote soil health and biodiversity, integrating effectively into Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems to provide targeted pest control and minimize environmental impact.
Phage Therapy Pesticides
Phage therapy pesticides, a novel biopesticide approach, utilize bacteriophages to specifically target and eliminate bacterial pathogens in crops, reducing the reliance on broad-spectrum synthetic pesticides and minimizing environmental impact. Integrating phage therapy into pest management enhances crop protection efficacy by offering targeted action, resistance management, and compatibility with sustainable agricultural practices.
Semiochemical Lures
Semiochemical lures, used in both synthetic pesticides and biopesticides within Integrated Pest Management (IPM), enhance pest monitoring and targeted control by exploiting pest communication signals such as pheromones and kairomones. These eco-friendly lures reduce reliance on broad-spectrum synthetic pesticides, promoting sustainable agriculture through species-specific attraction and disruption techniques.
Chitosan-based Biopesticides
Chitosan-based biopesticides offer a sustainable alternative to synthetic pesticides by enhancing plant immune responses and reducing chemical residues in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems. Their biodegradability, low toxicity, and effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pests make chitosan formulations crucial for eco-friendly crop protection strategies.
Synthetic Pyrethroid Resistance
Synthetic pyrethroid resistance poses a significant challenge in integrated pest management (IPM), reducing the effectiveness of widely used synthetic pesticides in controlling agricultural pests. Biopesticides offer a sustainable alternative by targeting pest populations with reduced resistance development, supporting long-term crop protection and environmental safety.
Insect Growth Regulator (IGR) Blending
In integrated pest management, blending synthetic insect growth regulators (IGRs) with biopesticides enhances pest control efficacy by targeting multiple life stages and reducing resistance development. This synergistic approach leverages the precise hormonal disruption of IGRs alongside the environmentally friendly microbial or botanical modes of biopesticides, optimizing crop protection and sustainability.
Antagonistic Fungal Biocontrol
Antagonistic fungal biocontrol agents, such as Trichoderma species, offer targeted pest suppression by outcompeting or parasitizing plant pathogens, enhancing soil health and reducing chemical residues associated with synthetic pesticides. Integrating these biopesticides within Integrated Pest Management (IPM) frameworks optimizes crop protection while mitigating environmental toxicity and resistance development linked to conventional agrochemical controls.
Nanoencapsulated Active Ingredients
Nanoencapsulated active ingredients in synthetic pesticides enable controlled release and enhanced stability, improving targeting efficiency in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems. Biopesticides using nanoencapsulation also offer environmentally friendly pest control with reduced toxicity and biodegradable carriers, supporting sustainable agriculture practices within IPM frameworks.
Endophytic Biopesticide Delivery
Endophytic biopesticide delivery integrates beneficial microbes within plant tissues, enhancing pest resistance while minimizing environmental impacts compared to synthetic pesticides. This targeted approach in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) promotes sustainable crop protection by reducing chemical residues and improving pest control efficacy.
Synthetic Pesticides vs Biopesticides for Integrated Pest Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com