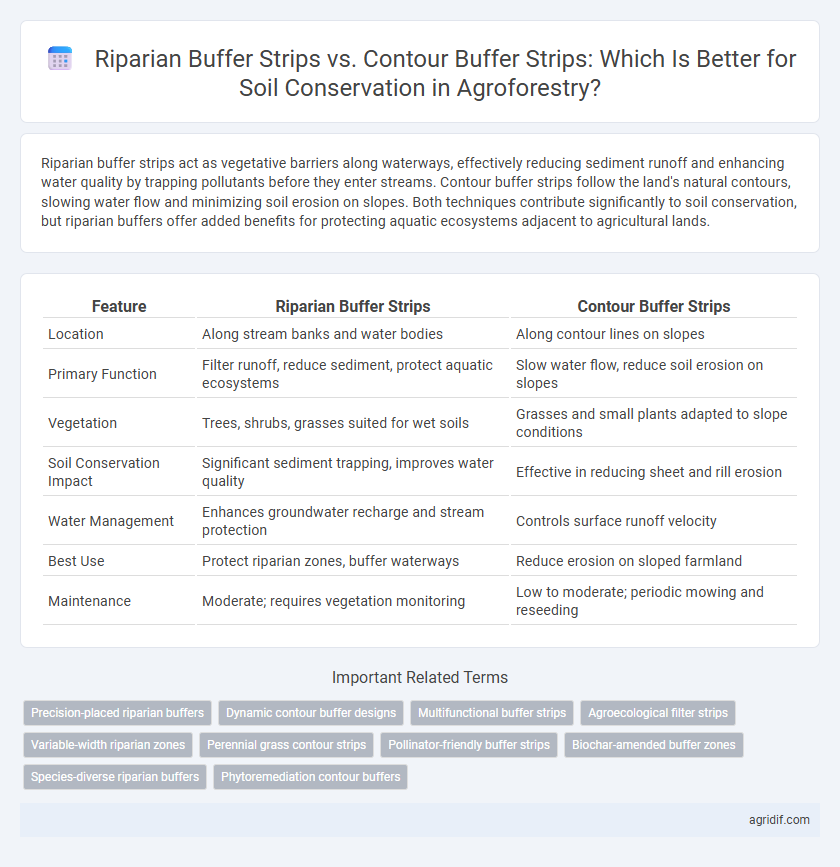
Riparian buffer strips act as vegetative barriers along waterways, effectively reducing sediment runoff and enhancing water quality by trapping pollutants before they enter streams. Contour buffer strips follow the land's natural contours, slowing water flow and minimizing soil erosion on slopes. Both techniques contribute significantly to soil conservation, but riparian buffers offer added benefits for protecting aquatic ecosystems adjacent to agricultural lands.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Riparian Buffer Strips | Contour Buffer Strips |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Along stream banks and water bodies | Along contour lines on slopes |
| Primary Function | Filter runoff, reduce sediment, protect aquatic ecosystems | Slow water flow, reduce soil erosion on slopes |
| Vegetation | Trees, shrubs, grasses suited for wet soils | Grasses and small plants adapted to slope conditions |
| Soil Conservation Impact | Significant sediment trapping, improves water quality | Effective in reducing sheet and rill erosion |
| Water Management | Enhances groundwater recharge and stream protection | Controls surface runoff velocity |
| Best Use | Protect riparian zones, buffer waterways | Reduce erosion on sloped farmland |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires vegetation monitoring | Low to moderate; periodic mowing and reseeding |
Introduction to Buffer Strips in Agroforestry
Riparian buffer strips are vegetated zones adjacent to water bodies that reduce sediment runoff and enhance water quality by filtering pollutants, while contour buffer strips follow the land's natural contours to minimize soil erosion on slopes. Both buffer strips serve as critical components in agroforestry systems for soil conservation, promoting biodiversity and improving watershed health. Selecting between riparian and contour buffer strips depends on landscape features, with riparian buffers best suited for protecting waterways and contour buffers designed to stabilize sloped agricultural fields.
Defining Riparian Buffer Strips
Riparian buffer strips are vegetated areas located adjacent to water bodies, designed to intercept pollutants and reduce soil erosion by stabilizing streambanks and filtering runoff. These strips often contain trees, shrubs, and grasses that enhance water quality and provide habitat for wildlife. In contrast to contour buffer strips placed along slope contours, riparian buffers primarily focus on protecting aquatic ecosystems through effective soil conservation near waterways.
Understanding Contour Buffer Strips
Contour buffer strips are strategically planted along the natural contours of sloped land, effectively reducing soil erosion by slowing water runoff and enhancing water infiltration. These strips are commonly composed of dense, perennial grasses or legumes that stabilize the soil and trap sediment, making them highly suitable for sloped agricultural fields. Unlike riparian buffer strips which protect waterways directly, contour buffer strips specifically target slope-induced erosion, offering a critical soil conservation tool in agroforestry systems.
Mechanisms of Soil Conservation in Riparian Buffers
Riparian buffer strips conserve soil by intercepting surface runoff and stabilizing stream banks through deep-rooted vegetation that reduces erosion and traps sediments. The dense root systems enhance soil structure, increase infiltration, and promote nutrient uptake, preventing nutrient leaching into waterways. These buffers also create microenvironments that support microbial activity, further stabilizing soil and improving overall watershed health.
Soil Erosion Control with Contour Buffer Strips
Contour buffer strips effectively reduce soil erosion by slowing surface runoff and promoting water infiltration along land contours, minimizing nutrient loss and sedimentation. Compared to riparian buffer strips, contour strips are strategically placed on agricultural slopes, directly intercepting runoff before it reaches waterways. Their role in soil conservation is critical in maintaining soil structure and preventing downhill soil displacement on incline terrains.
Comparative Benefits: Riparian vs. Contour Buffer Strips
Riparian buffer strips provide superior water quality protection by filtering runoff near waterways, effectively reducing sediment, nutrients, and pollutants before they enter streams. Contour buffer strips, installed along the natural land contours, primarily prevent soil erosion on slopes by slowing water flow and promoting infiltration. While riparian buffers excel in safeguarding aquatic ecosystems, contour buffers are more effective at controlling erosion across varied terrains, making each type beneficial depending on landscape and conservation goals.
Suitability for Different Landscapes and Farm Layouts
Riparian buffer strips are highly suitable for landscapes adjacent to water bodies, effectively reducing runoff and improving water quality in streamside areas. Contour buffer strips are ideal for sloped farmland, following the natural topography to minimize soil erosion by slowing water flow across the terrain. Both buffer strip types enhance soil conservation but require tailored implementation based on specific farm layouts and topographical conditions.
Impact on Water Quality and Nutrient Runoff
Riparian buffer strips, positioned alongside waterways, effectively reduce nutrient runoff and sediment flow by trapping pollutants before they enter water bodies, significantly improving water quality. Contour buffer strips, implemented along the natural land contours, also diminish soil erosion and nutrient loss but are less effective in directly protecting aquatic ecosystems compared to riparian buffers. Agriculture employing riparian buffers demonstrates a greater reduction in nitrogen and phosphorus loads, making them critical for maintaining watershed health.
Management Challenges and Best Practices
Riparian buffer strips require careful management to prevent nutrient runoff and maintain water quality, often involving native vegetation restoration and periodic monitoring to balance ecological benefits with agricultural productivity. Contour buffer strips demand precise contour farming techniques and regular maintenance to reduce soil erosion effectively, with challenges including equipment adaptation and weed control along contour lines. Best practices include integrating diverse plant species to enhance soil stability, implementing adaptive management plans based on site-specific conditions, and employing erosion control measures tailored to slope and soil type.
Recommendations for Buffer Strip Implementation in Agroforestry
Riparian buffer strips are recommended along waterways to intercept surface runoff, reduce nutrient leaching, and enhance aquatic habitat protection, while contour buffer strips are best suited on slopes to minimize soil erosion by following the land's natural contours. Effective implementation in agroforestry requires selecting buffer types based on topography, soil type, and crop system, with native vegetation favored for stability and biodiversity benefits. Regular monitoring and maintenance ensure buffer strips maintain their functionality for soil conservation and water quality over time.
Related Important Terms
Precision-placed riparian buffers
Precision-placed riparian buffer strips effectively reduce soil erosion and nutrient runoff by strategically targeting waterways, enhancing water quality and preserving aquatic ecosystems in agroforestry systems. In contrast, contour buffer strips follow land contours to minimize soil loss on slopes but may be less efficient in intercepting runoff compared to riparian buffers directly adjacent to water bodies.
Dynamic contour buffer designs
Riparian buffer strips, positioned along waterways, effectively reduce sediment runoff and protect water quality by stabilizing stream banks, while dynamic contour buffer strips, designed to follow the natural topography of slopes, offer enhanced soil conservation by intercepting surface runoff and minimizing erosion through adaptive placement and vegetation management. Dynamic contour buffer designs optimize agroforestry practices by integrating variable slope gradients and land-use patterns, resulting in improved rainfall infiltration and reduced nutrient leaching compared to static riparian buffers.
Multifunctional buffer strips
Multifunctional buffer strips, such as riparian and contour buffer strips, play a crucial role in soil conservation by reducing erosion, filtering runoff, and enhancing biodiversity in agroforestry systems. Riparian buffer strips stabilize stream banks and improve aquatic habitat quality, while contour buffer strips contour along slopes to effectively reduce surface runoff and soil loss on agricultural lands.
Agroecological filter strips
Riparian buffer strips, positioned along waterways, provide effective agroecological filter strips by reducing nutrient runoff and enhancing biodiversity, while contour buffer strips follow land contours to prevent soil erosion by slowing water flow on slopes. Both systems optimize soil conservation in agroforestry, but riparian buffers offer superior water quality protection and habitat benefits.
Variable-width riparian zones
Variable-width riparian buffer strips provide enhanced soil conservation by adapting their width based on slope and soil erosion risk, effectively reducing sediment runoff and improving water quality along stream banks. Compared to contour buffer strips, these dynamic buffer zones offer targeted protection in agroforestry systems by optimizing vegetation placement for maximum erosion control and nutrient retention.
Perennial grass contour strips
Perennial grass contour buffer strips effectively reduce soil erosion by slowing surface runoff and enhancing water infiltration along contour lines, making them ideal for managing slope-related soil loss in agroforestry systems. Riparian buffer strips primarily protect water quality by filtering runoff near waterways but may be less effective on sloped terrains compared to contour buffer strips with perennial grasses.
Pollinator-friendly buffer strips
Riparian buffer strips, planted along waterways with native flowering plants, provide critical pollen and nectar resources supporting diverse pollinator populations while effectively reducing soil erosion and nutrient runoff. Contour buffer strips follow land contours to control erosion on slopes but typically offer fewer floral resources, making riparian strips more beneficial for pollinator-friendly agroforestry systems focused on simultaneous soil conservation and biodiversity enhancement.
Biochar-amended buffer zones
Biochar-amended riparian buffer strips enhance soil conservation by improving water retention and nutrient cycling along waterways, reducing erosion and sediment runoff more effectively than contour buffer strips. Integrating biochar boosts microbial activity and soil structure in these zones, providing long-term stabilization benefits critical for agroforestry systems.
Species-diverse riparian buffers
Species-diverse riparian buffer strips enhance soil conservation by stabilizing stream banks, reducing erosion, and improving water quality through deep-rooted native trees and shrubs that intercept surface runoff and filter pollutants. Contour buffer strips, however, primarily reduce soil erosion on slopes by slowing runoff and promoting sediment deposition, but they lack the biodiversity benefits and aquatic ecosystem protection provided by riparian buffers.
Phytoremediation contour buffers
Riparian buffer strips primarily filter runoff and stabilize stream banks, while contour buffer strips, especially those utilizing phytoremediation, actively enhance soil conservation by absorbing and breaking down pollutants through plant root systems along agricultural contours. Phytoremediation contour buffers improve soil health by reducing erosion, trapping sediments, and detoxifying contaminants, making them highly effective in sustainable agroforestry soil management.
Riparian buffer strips vs contour buffer strips for soil conservation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com