The deep litter system promotes natural behaviors and provides better insulation, reducing stress and improving immunity in poultry. Cage systems offer easier management, space efficiency, and better control over hygiene, minimizing disease risks. Balancing animal welfare with production efficiency is crucial when choosing the appropriate poultry housing method.
Table of Comparison
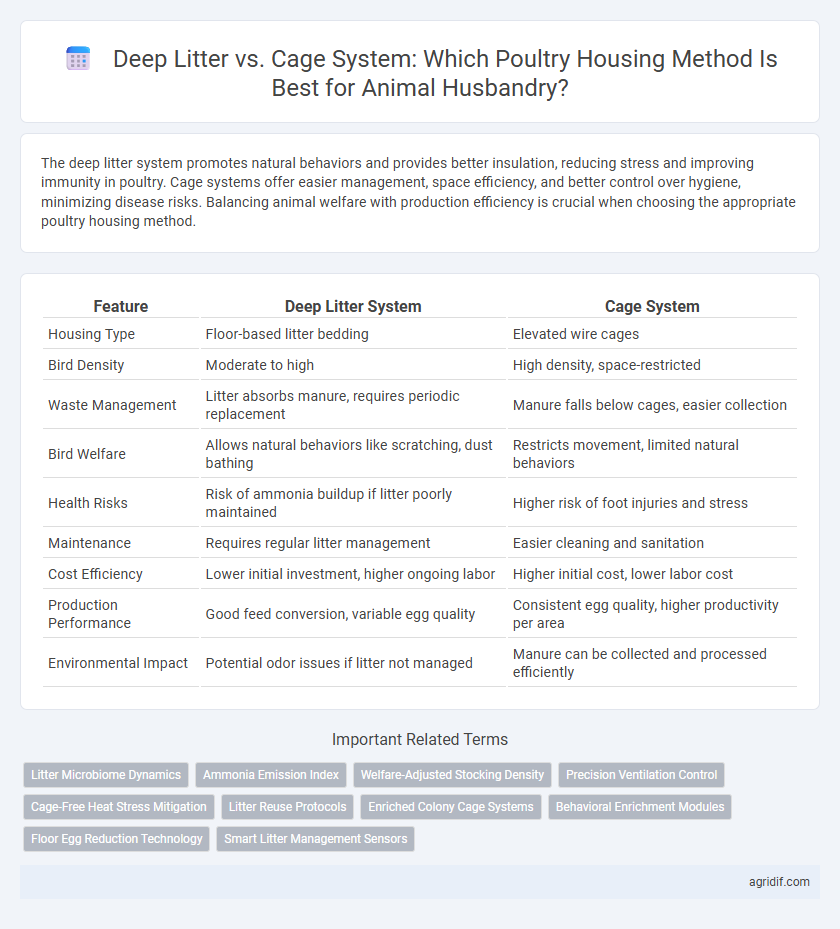
| Feature | Deep Litter System | Cage System |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Floor-based litter bedding | Elevated wire cages |
| Bird Density | Moderate to high | High density, space-restricted |
| Waste Management | Litter absorbs manure, requires periodic replacement | Manure falls below cages, easier collection |
| Bird Welfare | Allows natural behaviors like scratching, dust bathing | Restricts movement, limited natural behaviors |
| Health Risks | Risk of ammonia buildup if litter poorly maintained | Higher risk of foot injuries and stress |
| Maintenance | Requires regular litter management | Easier cleaning and sanitation |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment, higher ongoing labor | Higher initial cost, lower labor cost |
| Production Performance | Good feed conversion, variable egg quality | Consistent egg quality, higher productivity per area |
| Environmental Impact | Potential odor issues if litter not managed | Manure can be collected and processed efficiently |
Introduction to Poultry Housing Systems
Poultry housing systems primarily include the deep litter and cage systems, each offering distinct advantages for bird welfare and productivity. The deep litter system utilizes a bedding material such as wood shavings or rice hulls, promoting natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing, which enhance bird health. Conversely, the cage system confines birds individually or in small groups, maximizing space efficiency and ease of management while minimizing disease exposure.
Overview of the Deep Litter System
The Deep Litter System in poultry housing involves maintaining a thick layer of organic bedding material, such as straw or wood shavings, that progressively decomposes with bird droppings, providing a natural composting environment. This method promotes better ventilation, natural behavior expression, and improved litter management compared to cage systems, reducing stress and enhancing bird welfare. The microbial activity within the deep litter helps control pathogens and ammonia levels, supporting healthier poultry growth and sustainable livestock farming practices.
Overview of the Cage System
The cage system in poultry housing involves confining birds in small, individual or group cages made from wire mesh, designed to maximize space efficiency and simplify management. This system offers improved biosecurity, ease of feeding, watering, and egg collection while reducing labor costs and disease transmission. However, it often limits natural behaviors such as perching, dust bathing, and foraging, raising concerns about bird welfare and necessitating careful environmental control.
Comparative Cost Analysis: Deep Litter vs Cage System
The deep litter system incurs lower initial investment costs due to minimal infrastructure requirements, while the cage system demands higher capital for cage construction and equipment installation. Operational expenses in the deep litter method include regular bedding replacement and labor for manure management, whereas cage systems reduce labor costs but increase expenses related to equipment maintenance and feed distribution. Overall, deep litter offers cost-effectiveness in small to medium-scale operations, whereas cage systems prove economically viable for large-scale commercial poultry production with higher productivity.
Effects on Poultry Health and Welfare
Deep litter systems provide poultry with natural behaviors such as dust bathing and scratching, enhancing overall welfare and reducing stress-related illnesses. Cage systems, while efficient for space management, can lead to restricted movement and higher incidences of skeletal disorders and foot lesions. Studies reveal that poultry in deep litter environments generally exhibit stronger immune responses and lower rates of respiratory diseases compared to those in cage systems.
Productivity and Egg Yield in Both Systems
The deep litter system enhances poultry productivity by providing a natural environment that reduces stress and promotes better health, resulting in higher egg yield per bird. In contrast, the cage system offers controlled conditions that minimize disease but often restrict movement, which can negatively impact overall egg production and bird welfare. Studies indicate that while cage systems may lead to uniform egg size and ease of management, deep litter setups generally support improved growth rates and sustained egg-laying performance.
Environmental Impact and Waste Management
The deep litter system in poultry housing promotes natural biodegradation by allowing manure to mix with bedding materials, reducing the frequency of waste removal and minimizing ammonia emissions. In contrast, the cage system confines waste beneath the birds, requiring more frequent cleaning and potentially leading to higher concentrations of harmful gases if not managed properly. Deep litter systems facilitate better nutrient recycling and lower environmental pollution, making them more sustainable for waste management compared to conventional caged poultry housing.
Labor and Management Requirements
Deep litter systems for poultry housing demand more intensive daily labor for bedding maintenance, waste management, and regular monitoring of litter conditions to prevent disease. Cage systems reduce labor by simplifying feeding, watering, and cleaning processes but require specialized equipment and more management oversight to ensure bird welfare. Efficient operation of deep litter setups depends heavily on skilled management to balance moisture levels and ventilation, while cage systems rely on automated systems to maintain hygiene and regulate environmental parameters.
Biosecurity and Disease Control
Deep litter systems promote better biosecurity by enabling natural behaviors and reducing stress in poultry, which enhances immune responses and lowers disease susceptibility. Cage systems facilitate easier cleaning and manure management, minimizing pathogen accumulation but may induce stress-related immune suppression due to confinement. Effective disease control depends on rigorous hygiene protocols; deep litter requires regular monitoring to prevent ammonia buildup, while cage systems demand frequent disinfection to avoid cross-contamination.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Housing System for Poultry
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors and improve welfare through enriched environments, while cage systems offer precision in management and disease control. Selecting the ideal poultry housing depends on balancing welfare benefits, operational efficiency, and economic feasibility tailored to specific production goals. Evaluating factors such as flock size, labor availability, and biosecurity needs ensures optimal outcomes in poultry husbandry.
Related Important Terms
Litter Microbiome Dynamics
Deep litter systems promote a diverse and stable litter microbiome, enhancing pathogen suppression and nutrient recycling compared to cage systems. Cage systems limit microbial diversity by frequent cleaning and lack of organic material, potentially increasing disease susceptibility and reducing microbial ecosystem benefits in poultry housing.
Ammonia Emission Index
The Deep Litter system for poultry housing typically results in a lower Ammonia Emission Index compared to the Cage System due to better absorption and microbial decomposition of manure within the bedding material. In contrast, the Cage System often leads to higher ammonia emissions as manure accumulates directly beneath the cages, increasing volatilization and environmental impact.
Welfare-Adjusted Stocking Density
Welfare-adjusted stocking density in poultry housing varies significantly between deep litter and cage systems, with deep litter allowing more natural behaviors and better space utilization per bird. Research indicates that deep litter systems support improved welfare outcomes by accommodating higher stocking densities without compromising health, compared to the more restrictive cage systems that limit movement and natural behaviors.
Precision Ventilation Control
Precision ventilation control in deep litter systems enhances air quality by effectively reducing ammonia levels and moisture, promoting healthier poultry environments. Cage systems rely on targeted airflow management to maintain temperature and humidity, minimizing respiratory issues and optimizing bird welfare.
Cage-Free Heat Stress Mitigation
Deep litter systems enhance cage-free poultry welfare by providing natural behaviors and better ventilation, which reduces heat stress during high temperatures. These systems improve thermal comfort and reduce mortality rates compared to cage systems, making them ideal for heat stress mitigation in poultry housing.
Litter Reuse Protocols
Deep litter systems promote sustainable poultry farming by enabling effective litter reuse protocols that reduce waste and enhance microbial balance, contributing to improved bird health. Proper management involves periodic turning, moisture control, and pathogen monitoring to maintain litter quality and prevent disease recurrence commonly associated with cage systems.
Enriched Colony Cage Systems
Enriched colony cage systems for poultry housing improve animal welfare by providing increased space, perches, and nesting areas compared to traditional cage systems, reducing stress and promoting natural behaviors. These systems enhance productivity and health while maintaining biosecurity and ease of management in commercial poultry operations.
Behavioral Enrichment Modules
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors such as scratching, dust bathing, and foraging by providing a rich substrate environment, enhancing poultry welfare through increased behavioral enrichment modules. In contrast, cage systems limit movement and restrict expression of innate behaviors, resulting in reduced behavioral enrichment and potential stress-related issues in confined birds.
Floor Egg Reduction Technology
The Deep Litter system significantly reduces floor egg incidence by promoting natural hen behaviors and providing better comfort, which decreases stress-induced laying outside nests compared to the Cage system. Enhanced moisture control and regular litter management in Deep Litter housing further minimize floor egg contamination and improve overall poultry welfare.
Smart Litter Management Sensors
Smart litter management sensors in deep litter poultry housing monitor moisture, temperature, and ammonia levels in real-time, optimizing bird comfort and health while reducing disease risk. Compared to traditional cage systems, these sensors enhance environmental control and improve overall farm biosecurity through precise data-driven interventions.
Deep Litter vs Cage System for Poultry Housing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com