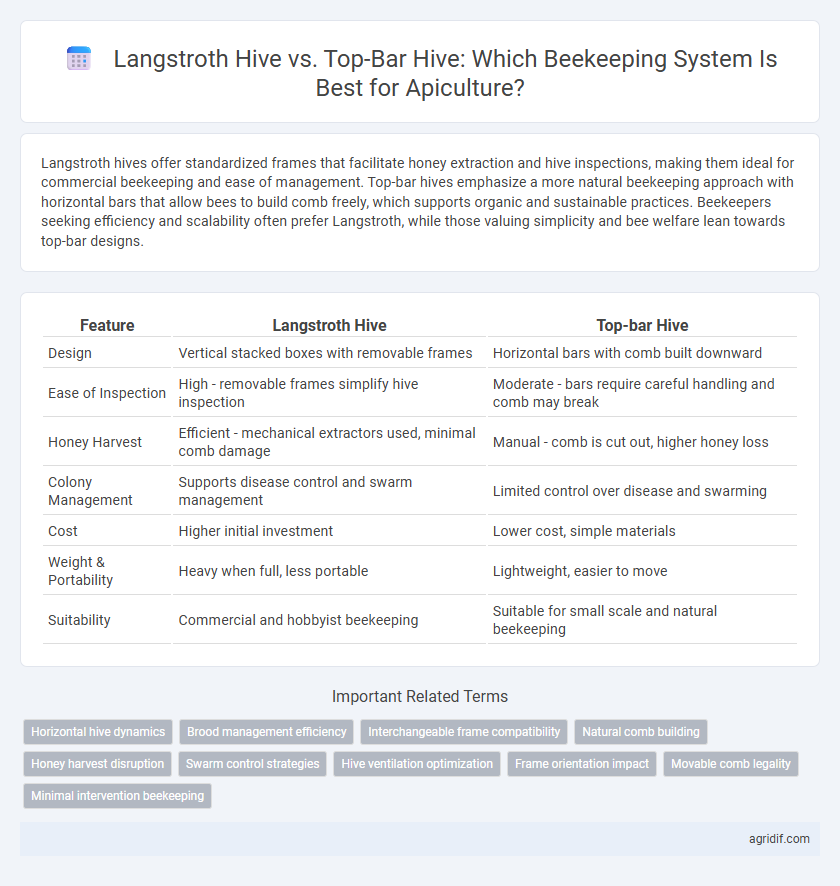
Langstroth hives offer standardized frames that facilitate honey extraction and hive inspections, making them ideal for commercial beekeeping and ease of management. Top-bar hives emphasize a more natural beekeeping approach with horizontal bars that allow bees to build comb freely, which supports organic and sustainable practices. Beekeepers seeking efficiency and scalability often prefer Langstroth, while those valuing simplicity and bee welfare lean towards top-bar designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Langstroth Hive | Top-bar Hive |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Vertical stacked boxes with removable frames | Horizontal bars with comb built downward |
| Ease of Inspection | High - removable frames simplify hive inspection | Moderate - bars require careful handling and comb may break |
| Honey Harvest | Efficient - mechanical extractors used, minimal comb damage | Manual - comb is cut out, higher honey loss |
| Colony Management | Supports disease control and swarm management | Limited control over disease and swarming |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, simple materials |
| Weight & Portability | Heavy when full, less portable | Lightweight, easier to move |
| Suitability | Commercial and hobbyist beekeeping | Suitable for small scale and natural beekeeping |
Introduction to Beekeeping Systems
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked frames designed for efficient honey extraction and hive management, making them ideal for commercial beekeeping. Top-bar hives consist of horizontal bars where bees build natural comb, preferred by hobbyists seeking a more ecological and hands-on approach. Understanding the structural differences and management styles of Langstroth and Top-bar hives is essential for selecting the most suitable beekeeping system.
Overview of the Langstroth Hive
The Langstroth hive, invented by Reverend Lorenzo Langstroth in 1852, is the most widely used beekeeping system globally due to its modular design and removable frames that facilitate hive inspection and honey extraction. Its vertically stacked rectangular boxes with standardized frames allow for efficient space management, disease control, and colony expansion. The Langstroth hive's versatility and compatibility with commercial beekeeping equipment make it an industry standard compared to alternative systems like the Top-bar hive.
Understanding Top-bar Hive Design
The top-bar hive design features horizontal bars where bees build natural comb, promoting easy inspection and minimal disruption to the colony. Unlike the Langstroth hive's removable frames with pre-formed foundation, top-bar hives support more sustainable beekeeping by allowing bees to use their own wax and build comb according to their natural patterns. This system is favored for simplicity, reduced equipment cost, and fostering stronger colony health by encouraging natural behaviors.
Hive Construction and Materials Comparison
Langstroth hives feature modular wooden boxes with removable frames, allowing efficient honey extraction and hive inspection, typically constructed from pine or cedar for durability and insulation. Top-bar hives use a single long box with bars across the top for comb attachment, often made from lightweight, untreated wood to emulate natural bee habitats and facilitate manual comb harvesting. Both designs prioritize lightweight materials but differ in structural complexity and ease of maintenance, influencing beekeeper preferences based on honey production goals and environmental conditions.
Colony Management and Inspection Efficiency
Langstroth hives provide standardized frames that facilitate easy colony inspection and efficient management by allowing beekeepers to remove individual frames without disturbing the entire hive, promoting effective monitoring of brood health and honey stores. In contrast, top-bar hives offer a natural comb-building process that enhances colony comfort but requires more careful handling during inspections, potentially slowing colony management due to the lack of interchangeable frames and increased risk of comb damage. Efficient colony management favors Langstroth hives for their structure, while top-bar hives support natural behaviors at the expense of inspection speed and ease.
Honey Yield and Harvesting Methods
Langstroth hives generally produce higher honey yields due to their standardized frames that allow for efficient space management and easier inspection. Top-bar hives yield less honey but offer a more natural comb-building process with horizontal bars, which can simplify harvesting by manually removing combs without heavy lifting. Harvesting from Langstroth hives involves uncapping frames and using extractors, whereas top-bar hive honey is often collected by crushing combs, resulting in less refined but more artisanal honey.
Bee Health and Pest Management
Langstroth hives offer standardized frames that facilitate effective hive inspections and pest control, reducing Varroa mite infestations and promoting overall bee health. Top-bar hives provide a natural comb-building environment, which can minimize chemical treatments but may require more vigilant monitoring for pests like wax moths and small hive beetles. Selecting between these systems depends on balancing ease of disease management in Langstroth hives with the organic, low-intervention approach of top-bar hives for sustainable apiculture.
Cost and Accessibility for Beekeepers
Langstroth hives typically require a higher initial investment due to their standardized design and need for additional equipment such as frames and foundation, which may limit accessibility for beginner beekeepers. Top-bar hives are often more cost-effective, featuring simpler construction and fewer components, making them accessible for hobbyists and small-scale apiarists with limited budgets. While Langstroth hives facilitate higher honey yields, the affordability and ease of assembly of top-bar hives offer practical benefits for beekeepers prioritizing cost efficiency and hands-on management.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Langstroth hives offer modular design and ease of management but rely on manufactured materials like plastic foundation sheets, affecting sustainability. Top-bar hives use natural materials like wood and promote less invasive honey harvesting, reducing stress on bee colonies and minimizing environmental disruption. Choosing top-bar hives supports ecological beekeeping practices by encouraging biodiversity and reducing synthetic inputs in apiculture.
Choosing the Right Hive for Your Apiary
Langstroth hives provide standardized, removable frames that facilitate honey extraction and hive inspections, making them ideal for commercial beekeeping and scalability. Top-bar hives offer a more natural comb-building environment with easy hive access, preferred by hobbyists seeking low-maintenance and sustainable beekeeping methods. Selecting between Langstroth and top-bar hives depends on apiary size, beekeeper goals, and management style, ensuring optimal colony health and honey production.
Related Important Terms
Horizontal hive dynamics
Langstroth hives feature vertically stacked rectangular boxes with removable frames, optimizing honey extraction and colony management through standardized, modular design, while top-bar hives use horizontally oriented bars allowing bees to build natural combs, enhancing colony health but requiring more manual intervention for inspection. Horizontal hive dynamics in top-bar systems promote natural bee behavior and ventilation but can complicate hive manipulation compared to the efficient frame handling of Langstroth hives.
Brood management efficiency
Langstroth hives offer superior brood management efficiency with removable frames that allow precise inspection and manipulation of brood cells, supporting better disease control and hive health. Top-bar hives, while promoting natural comb building, present challenges in brood inspection due to fixed combs, potentially hindering timely brood assessments and interventions.
Interchangeable frame compatibility
Langstroth hives feature standardized, interchangeable frames measuring approximately 19 x 9 inches, allowing easy replacement and expansion within and across most Langstroth systems. In contrast, top-bar hives use individual, non-interchangeable bars tailored to each hive's dimensions, limiting frame compatibility and requiring custom management for each unit.
Natural comb building
Langstroth hives utilize removable frames that guide bees in forming uniform combs, facilitating easy inspection and honey extraction but restricting natural comb construction. Top-bar hives encourage bees to build combs freely along horizontal bars, promoting natural comb building and better mimicking wild bee behavior, though requiring more careful management during harvest.
Honey harvest disruption
Langstroth hives allow for efficient honey harvest with minimal disruption to the colony due to removable frames that can be inspected individually, preserving hive stability. Top-bar hives often cause greater disturbance during honey collection because combs are cut and removed, which can stress the bees and reduce overall productivity.
Swarm control strategies
Langstroth hives allow precise swarm control through removable frames enabling easy inspection and queen management, while top-bar hives rely on natural comb formation, making swarm prevention less controlled but encouraging natural behavior. Swarm control in Langstroth systems often involves techniques like queen excluders and brood box manipulation, whereas top-bar hives depend on colony splitting and regular monitoring to reduce swarming tendencies.
Hive ventilation optimization
Langstroth hives feature adjustable frames and screened bottom boards that enhance airflow and reduce moisture buildup, optimizing hive ventilation and improving colony health. Top-bar hives rely on natural gaps and manual intervention for ventilation, which can limit airflow efficiency but allow better temperature regulation in warmer climates.
Frame orientation impact
Langstroth hives feature vertically oriented frames that promote efficient honey extraction and hive inspection with minimal disturbance to bees, while top-bar hives utilize horizontally oriented bars encouraging natural comb construction but complicating hive management and honey harvesting. Frame orientation directly influences airflow, brood pattern, and ease of hive manipulation, impacting overall colony health and beekeeping productivity.
Movable comb legality
Langstroth hives feature movable frames allowing beekeepers to inspect, manage, and harvest honey with legal compliance in many regions, promoting hive health and pest control. Top-bar hives typically have fixed combs, limiting mobility and often facing legal restrictions due to challenges in management and disease prevention.
Minimal intervention beekeeping
Langstroth hives enable efficient honey extraction with removable frames, promoting organized hive management but require regular inspection and maintenance. Top-bar hives support minimal intervention beekeeping by allowing bees to build natural comb with less disturbance, fostering a more sustainable and low-impact approach to hive care.
Langstroth hive vs Top-bar hive for beekeeping systems Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com