Broadcast seeding spreads seeds evenly across the field surface, offering simplicity and speed but often resulting in uneven seed placement and lower germination rates. Precision planting ensures accurate seed depth and spacing, enhancing uniform crop emergence and improving yield potential through optimized resource use. Choosing between broadcast seeding and precision planting depends on crop type, soil conditions, and desired production efficiency.
Table of Comparison
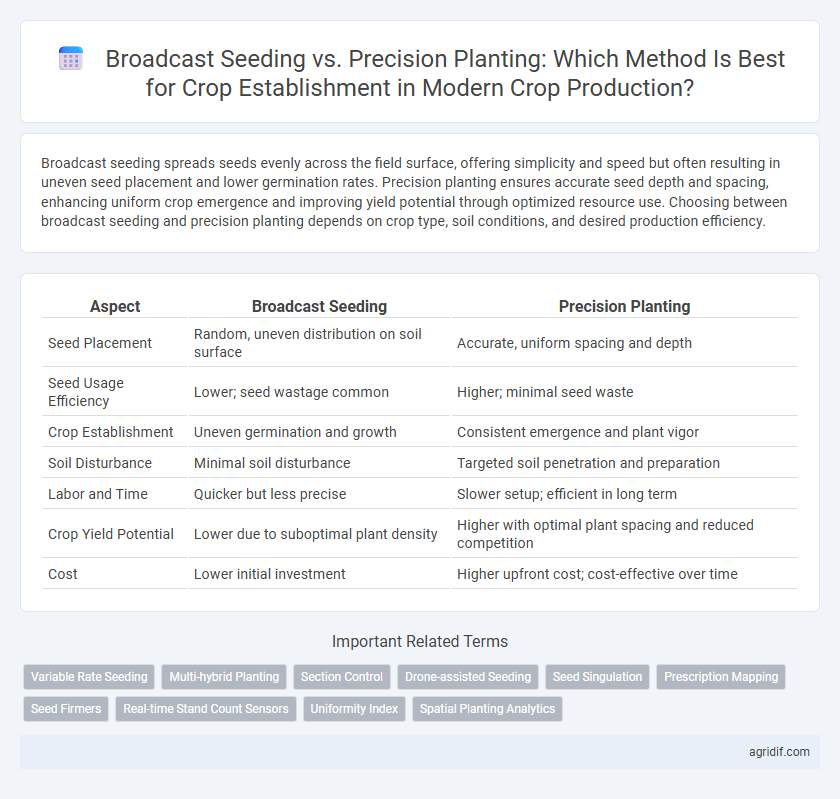
| Aspect | Broadcast Seeding | Precision Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Placement | Random, uneven distribution on soil surface | Accurate, uniform spacing and depth |
| Seed Usage Efficiency | Lower; seed wastage common | Higher; minimal seed waste |
| Crop Establishment | Uneven germination and growth | Consistent emergence and plant vigor |
| Soil Disturbance | Minimal soil disturbance | Targeted soil penetration and preparation |
| Labor and Time | Quicker but less precise | Slower setup; efficient in long term |
| Crop Yield Potential | Lower due to suboptimal plant density | Higher with optimal plant spacing and reduced competition |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost; cost-effective over time |
Introduction to Crop Establishment Methods
Broadcast seeding involves scattering seeds uniformly over the soil surface, enabling faster sowing but often resulting in uneven seed placement and variable emergence rates. Precision planting delivers seeds individually into predefined spacings and depths, optimizing seed-to-soil contact and promoting uniform crop emergence. Choosing between these methods influences plant population density, resource use efficiency, and overall yield potential in crop production.
Understanding Broadcast Seeding
Broadcast seeding involves evenly scattering seeds across the soil surface, facilitating rapid coverage and ease of application for crops like cereals and forage grasses. This method often results in variable seed placement depth and spacing, potentially leading to uneven emergence and competition among seedlings. Understanding the trade-offs of broadcast seeding, including lower equipment cost but reduced planting accuracy, is essential for optimizing crop establishment compared to precision planting techniques.
What is Precision Planting?
Precision planting is an advanced agricultural technique that precisely places seeds at optimal depth and spacing to enhance crop establishment and yield. By utilizing GPS technology, sensor data, and variable rate control, it ensures uniform seed distribution, reduces seed waste, and maximizes field productivity. Compared to broadcast seeding, precision planting offers improved germination rates, better resource efficiency, and increased overall crop performance.
Equipment and Technology Comparison
Broadcast seeding uses spreaders to distribute seeds widely and quickly but often results in uneven seed placement and variable crop emergence, whereas precision planting employs advanced GPS-guided machinery to place seeds at exact intervals and depths, optimizing plant population and yield potential. Precision planters incorporate sensors and real-time data analytics to adjust seeding rates and monitor seed placement, enhancing efficiency and reducing seed waste compared to traditional broadcast seeders. The higher initial investment in precision equipment is offset by improved crop establishment uniformity and increased overall productivity in modern farming operations.
Seed Distribution Uniformity
Broadcast seeding disperses seeds randomly over the field surface, resulting in less uniform seed distribution and variable plant spacing, which can reduce overall crop yield potential. Precision planting places seeds at consistent depths and precise intervals, ensuring optimal seed spacing and improved emergence rates. Uniform seed distribution achieved through precision planting enhances resource utilization, promotes even crop development, and increases harvest efficiency.
Impact on Germination and Crop Stand
Broadcast seeding evenly disperses seeds over the soil surface, which can result in uneven seed depth and variable germination rates due to inconsistent seed-to-soil contact. Precision planting places seeds at uniform depth and spacing, enhancing soil contact, promoting uniform germination, and leading to a more consistent and healthy crop stand. Studies show precision planting can improve germination rates by up to 15% and increase overall stand establishment, optimizing yield potential in various cropping systems.
Weed Management Differences
Broadcast seeding spreads seeds uniformly across the field, resulting in less precise spacing that can create gaps favorable for weed growth, complicating weed management efforts. Precision planting places seeds at exact depths and intervals, promoting uniform crop emergence and stronger canopy closure, which suppresses weed proliferation naturally. Enhanced targeting in precision planting reduces the reliance on herbicides by minimizing weed competition during early crop establishment phases.
Cost Analysis: Broadcast vs Precision
Broadcast seeding typically involves lower upfront equipment costs but may lead to higher seed wastage and uneven crop stands, increasing overall input expenses. Precision planting requires a significant investment in technology and machinery but enhances seed placement accuracy, improving germination rates and yield potential, which can reduce variable costs per acre. Considering long-term profitability, precision planting often yields better cost-efficiency through optimized input use and higher crop uniformity compared to broadcast seeding.
Yield Outcomes and Efficiency
Precision planting significantly enhances yield outcomes and efficiency by ensuring uniform seed spacing and depth, which promotes optimal plant growth and resource utilization. Broadcast seeding generally leads to uneven seed distribution, resulting in variable plant populations and increased competition, ultimately reducing yield potential. Studies indicate that precision planting can improve crop emergence rates by up to 15% and increase yield by 10-20% compared to broadcast methods.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Broadcast seeding distributes seeds uniformly over the soil surface, often requiring higher seed rates and leading to increased soil disturbance and potential waste, which can negatively impact soil health and contribute to erosion. Precision planting places seeds at exact depths and spacing, optimizing seed use efficiency and minimizing soil disruption, thereby enhancing water retention and reducing input runoff. This targeted approach supports sustainable crop establishment by promoting resource conservation and lowering environmental footprint compared to traditional broadcasting methods.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Seeding
Variable Rate Seeding with precision planting enhances crop establishment by optimizing seed placement and density, leading to improved germination and higher yields compared to broadcast seeding's uniform seed distribution that often results in uneven plant emergence. Precision planting technology adjusts seed rates in real-time based on soil variability and field conditions, maximizing resource use efficiency and reducing seed waste.
Multi-hybrid Planting
Broadcast seeding offers simple distribution of seeds but often leads to uneven plant spacing, whereas precision planting enhances crop establishment by accurately placing multi-hybrid seeds at optimal depths and intervals, improving resource use efficiency and yield potential. Multi-hybrid planting with precision technology allows spatial variation in genotype deployment, optimizing hybrid performance in diverse field conditions for improved overall crop productivity.
Section Control
Broadcast seeding disperses seeds uniformly across the field but often leads to uneven germination and higher seed wastage, while precision planting uses GPS-guided section control to optimize seed placement and spacing, resulting in improved crop establishment and resource efficiency. Section control technology in precision planting minimizes overlap and skips, reducing seed costs and enhancing yield potential by ensuring consistent plant populations.
Drone-assisted Seeding
Drone-assisted seeding enhances precision planting by enabling targeted seed placement, improving germination rates and reducing seed waste compared to traditional broadcast seeding. This technology optimizes crop establishment through accurate soil coverage and uniform seed distribution, leading to higher yields and resource efficiency.
Seed Singulation
Broadcast seeding disperses seeds uniformly across the field but often results in uneven seed singulation, leading to inconsistent germination and crop stands. Precision planting uses advanced technology to place individual seeds at optimal spacing and depth, enhancing seed singulation accuracy and improving overall crop establishment and yield potential.
Prescription Mapping
Broadcast seeding offers uniform seed distribution but often lacks the site-specific accuracy of precision planting, which utilizes prescription mapping to optimize seed placement based on soil variability and crop requirements. Prescription mapping integrates GPS and sensor data to tailor seeding rates and patterns, enhancing crop establishment uniformity and increasing overall yield potential.
Seed Firmers
Seed firmers enhance seed-to-soil contact in both broadcast seeding and precision planting, crucial for uniform germination and optimal crop establishment; however, precision planting paired with seed firmers ensures exact seed placement and consistent depth, significantly improving emergence rates and early vigor compared to the more variable results of broadcast seeding. Effective use of seed firmers in precision planting contributes to better stand uniformity, reduced seed wastage, and increased overall crop yield potential.
Real-time Stand Count Sensors
Real-time stand count sensors enable precise monitoring of crop population during both broadcast seeding and precision planting, enhancing yield predictions and management decisions. Precision planting paired with these sensors improves seed placement accuracy and emergence uniformity compared to broadcast seeding, resulting in optimized resource use and higher overall crop productivity.
Uniformity Index
Broadcast seeding often results in lower Uniformity Index due to uneven seed distribution and variable plant spacing, which can lead to inconsistent crop emergence. Precision planting enhances crop establishment by delivering seeds at consistent depths and spacing, significantly increasing the Uniformity Index and promoting uniform growth across the field.
Spatial Planting Analytics
Broadcast seeding distributes seeds uniformly across the field but often results in uneven plant spacing and variable emergence, whereas precision planting places seeds at exact intervals using GPS-guided technology to optimize spatial planting analytics for improved yield prediction and resource efficiency. Spatial planting analytics integrates data from precision planters to monitor plant spacing, emergence uniformity, and growth patterns, enabling targeted agronomic interventions and enhanced crop establishment.
Broadcast seeding vs Precision planting for crop establishment Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com